|
Lake Ballivián
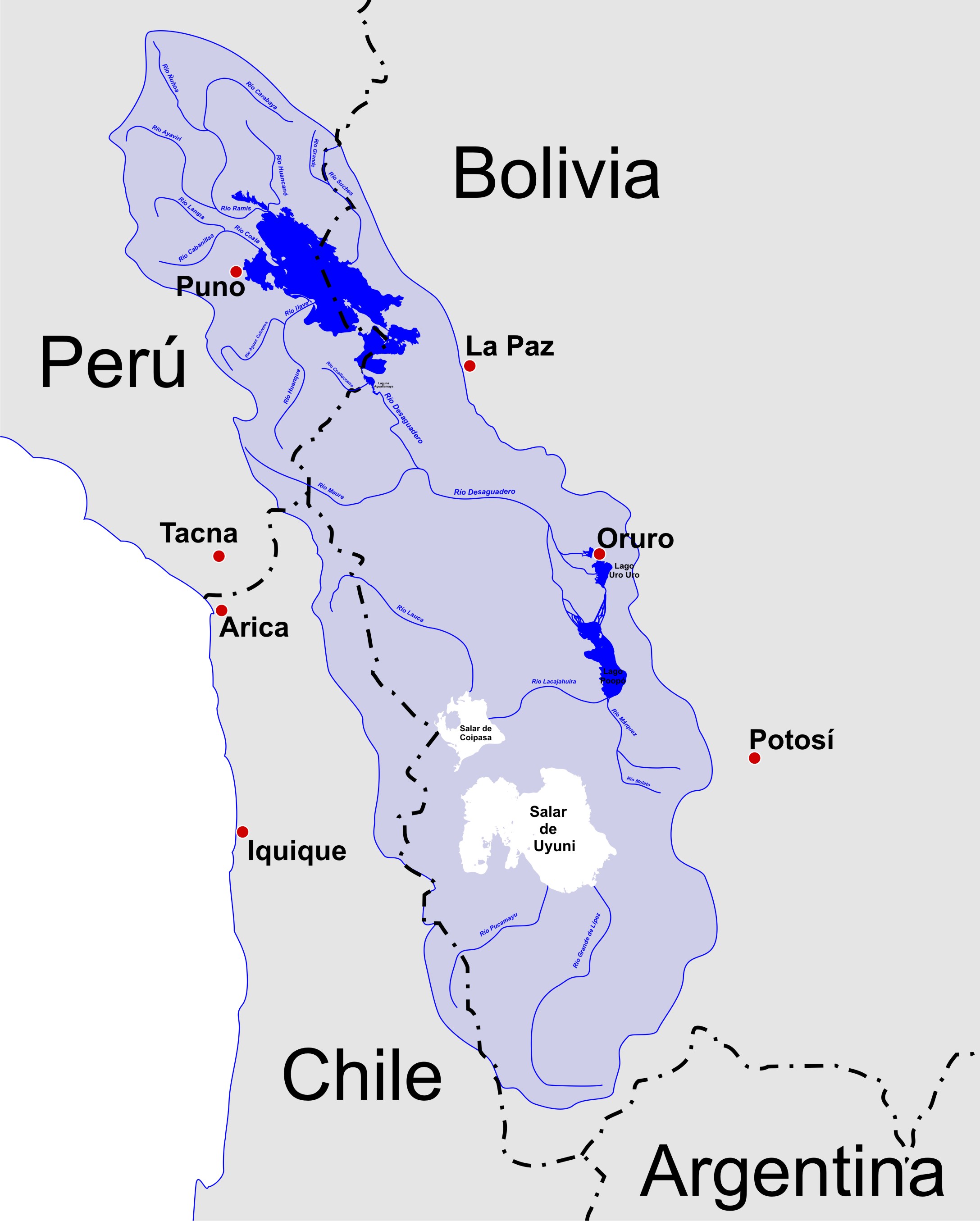
Lake Ballivián is an ancient lake in the Altiplano of South America and is named after the Bolivian scholar Don Manuel Vicente Ballivian. It is part of a series of lakes which developed in the Titicaca basin along with Lake Mataro and Lake Cabana, reaching an altitude of . Lake Ballivián itself is of late Quaternary age and may have influenced the spread and development of animals in the Altiplano. In the southern Altiplano, Lake Escara may be coeval with Lake Ballivián. Context The Altiplano in South America is a high plateau between the Eastern Cordillera and the Western Cordillera with an average altitude of and a surface area of . A number of evaporation landforms can be found in the Altiplano, including Salar de Uyuni and Salar de Coipasa. In the northern Altiplano lies Lake Titicaca. While the present-day Altiplano has an arid-semiarid climate, it was formerly occupied by large lakes that grew and dried out in many phases. Of these lakes, Lake Ballivián and La ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Altiplano
The Altiplano (Spanish for "high plain"), Collao (Quechua and Aymara: Qullaw, meaning "place of the Qulla") or Andean Plateau, in west-central South America, is the most extensive high plateau on Earth outside Tibet. The plateau is located at the latitude of the widest part of the north-south-trending Andes. The bulk of the Altiplano lies in Bolivia, but its northern parts lie in Peru, and its southwestern fringes lie in Chile. There are on the plateau several cities in each of these three nations, including El Alto, La Paz, Oruro, and Puno. The northeastern part of the Altiplano is more humid than the southwestern part, which has several salares (salt flats), due to its aridity. At the Bolivia–Peru border lies Lake Titicaca, the largest lake in South America. Farther south, in Bolivia, there was until recently a lake, Lake Poopó, but by December 2015 it had completely dried up, and was declared defunct. It is unclear whether that lake, which had been the second-largest in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gulf
A gulf is a large inlet from the ocean into the landmass, typically with a narrower opening than a bay, but that is not observable in all geographic areas so named. The term gulf was traditionally used for large highly-indented navigable bodies of salt water that are enclosed by the coastline. Many gulfs are major shipping areas, such as the Persian Gulf, Gulf of Mexico, Gulf of Finland, and Gulf of Aden The Gulf of Aden ( ar, خليج عدن, so, Gacanka Cadmeed 𐒅𐒖𐒐𐒕𐒌 𐒋𐒖𐒆𐒗𐒒) is a deepwater gulf of the Indian Ocean between Yemen to the north, the Arabian Sea to the east, Djibouti to the west, and the Guardafui Channe .... See also * References External links * {{Authority control Bodies of water Coastal and oceanic landforms Coastal geography Oceanographical terminology ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saale Glaciation
The Saale glaciation or Saale Glaciation, sometimes referred to as the Saalian glaciation, Saale cold period (german: Saale-Kaltzeit), Saale complex (''Saale-Komplex'') or Saale glacial stage (''Saale-Glazial'', colloquially also the ''Saale-Eiszeit'' or ''Saale-Zeit''), covers the middle of the three large glaciations in Northern Europe and the northern parts of Eastern, Central and Western Europe by the Scandinavian Inland Ice Sheet between the older Elster glaciation and the younger Weichselian glaciation, also called the Last Glacial Period. Age and definitions It succeeded the Holstein interglacial and was followed by the Eemian interglacial. The Saale complex is currently estimated, depending on the source, as existing from around 300,000 to 130,000 years ago or 347,000 to 128,000 years ago (duration: around 219,000 years), roughly contemporaneous with the glaciation of the Riss Glacial in the Alpine region. The actual "ice age" includes only part of the Saale glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
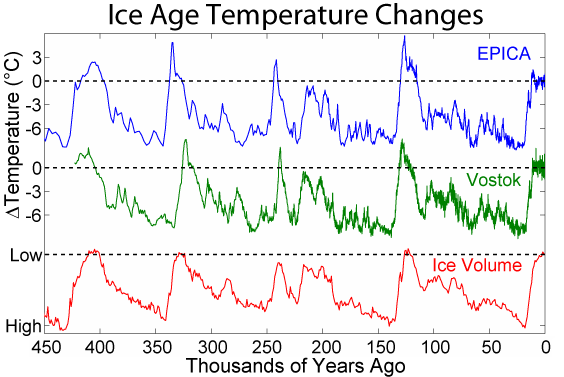
Interglacial
An interglacial period (or alternatively interglacial, interglaciation) is a geological interval of warmer global average temperature lasting thousands of years that separates consecutive glacial periods within an ice age. The current Holocene interglacial began at the end of the Pleistocene, about 11,700 years ago. Pleistocene During the 2.5 million years of the Pleistocene, numerous glacials, or significant advances of continental ice sheets, in North America and Europe, occurred at intervals of approximately 40,000 to 100,000 years. The long glacial periods were separated by more temperate and shorter interglacials. During interglacials, such as the present one, the climate warms and the tundra recedes polewards following the ice sheets. Forests return to areas that once supported tundra vegetation. Interglacials are identified on land or in shallow epicontinental seas by their paleontology. Floral and faunal remains of species pointing to temperate climate and indicating a s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trough (geology)
In geology, a trough is a linear structural depression that extends laterally over a distance. Although it is less steep than a trench, a trough can be a narrow basin or a geologic rift. These features often form at the rim of tectonic plates. There are various oceanic troughs on the ocean floors. Examples of oceanic troughs * Benue Trough * Cayman Trough * Kings Trough * Hesperides Trough * Nankai Trough * Northumberland Trough * Okinawa Trough in the East China Sea * Rockall Trough and others along the rift of the mid-oceanic ridge * Salton Trough * South Shetland Trough * Suakin TroughDinwiddie, Robert et al. (2008) ''Ocean: The World's Last Wilderness Revealed'', London, Dorling Kindersley, page 452. in the Red Sea * Timor Trough See also * Walker Lane * Oceanic basin In hydrology, an oceanic basin (or ocean basin) is anywhere on Earth that is covered by seawater. Geologically, ocean basins are large geologic basins that are below sea level. Most ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Desaguadero River (Bolivia And Peru)
The Desaguadero River, also known as Risawariru or Uchusumain, is a river shared between Bolivia and Peru. It drains Lake Titicaca from the southern part of the river basin, flowing south and draining approximately five percent of the lake's flood waters into Lake Uru Uru and Lake Poopó. Its source in the north is very near the Peruvian border. It is navigable only by small craft and supports indigenous communities such as the Uru Muratu community. See also * Awallamaya Lake * Desaguadero River (Argentina) from Argentina Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the second-largest country in South America after Brazil, th .... Notes External links Management issues in the Lake Titicaca and Lake Poopo system: Importance of developing a water budget Rivers of Peru Rivers of La Paz Department (Bolivia) Rivers of Oruro Department ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mauri River
The Mauri River is a river of Bolivia and Peru. It rises on the frontier between Chile and Bolivia near Charaña and flows east-northeast for about 100 km where it joins the Desaguadero. In fact the Mauri is much larger than the Desaguadero at this point, but below the confluence the name Desaguadero prevails. See also * List of rivers of Bolivia *List of rivers of Peru This is a list of rivers of Peru, that are at least partially in Peru. The Peruvian government has published guidelines for the preparation of river flow studies in April 2015. Longest rivers The lengths of the following 10 rivers are according to ... References *Rand McNally, The New International Atlas, 1993. Rivers of La Paz Department (Bolivia) Rivers of Peru Rivers of Tacna Region {{Peru-river-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calacoto
Calacoto (hispanicized spelling) or Qalaqutu (Aymara ''qala'' stone, ''qutu'' pile, heap, Aymara-Spanish dictionary: ''Qala'' ''(s.) - Piedra, duro. Cantera.'' ''Qutu'' ''(s.) - Montón.'' "stone pile") is a neighborhood in La Paz Municipality, Bolivia. It is located in the southern part of the city and is considered one of the largest residential zones due to the cost of the houses and the services available. The population in this neighborhood has a medium to high income level. The zone is located about 15 kilometers from downtown. Calacoto is located in the central zone of the ''Zona Sur'' which is considered the biggest residential area i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanic
A volcano is a rupture in the crust of a planetary-mass object, such as Earth, that allows hot lava, volcanic ash, and gases to escape from a magma chamber below the surface. On Earth, volcanoes are most often found where tectonic plates are diverging or converging, and most are found underwater. For example, a mid-ocean ridge, such as the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, has volcanoes caused by divergent tectonic plates whereas the Pacific Ring of Fire has volcanoes caused by convergent tectonic plates. Volcanoes can also form where there is stretching and thinning of the crust's plates, such as in the East African Rift and the Wells Gray-Clearwater volcanic field and Rio Grande rift in North America. Volcanism away from plate boundaries has been postulated to arise from upwelling diapirs from the core–mantle boundary, deep in the Earth. This results in hotspot volcanism, of which the Hawaiian hotspot is an example. Volcanoes are usually not created where two tectonic plate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pacific Ocean
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the continents of Asia and Oceania in the west and the Americas in the east. At in area (as defined with a southern Antarctic border), this largest division of the World Ocean—and, in turn, the hydrosphere—covers about 46% of Earth's water surface and about 32% of its total surface area, larger than Earth's entire land area combined .Pacific Ocean . '' Britannica Concise.'' 2008: Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. The centers of both the |
Gravel
Gravel is a loose aggregation of rock fragments. Gravel occurs naturally throughout the world as a result of sedimentary and erosive geologic processes; it is also produced in large quantities commercially as crushed stone. Gravel is classified by particle size range and includes size classes from granule- to boulder-sized fragments. In the Udden-Wentworth scale gravel is categorized into granular gravel () and pebble gravel (). ISO 14688 grades gravels as fine, medium, and coarse, with ranges 2–6.3 mm to 20–63 mm. One cubic metre of gravel typically weighs about 1,800 kg (or a cubic yard weighs about 3,000 lb). Gravel is an important commercial product, with a number of applications. Almost half of all gravel production is used as aggregate for concrete. Much of the rest is used for road construction, either in the road base or as the road surface (with or without asphalt or other binders.) Naturally occurring porous gravel deposits have a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
La Paz River
The Choqueyapu River, sometimes called the La Paz River, is a river in the La Paz Department of Bolivia. It belongs to the drainage basin of the Amazon. The river originates in a spring called Achachi Qala (Aymara: ''achachi'' border stone, old, grandfather, ''qala'' stone) in the Cordillera Real near the mountain Chacaltaya at a height of 5,395 m. It crosses the city La Paz from north to south. South of Illimani and north of the Kimsa Cruz mountain range it turns to the east; at this point it is better known as the La Paz River. The confluence with Cotacajes River is the beginning of the Beni River, also known as Alto Beni ("high Beni") in this region. The river is known to be contaminated with sewage, with enteropathogenic bacteria which is believed to contribute to the high incidence of diarrheal disease in the city of La Paz. Tributaries include the Amutara River. See also *List of rivers of Bolivia This is a list of rivers in Bolivia. By drainage basin This list is arr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |


.jpg)
