|
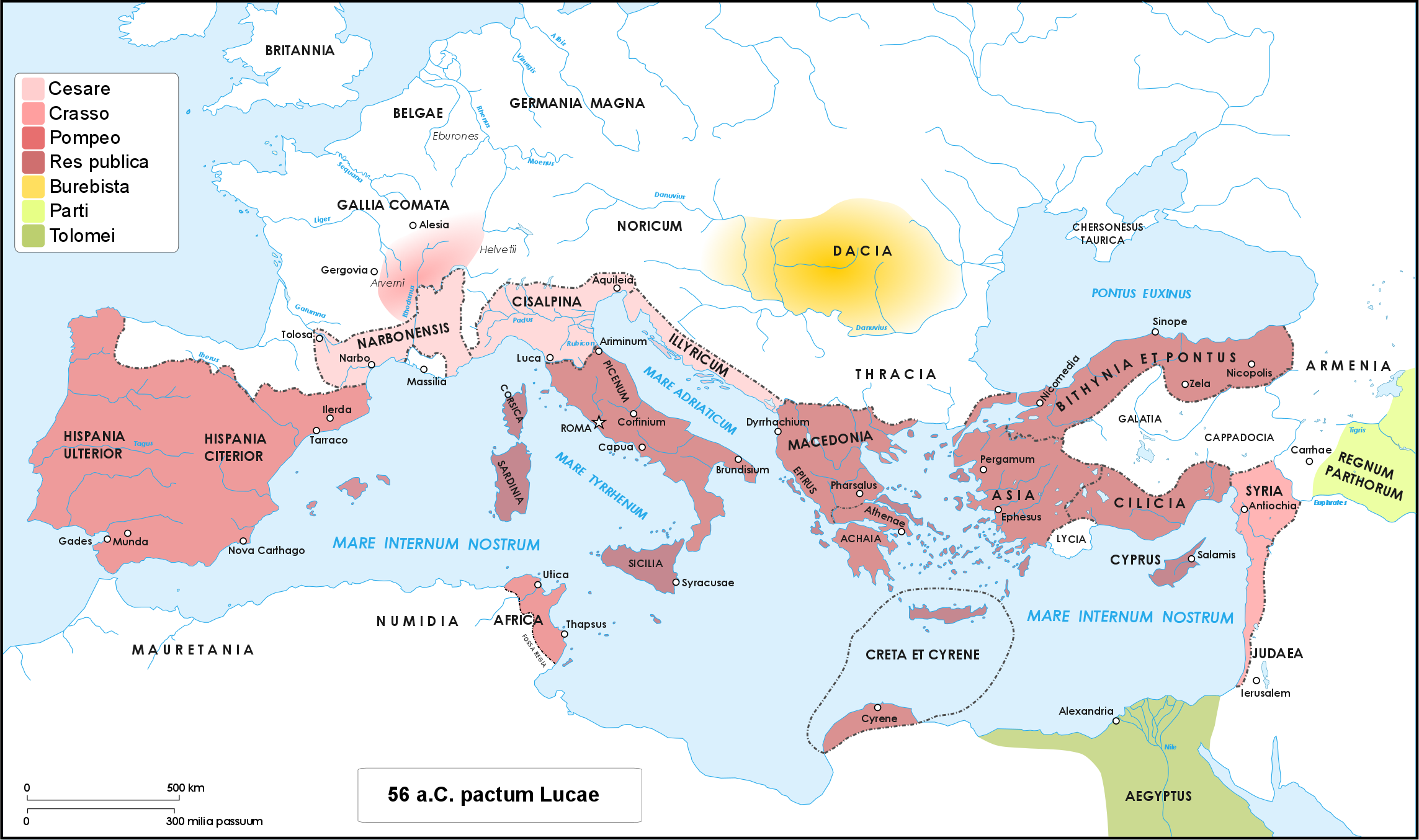
Luca Conference
The Luca Conference was a 56 BC meeting of the three Roman politicians of the First Triumvirate — Caesar, Pompey and Crassus — that took place at the town of Luca (modern Lucca, in Tuscany), near Pisa. Luca was the southern most town in the then Roman province of Cisalpine Gaul, where Caesar was serving as Governor. The meeting renewed the fraying political alliance, and further cemented the three men's increasing consolidation of power in the Roman Republic. Background The Roman general Julius Caesar was in the midst of fighting the Gallic Wars. At the end of 57 BC, he had conquered much of Gaul and had been awarded a 15-day ''supplicatio'', a feast of thanksgiving, longer than any before. Caesar's ''gravitas'' was growing quickly, and he aimed to leverage it to his advantage. Rome was in turmoil. “Caesar had already been away for two years, and the time had not passed quietly in Rome. His consulship had been controversial, but in many ways was mild in comparison with ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Triumvirate Of Caesar, Crassius And Pompey
First most commonly refers to: * First, the ordinal form of the number 1 First or 1st may also refer to: Acronyms * Faint Images of the Radio Sky at Twenty-Centimeters, an astronomical survey carried out by the Very Large Array * Far Infrared and Sub-millimetre Telescope, of the Herschel Space Observatory * For Inspiration and Recognition of Science and Technology, an international youth organization * Forum of Incident Response and Security Teams, a global forum Arts and entertainment Albums * ''1st'' (album), by Streets, 1983 * ''1ST'' (SixTones album), 2021 * ''First'' (David Gates album), 1973 * ''First'', by Denise Ho, 2001 * ''First'' (O'Bryan album), 2007 * ''First'' (Raymond Lam album), 2011 Extended plays * ''1st'', by The Rasmus, 1995 * ''First'' (Baroness EP), 2004 * ''First'' (Ferlyn G EP), 2015 Songs * "First" (Lindsay Lohan song), 2005 * "First" (Cold War Kids song), 2014 * "First", by Lauren Daigle from the album '' How Can It Be'', 2015 * "First", ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plutarch
Plutarch (; , ''Ploútarchos'', ; – 120s) was a Greek Middle Platonist philosopher, historian, biographer, essayist, and priest at the Temple of Apollo (Delphi), Temple of Apollo in Delphi. He is known primarily for his ''Parallel Lives'', a series of biographies of illustrious Greeks and Romans, and ''Moralia'', a collection of essays and speeches. Upon becoming a Roman citizen, he was possibly named Lucius Mestrius Plutarchus (). Family Plutarch was born to a prominent family in the small town of Chaeronea, about east of Delphi, in the Greek region of Boeotia. His family was long established in the town; his father was named Autobulus and his grandfather was named Lamprias. His brothers, Timon and Lamprias, are frequently mentioned in his essays and dialogues, which speak of Timon in particular in the most affectionate terms. Studies and life Plutarch studied mathematics and philosophy in Athens under Ammonius of Athens, Ammonius from AD 66 to 67. He attended th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was a civil war during the late Roman Republic between two factions led by Julius Caesar and Pompey. The main cause of the war was political tensions relating to Caesar's place in the Republic on his expected return to Rome on the expiration of his Lex Vatinia, governorship in Roman Gaul, Gaul. Before the war, Caesar had led an Gallic Wars, invasion of Gaul for almost ten years. A build-up of tensions starting in late 50 BC, with both Caesar and Pompey refusing to back down, led to the outbreak of civil war. Pompey and his allies induced the Roman Senate, Senate to demand Caesar give up his provinces and armies in the opening days of 49 BC. Caesar refused and instead Crossing the Rubicon, marched on Rome. The war was fought in Italy, Illyria, Greece in the Roman era, Greece, Ptolemaic Egypt, Egypt, Africa (Roman province), Africa, and Hispania. The decisive events occurred in Greece in 48 BC: Pompey defeated Caesar at the Battle of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Carrhae
The Battle of Carrhae () was fought in 53 BC between the Roman Republic and the Parthian Empire near the ancient town of Carrhae (present-day Harran, Turkey). An invading force of seven Roman legion, legions of Roman heavy infantry under Marcus Licinius Crassus was lured into the desert and decisive battle, decisively defeated by a mixed cavalry army of heavy cataphracts and light horse archers led by the Parthian general Surena. On such flat terrain, the Legion proved to have no viable tactics against the highly mobile Parthian horsemen, and the slow and vulnerable Roman formations were surrounded, exhausted by constant attacks, and eventually crushed. Crassus was killed along with the majority of his army. It is commonly seen as one of the earliest and most important Roman–Persian Wars, battles between the Roman and Parthian Empires and one of the most crushing defeats in Roman history. According to the poet Ovid in Book 6 of his poem ''Fasti (poem), Fasti'', the battle occur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Campania
Campania is an administrative Regions of Italy, region of Italy located in Southern Italy; most of it is in the south-western portion of the Italian Peninsula (with the Tyrrhenian Sea to its west), but it also includes the small Phlegraean Islands and the island of Capri. The capital of the region is Naples. Campania has a population of 5,575,025 as of 2025, making it Italy's third most populous region, and, with an area of , its most densely populated region. Based on its Gross domestic product, GDP, Campania is also the most economically productive region in Southern Italy List of Italian regions by GDP, and the 7th most productive in the whole country. Naples' urban area, which is in Campania, is the List of urban areas in the European Union, eighth most populous in the European Union. The region is home to 10 of the 58 List of World Heritage Sites in Italy, UNESCO sites in Italy, including Pompeii and Herculaneum, the Royal Palace of Caserta, the Amalfi Coast, the Longobardian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Publius Licinius Crassus (son Of Triumvir)
Publius Licinius Crassus (86 or 82 – 53 BC) was one of two sons of Marcus Licinius Crassus, the so-called "triumvir", and Tertulla, daughter of Marcus Terentius Varro Lucullus., p.831 He belonged to the last generation of Roman ''nobiles'' who came of age and began a political career before the collapse of the Republic. His peers included Marcus Antonius, Marcus Junius Brutus, Decimus Junius Brutus Albinus, the poet Gaius Valerius Catullus, and the historian Gaius Sallustius Crispus. Publius Crassus served under Julius Caesar in Gaul from 58 to 56 BC. Too young to receive a formal commission from the senate, Publius distinguished himself as a commanding officer in campaigns among the Armorican nations (Brittany) and in Aquitania. He was highly regarded by Caesar and also by Cicero, who praised his speaking ability and good character. Upon his return to Rome, Publius married Cornelia Metella, the intellectually gifted daughter of Metellus Scipio, and began his acti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tribune Of The Plebs
Tribune of the plebs, tribune of the people or plebeian tribune () was the first office of the Roman Republic, Roman state that was open to the plebs, plebeians, and was, throughout the history of the Republic, the most important check on the power of the Roman Senate and Roman magistrate, magistrates. These tribunes had the power to convene and preside over the ''Plebeian Council, Concilium Plebis'' (people's assembly); to summon the senate; to propose legislation; and to intervene on behalf of plebeians in legal matters; but the most significant power was to veto the actions of the Roman consul, consuls and other magistrates, thus protecting the interests of the plebeians as a class. The tribunes of the plebs were typically found seated on Tribune bench, special benches set up for them in the Roman Forum. The tribunes were sacrosanct, meaning that any assault on their person was punishable by death. In Roman Empire, imperial times, the powers of the tribunate were granted to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus (consul 54 BC)
Lucius Domitius Ahenobarbus, consul in 54 BC, was an enemy of Julius Caesar and a strong supporter of the aristocratic () party in the late Roman Republic. He was Nero's great-great-grandfather. Biography Ahenobarbus was born as the son of consul Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus. His grandfather Gnaeus Domitius Ahenobarbus was a general and consul who led a campaign to conquer southern Gaul against the Allobroges. He is first mentioned in 70 BC by Cicero as a witness against Verres. In 61, he was curule aedile, when he exhibited a hundred Numidian lions, and continued the games so long that the people were obliged to leave the circus before the exhibition was over, in order to take food, which was the first time they had done so. This pause in the games was called ''diludium''. He married Porcia, the sister of Cato the Younger, and in his aedileship supported the latter in his proposals against bribery at elections, which were directed against Pompey, who was purchasing votes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lictor
A lictor (possibly from Latin language, Latin ''ligare'', meaning 'to bind') was a Ancient Rome, Roman civil servant who was an attendant and bodyguard to a Roman magistrate, magistrate who held ''imperium''. Roman records describe lictors as having existed since the Roman Kingdom, and may have originated with the Etruscan civilization, Etruscans. Origin The lictors are said in the ancient antiquarian sources to go back to the regal period. There are two main traditions. The first is from Dionysius of Halicarnassus. He claimed that Etruscan envoys numbering twelve (one for each Etruscan city) gifted the king Lucius Tarquinius Priscus fasces – symbolising military leadership of the twelve Etruscan communities – on his accession. With the approval of the Roman Senate, Senate, Tarquin then appointed twelve lictors to attend to him when exercising military and civil authority. The second is in Livy, which attributes the first lictors to the king Romulus. Livy also sides with an Et ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperium
In ancient Rome, ''imperium'' was a form of authority held by a citizen to control a military or governmental entity. It is distinct from '' auctoritas'' and '' potestas'', different and generally inferior types of power in the Roman Republic and Empire. One's ''imperium'' could be over a specific military unit, or it could be over a province or territory. Individuals given such power were referred to as curule magistrates or promagistrates. These included the curule aedile, the praetor, the consul, the ''magister equitum'', and the dictator. In a general sense, ''imperium'' was the scope of someone's power, and could include anything, such as public office, commerce, political influence, or wealth. Ancient Rome ''Imperium'' originally meant absolute or kingly power—the word being derived from the Latin verb ''imperare'' (to command)—which became somewhat limited under the Republic by the collegiality of the republican magistrates and the right of appeal, or '' provoc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cicero
Marcus Tullius Cicero ( ; ; 3 January 106 BC – 7 December 43 BC) was a Roman statesman, lawyer, scholar, philosopher, orator, writer and Academic skeptic, who tried to uphold optimate principles during the political crises that led to the establishment of the Roman Empire. His extensive writings include treatises on rhetoric, philosophy and politics. He is considered one of Rome's greatest orators and prose stylists and the innovator of what became known as "Ciceronian rhetoric". Cicero was educated in Rome and in Greece. He came from a wealthy municipal family of the Roman equestrian order, and served as consul in 63 BC. He greatly influenced both ancient and modern reception of the Latin language. A substantial part of his work has survived, and he was admired by both ancient and modern authors alike. Cicero adapted the arguments of the chief schools of Hellenistic philosophy in Latin and coined a large portion of Latin philosophical vocabulary via ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |