|
Löfgren Syndrome
Löfgren syndrome is a type of acute sarcoidosis, an inflammatory disorder characterized by swollen lymph nodes in the chest, tender red nodules on the shins, fever and arthritis. It is more common in women than men, and is more frequent in those of Scandinavian, Irish, African and Puerto Rican heritage. It was described in 1953 by Sven Halvar Löfgren, a Swedish clinician. Some have considered the condition to be imprecisely defined. Signs and symptoms It is characterized by enlargement of the lymph nodes near the inner border of the lungs (called " hilar lymphadenopathy") as seen on x-ray, and tender red nodules ( erythema nodosum) are classically present on the shins, predominantly in women. It may also be accompanied by arthritis (more prominent in men) and fever. The arthritis is often acute and involves the lower extremities, particularly the ankles. Löfgren syndrome consists of the triad of erythema nodosum, bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy on chest radiograph, and joi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
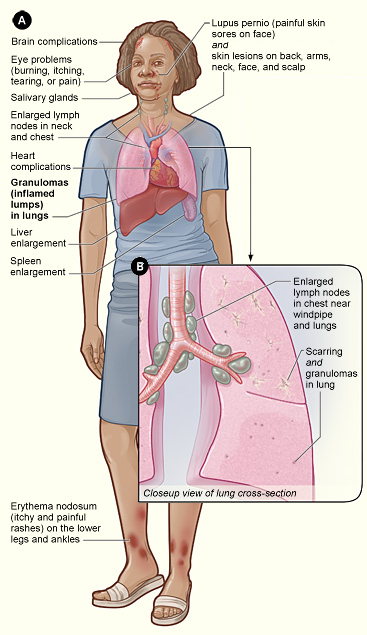
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chest Radiograph
A chest radiograph, chest X-ray (CXR), or chest film is a projection radiograph of the chest used to diagnose conditions affecting the chest, its contents, and nearby structures. Chest radiographs are the most common film taken in medicine. Like all methods of radiography, chest radiography employs ionizing radiation in the form of X-rays to generate images of the chest. The mean radiation dose to an adult from a chest radiograph is around 0.02 mSv (2 mrem) for a front view (PA, or posteroanterior) and 0.08 mSv (8 mrem) for a side view (LL, or latero-lateral). Together, this corresponds to a background radiation equivalent time of about 10 days. Medical uses Conditions commonly identified by chest radiography * Pneumonia * Pneumothorax * Interstitial lung disease * Heart failure * Bone fracture * Hiatal hernia * Pulmonary tuberculosis Chest radiographs are used to diagnose many conditions involving the chest wall, including its bones, and also structures contained ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Autoimmune Diseases
An autoimmune disease is a condition that results from an anomalous response of the adaptive immune system, wherein it mistakenly targets and attacks healthy, functioning parts of the body as if they were foreign organisms. It is estimated that there are more than 80 recognized autoimmune diseases, with recent scientific evidence suggesting the existence of potentially more than 100 distinct conditions. Nearly any body part can be involved. Autoimmune diseases are a separate class from autoinflammatory diseases. Both are characterized by an immune system malfunction which may cause similar symptoms, such as rash, swelling, or fatigue, but the cardinal cause or mechanism of the diseases is different. A key difference is a malfunction of the innate immune system in autoinflammatory diseases, whereas in autoimmune diseases there is a malfunction of the adaptive immune system. Symptoms of autoimmune diseases can significantly vary, primarily based on the specific type of the diseas ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syndromes Affecting The Respiratory System
A syndrome is a set of medical signs and symptoms which are correlated with each other and often associated with a particular disease or disorder. The word derives from the Greek σύνδρομον, meaning "concurrence". When a syndrome is paired with a definite cause this becomes a disease. In some instances, a syndrome is so closely linked with a pathogenesis or cause that the words ''syndrome'', ''disease'', and ''disorder'' end up being used interchangeably for them. This substitution of terminology often confuses the reality and meaning of medical diagnoses. This is especially true of inherited syndromes. About one third of all phenotypes that are listed in OMIM are described as dysmorphic, which usually refers to the facial gestalt. For example, Down syndrome, Wolf–Hirschhorn syndrome, and Andersen–Tawil syndrome are disorders with known pathogeneses, so each is more than just a set of signs and symptoms, despite the ''syndrome'' nomenclature. In other instances, a syn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sarcoidosis
Sarcoidosis (; also known as Besnier–Boeck–Schaumann disease) is a disease involving abnormal collections of White blood cell, inflammatory cells that form lumps known as granulomata. The disease usually begins in the lungs, skin, or lymph nodes. Less commonly affected are the eyes, liver, heart, and Human brain, brain, though any Organ (anatomy), organ can be affected. The signs and symptoms depend on the organ involved. Often, no symptoms or only mild symptoms are seen. When it affects the lungs, wheezing, coughing, shortness of breath, or chest pain may occur. Some may have Löfgren syndrome with fever, Bilateral hilar lymphadenopathy, enlarged hilar lymph nodes, arthritis, and a rash known as erythema nodosum. The cause of sarcoidosis is unknown. Some believe it may be due to an immune reaction to a trigger such as an infection or chemicals in those who are genetically predisposed. Those with affected family members are at greater risk. Diagnosis is partly based on signs ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Cutaneous Conditions
Many skin conditions affect the human integumentary system—the organ system covering the entire surface of the Human body, body and composed of Human skin, skin, hair, Nail (anatomy), nails, and related muscle and glands. The major function of this system is as a barrier against the external environment. The skin weighs an average of four kilograms, covers an area of two square metres, and is made of three distinct layers: the epidermis (skin), epidermis, dermis, and subcutaneous tissue. The two main types of human skin are: glabrous skin, the hairless skin on the palms and soles (also referred to as the "palmoplantar" surfaces), and hair-bearing skin.Burns, Tony; ''et al''. (2006) ''Rook's Textbook of Dermatology CD-ROM''. Wiley-Blackwell. . Within the latter type, the hairs occur in structures called pilosebaceous units, each with hair follicle, sebaceous gland, and associated arrector pili muscle. Embryology, In the embryo, the epidermis, hair, and glands form from the ectod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lupus Pernio
Lupus pernio is a chronic raised indurated (hardened) lesion of the skin, often purplish in color. It is seen on the nose, ears, cheeks, lips, and forehead. It is pathognomonic of sarcoidosis. The name "lupus pernio" is a misnomer, as microscopically this disease shows granulomatous infiltration and does not have features of either lupus nor pernio. Signs and symptoms The hallmarks of lupus pernio are violaceous or erythematous, indurated plaques that are mostly found on the cheeks and nose in the center of the face. Rarely, lesions may also affect the dorsum of the hands and feet and the ears. The symptoms of lupus pernio range from a few tiny nodules on the nose to vibrant plaques that cover both cheeks. Lupus pernio lesions begin slowly but eventually penetrate and indurate into the underlying bone and cartilage, resulting in deformity. There is a higher chance of extracutaneous involvement, especially in the respiratory tract, in lupus pernio. Causes The cause of cutane ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Disease Modifying Antirheumatic Drug
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs) comprise a category of otherwise unrelated disease-modifying drugs defined by their use in rheumatoid arthritis to slow down disease progression. The term is often used in contrast to nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (which refers to agents that treat the inflammation, but not the underlying cause) and steroids (which blunt the immune response but are insufficient to slow down the progression of the disease). The term "antirheumatic" can be used in similar contexts, but without making a claim about an effect on the disease course. Other terms that have historically been used to refer to the same group of drugs are "remission-inducing drugs" (RIDs) and "slow-acting antirheumatic drugs" (SAARDs). Terminology Although the use of the term DMARDs was first propagated in rheumatoid arthritis (hence their name), the term has come to pertain to many other diseases, such as Crohn's disease, lupus erythematosus, Sjögren syndrome, immun ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prednisone
Prednisone is a glucocorticoid medication mostly used to immunosuppressive drug, suppress the immune system and decrease inflammation in conditions such as asthma, COPD, and rheumatologic diseases. It is also used to treat high blood calcium due to cancer and adrenal insufficiency along with other steroids. It is taken Oral administration, by mouth. Common side effects may include cataracts, Osteoporosis, bone loss, easy bruising, muscle weakness, and oral candidiasis, thrush. Other side effects include weight gain, swelling, high blood sugar, increased risk of infection, and psychosis. It is generally considered safe in pregnancy and low doses appear to be safe while the user is breastfeeding. After prolonged use, prednisone must be stopped gradually. Prednisone is a prodrug and must be converted to prednisolone by the liver before it becomes active. Prednisolone then binds to glucocorticoid receptors, activating them and triggering changes in gene expression. Prednison ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Colchicine
Colchicine is a medication used to prevent and treat gout, to treat familial Mediterranean fever and Behçet's disease, and to reduce the risk of myocardial infarction. The American College of Rheumatology recommends colchicine, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or steroids in the treatment of gout. Other uses for colchicine include the management of pericarditis. Colchicine is taken by mouth. The injectable route of administration for colchicine can be toxic. In 2008, the US Food and Drug Administration removed all injectable colchicine from the US market. Colchicine has a narrow therapeutic index, so overdosing is a significant risk. Common side effects of colchicine include gastrointestinal upset, particularly at high doses. Severe side effects may include pancytopenia (low blood cell counts) and rhabdomyolysis (damage to skeletal muscle), and the medication can be deadly in overdose. Whether colchicine is safe for use during pregnancy is unclear, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nonsteroidal Anti-inflammatory Drug
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) are members of a Indication (medicine), therapeutic drug class which Analgesic, reduces pain, Anti-inflammatory, decreases inflammation, Antipyretic, decreases fever, and Antithrombotic, prevents blood clots. Side effects depend on the specific drug, its dose and duration of use, but largely include an increased risk of Stomach ulcers, gastrointestinal ulcers and bleeds, heart attack, and kidney disease. The term ''non-steroidal'', common from around 1960, distinguishes these drugs from corticosteroids, another class of anti-inflammatory drugs, which during the 1950s had acquired a bad reputation due to overuse and side-effect problems after their introduction in 1948. NSAIDs work by inhibiting the activity of cyclooxygenase enzymes (the COX-1 and COX-2 isozyme, isoenzymes). In cells, these enzymes are involved in the synthesis of key biological mediators, namely prostaglandins, which are involved in inflammation, and thromboxanes, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |