|
Lü Xiang (table Tennis)
The Battle of Nanpi happened in the first month of 205, during the period known as the end of the Han dynasty. The battle spelled the annihilation of Yuan Tan, one of Yuan Shao's sons vying to succeed their father, by their common enemy Cao Cao, one of the serving Three Ducal Ministers. Having already dealt a major blow to another son Yuan Shang, Cao Cao's victory at Nanpi gave him uncontested control of the North China Plain, while the remnant Yuan power blocs were chased further north. Background Yuan Shao, the powerful warlord of northern China, had been decisively defeated at the Battle of Guandu by Cao Cao in 200. Two years later, he died, leaving his expansive territories of Ji province, Qing province, Bing province, and You province to his three sons and a nephew: Yuan Tan, Yuan Xi, Yuan Shang, and Gao Gan. Although the eldest son was expected to succeed his father, Yuan Shang's supporters forged a document declaring the youngest son, him, as the successor. Yuan Tan, pred ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
End Of The Han Dynasty
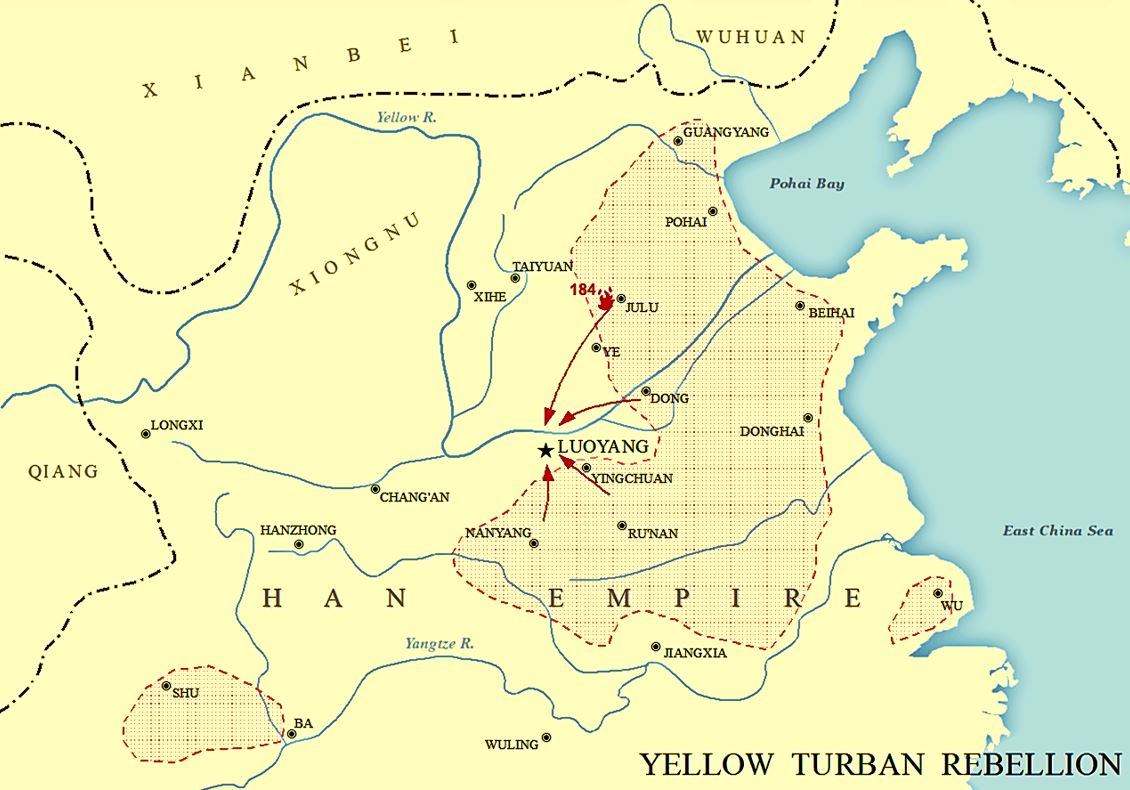
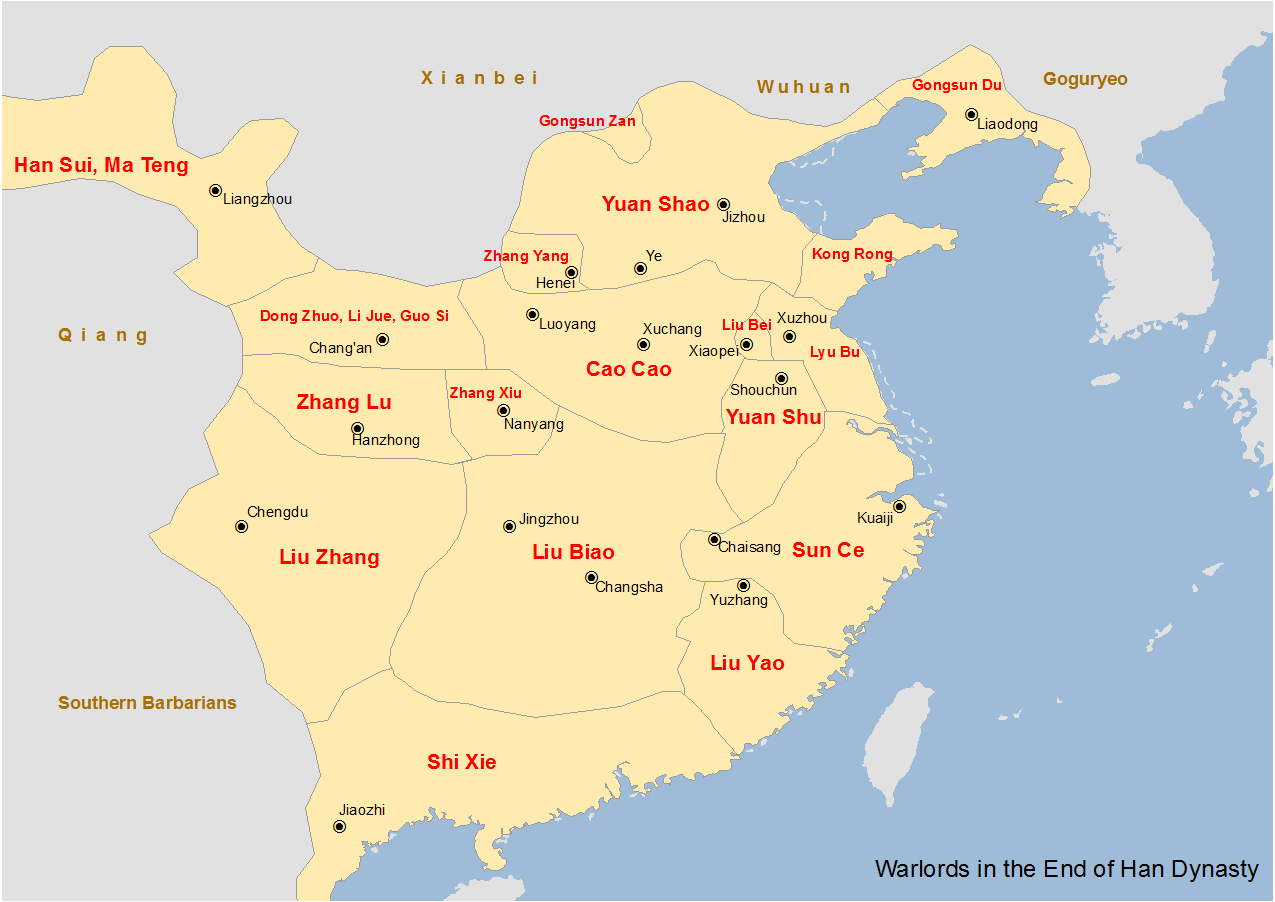
The end of the (Eastern) Han dynasty was the period of History of China, Chinese history from 189 to 220 CE, roughly coinciding with the tumultuous reign of the Han dynasty's last ruler, Emperor Xian of Han, Emperor Xian. It was followed by the Three Kingdoms era (220–280 CE). During the end of the Han dynasty, the country was thrown into turmoil by the Yellow Turban Rebellion (184–205). Meanwhile, the Han Empire's institutions were destroyed by the warlord Dong Zhuo and fractured into regional regimes ruled by various warlords, some of whom were nobles and officials of the Han imperial court. The warlord Cao Cao took control of Emperor Xian and his court in 196 and began gradually reunifying the empire. Cao Cao ostensibly operated under Emperor Xian's rule, though in reality the emperor was a hostage. Cao Cao's efforts to reunify China were rebuffed at the Battle of Red Cliffs in 208-209, when his armies were defeated by the allied forces of Sun Quan and Liu Bei. The Han d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Qing Province
Qingzhou or Qing Province was one of the Nine Provinces of ancient China dating back to BCE that later became one of the thirteen provinces of the Han dynasty (206 BCE–220 CE). The Nine Provinces were first described in the ''Tribute of Yu'' chapter of the classic ''Book of Documents'', with Qingzhou lying to the east of Yuzhou and north of Yangzhou. Qingzhou's primary territory included most of modern Shandong province except the southwest corner. History Ancient times The territory takes its name from the ''Tribute of Yu'' wherein Yu the Great wrote: "Between the sea and Mount Tai there is only Qingzhou". In around 5,000 BCE the area was the cradle of Dongyi culture. During the Xia and Shang dynasties, it was home to the Shuangjiu (, ''Shuǎngjīu''), Jize (, ''Jìzé''), and Pangboling (, ''Pángbólíng'') clans and the state of Pugu. Zhou dynasty Following the Duke of Zhou's BCE successful campaign against the Dongyi states allied with the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xin Pi
Xin Pi (before 175 - 235), courtesy name Zuozhi, was an official of the state of Cao Wei during the Three Kingdoms period of China. Along with his elder brother Xin Ping, he started his career in the late Eastern Han dynasty as an adviser to the warlord Yuan Shao. Following Yuan Shao's death and a power struggle between Yuan Shao's sons Yuan Tan and Yuan Shang, Xin Pi initially sided with Yuan Tan but later defected to Yuan Shao's rival Cao Cao, while seeking Cao Cao's aid on Yuan Tan's behalf in the fight against Yuan Shang. As a result, his family members were executed by Shen Pei, a Yuan Shang loyalist who blamed Xin Pi for the downfall of the Yuan family. After avenging his family, Xin Pi served as an official under Cao Cao, who controlled the Han central government and the figurehead Emperor Xian. After the Cao Wei state replaced the Eastern Han dynasty, Xin Pi continued serving under Cao Cao's successor Cao Pi, the first Wei emperor, and later under Cao Rui, Cao Pi's s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Records Of The Three Kingdoms
The ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'' is a Chinese official history written by Chen Shou in the late 3rd century CE, covering the end of the Han dynasty (220 CE) and the subsequent Three Kingdoms period (220–280 CE). It is regarded as to be the authoritative source text for these periods. Compiled following the reunification of China under the Jin dynasty (266–420), the work chronicles the political, social, and military events within rival states Cao Wei, Shu Han and Eastern Wu into a single text organized by individual biography. The ''Records'' are the primary source of information for the 14th-century historical novel '' Romance of the Three Kingdoms'', considered to be one of the four classic novels emblematic of written vernacular Chinese. While large subsections of the work have been selected and translated into English, the entire corpus has yet to receive an unabridged English translation. Origin and structure The '' Book of Han'' and ''Records of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zhao (state)
Zhao () was one of the seven major State (Ancient China), states during the Warring States period of ancient China. It emerged from the Partition of Jin, tripartite division of Jin, along with Han (Warring States), Han and Wei (state), Wei, in the 5th century BC. Zhao gained considerable strength from the military reforms initiated during the reign of King Wuling of Zhao, King Wuling, but suffered a crushing defeat at the hands of Qin (state), Qin at the Battle of Changping. Its territory included areas in the modern provinces of Inner Mongolia, Hebei, Shanxi and Shaanxi. It bordered the states of Qin, Wei, and Yan (state), Yan, as well as various nomadic peoples including the Donghu people, Hu and Xiongnu. Its capital was Handan, in modern Hebei province. Zhao was home to the Chinese Legalism, administrative philosopher Shen Dao, Confucian Xun Kuang, and Gongsun Long, who is affiliated to the school of names. Origins and ascendancy The Zhao (surname), Zhao clan within Jin ( ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zang Ba
Zang Ba ( 162–230s), courtesy name Xuangao, was a military general who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty and Three Kingdoms period of China. He served the warlord Tao Qian initially, followed by Lü Bu and finally Cao Cao and his successors, but for the most part of his career, he remained semi-autonomous over his troops and eastern China. The years of his birth and death are not recorded, but he served the state of Cao Wei in the Three Kingdoms period until the reign of the second Wei emperor, Cao Rui. During his life he was granted autonomous power over Qing and Xu provinces. He eventually held the title of marquis of various counties within, but by the time of his death held the appointment Bearer of the Golden Mace (執金吾; i.e., police chief of the imperial capital). Biography Zang Ba was originally from Hua County (), Taishan Commandery, which is around present-day Fei County, Shandong. According to the ''Records of the Three Kingdoms'', Zang Ba's father ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pingyuan County, Shandong
Pingyuan County () is a county in the northwest of Shandong province, People's Republic of China. It is administered by the prefecture-level city of Dezhou. It has an area of . History At the end of the Han dynasty, Liu Bei began his political career as prefect of Pingyuan Commandery. The town was one of the starts for the anti-Western Boxer Rebellion. The population was 437,584 in 1999. Administrative divisions , this County is divided to 2 subdistricts, 7 towns and 3 townships. ;Subdistricts *Longmen Subdistrict () *Taoyuan Subdistrict () ;Towns * Wangfenglou () * Qiancao () * Encheng () * Wangmiao () * Wanggaopu () * Zhanghua () *Jiaozhan Jiaozhan () is a town in Pingyuan County, Dezhou, in northwestern Shandong province, China China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. With population of China, a population exceeding 1.4 billion, ... () ;Townships *Fangzi Township () *Wangdagua Township () *Santang Township () Cl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liu Biao
Liu Biao () () ( 151 – September 208), courtesy name Jingsheng, was a Chinese military general, politician, and warlord who lived in the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He is best known for serving as the governor of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) from 192 until his death in 208. He was also a member of the extended family of the Han emperors through his ancestor Liu Yu, the fifth son of Emperor Jing. Liu Biao was described as a handsome man and was over eight '' chi'' tall (1.86 metres). Life In 166 to 167, when Liu Biao was 17 (by East Asian reckoning), he became a student of Wang Chang (grandfather of Wang Can). At the time, Wang Chang was Administrator of Nanyang (南阳太守). Liu Biao gained control of Jing Province (covering present-day Hubei and Hunan) in 190 CE, when Dong Zhuo appointed him to the position after the death of its previous governor (or inspector), Wang Rui. Liu Biao later started a war against the warlord Yuan Shu and his ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wang Xiu
Wang Xiu ( 190s–210s), courtesy name Shuzhi, was a Chinese politician who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He rose up to the highest echelon of government under the warlord Cao Cao, then the ''de facto'' head of the Han central government, in the lead-up to the Three Kingdoms period. He was known for being compassionate and daring. Early life Wang Xiu was born in Yingling, Beihai Commandery, Qing Province, which is present-day Changle County, Shandong. His mother died when he was a young boy. At age 19, he travelled away to study, and sometime between 190 and 193 was drafted by Kong Rong to administer the district of Gaomi (), about 60 km from his hometown. As a district magistrate, Wang Xiu declared collective responsibility for harbouring criminals, helping to restore central authority over local magnates. Kong Rong nominated him as a ''xiaolian'', although Wang Xiu several times tried to bow out of the nomination in favour of Bing Yuan (). As centr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ye, China
Ye or Yecheng () was an ancient Chinese city located in what is now Linzhang County, Handan, Hebei province and neighbouring Anyang, Henan province. Ye was first built in the Spring and Autumn period by Duke Huan of Qi, and by the time of the Warring States period the city belonged to the state of Wei. During the Han dynasty, Ye was the seat of Wei Commandery and an important regional center. Following the collapse of Han rule, Ye served as the military headquarters of the warlords Yuan Shao and Cao Cao. Under the latter's rule, Ye transformed into a political and economic center of northeastern China during the Three Kingdoms period, and during the Sixteen Kingdoms and Northern dynasties, the city served as the capital for the Later Zhao, Ran Wei, Former Yan, Eastern Wei and Northern Qi dynasties. History In 204, Cao Cao wrestled the city of Ye from Yuan Shao's son Yuan Shang. As the preceding battle of Ye had destroyed the inner city, Cao Cao set about rebuilding th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Liyang
The Battle of Liyang, fought between October 202 and June 203 in the late Eastern Han dynasty, was an invasion attempt by the warlord Cao Cao against the brothers Yuan Shang and Yuan Tan, the sons of Cao's rival Yuan Shao. The battle in October 202 was the first between the two factions since the death of Yuan Shao four months earlier. Although it ended in Cao Cao's withdrawal, events in this battle brought tensions between the Yuan brothers to the surface as Yuan Tan mutinied against his younger brother Yuan Shang after Cao Cao's temporary exit from the scene. Background After years of civil war since the failed campaign against Dong Zhuo, two major factions emerged from the multitudes of feuding warlords: one led by the northern warlord Yuan Shao who nominally controlled the provinces of Ji, Qing, Bing, and You; the other led by his former friend and subordinate Cao Cao, who, in addition to the three provinces of Yan, Yu, and Xu, also had the imperial court and the Han Em ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gao Gan
Gao Gan () (died 206), courtesy name Yuancai, was a minor warlord who lived during the late Eastern Han dynasty of China. He was a maternal nephew and subordinate of the warlord Yuan Shao. Life Gao Gan was from an influential family in Yu County (), Chenliu Commandery (), which is around present-day Qi County, Kaifeng, Henan. He was also a maternal nephew of the warlord Yuan Shao, who controlled most of the territories in northern China from the 190s to his death in 202. Gao Gan held the appointment of Inspector () of Bing Province, which was one of the four provinces in northern China under Yuan Shao's control around 200 CE. He governed Bing Province for about seven years. In 200 CE, Yuan Shao lost the Battle of Guandu against his rival, Cao Cao, who controlled the Han central government and the figurehead Emperor Xian. After Yuan Shao's defeat, only the troops under Gao Gan's command in Bing Province, numbering about 50,000, were the most organised and highest in morale a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |