|
Loricata
Loricata is a clade of archosaur reptiles that includes crocodilians and some of their Triassic relatives, such as ''Postosuchus'' and ''Prestosuchus''. More specifically, Loricata includes Crocodylomorpha (the persistent archosaur subset which crocodilians belong to) and most "rauisuchians", a paraphyletic grade of large terrestrial pseudosuchians which were alive in the Triassic period and ancestral to crocodylomorphs. Loricata is one branch of the group Paracrocodylomorpha; the other branch is the clade Poposauroidea, an unusual collection of strange "rauisuchians" including bipedal, herbivorous, and sail-backed forms. The vast majority of typical "rauisuchians", which were usually quadrupedal predators, occupy basal (early-branching) rungs of Loricata leading up to crocodylomorphs. History and Classification Loricata was initially named in a completely different context by German naturalist Blasius Merrem in his 1820 ''Versuch eines Systems der Amphibien''. Merrem consid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rauisuchia
"Rauisuchia" is a paraphyletic group of mostly large and carnivorous Triassic archosaurs. Rauisuchians are a category of archosaurs within a larger group called Pseudosuchia, which encompasses all archosaurs more closely related to crocodilians than to birds and other dinosaurs. First named in the 1940s, Rauisuchia was a name exclusive to Triassic archosaurs which were generally large (often ), carnivorous, and quadrupedal with a pillar-erect hip posture, though exceptions exist for all of these traits. Rauisuchians, as a traditional Taxonomy, taxonomic group, were considered distinct from other Triassic archosaur groups such as early dinosaurs, phytosaurs (crocodile-like carnivores), aetosaurs (armored herbivores), and Crocodylomorpha, crocodylomorphs (lightly-built crocodilian ancestors). However, more recent studies on archosaur evolution have upended this idea based on phylogenetic analyses and cladistics, a modern approach to taxonomy based on clades (nested Monophyly, monop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestosuchus
''Prestosuchus'' (meaning "Prestes crocodile") is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian in the group Loricata, which also includes ''Saurosuchus'' and ''Postosuchus''. It has historically been referred to as a "rauisuchian", and was the defining member of the family Prestosuchidae, though the validity of both of these groups is questionable: Rauisuchia is now considered Paraphyly, paraphyletic and Prestosuchidae is Polyphyly, polyphyletic in its widest form. History of study The holotype of ''Prestosuchus chiniquensis'' was discovered by Wilhelm Rau alongside the holotype of ''Rauisuchus tiradentes'' in the Santa Maria Formation at the Paleontological Site Chiniquá, near the city of São Pedro do Sul, Rio Grande do Sul, São Pedro do Sul in 1928 or 1929, and the fossils were shipped back to Germany for study by the German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene. Von Huene named the genus ''Prestosuchus'' in 1938 in honor of Vicentino Prestes de Almeida. This site is located in the geop ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paracrocodylomorpha
Paracrocodylomorpha is a clade of pseudosuchian archosaurs. The clade includes the diverse and unusual group Poposauroidea as well as the generally carnivorous and quadrupedal members of Loricata, including modern crocodylians. Paracrocodylomorpha was named by paleontologist J. Michael Parrish in 1993, although the group is now considered to encompass more reptiles than his original definition intended. The most recent definition of Paracrocodylomorpha, as defined by Sterling Nesbitt in 2011, is "the least inclusive clade containing ''Poposaurus'' and ''Crocodylus niloticus'' (the Nile crocodile). Most groups of paracrocodylomorphs became extinct at the end of the Triassic period, with the exception of the crocodylomorphs, from which crocodylians such as crocodiles and alligators evolved in the latter part of the Mesozoic. History and definition Parrish (1993) defined Paracrocodylomorpha as the last common ancestor of " Poposauridae" and Crocodylomorpha and all of its descend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Decuriasuchus
''Decuriasuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan from the Middle Triassic period (Ladinian stage). It is a carnivorous archosaur that lived in what is now southern Brazil, in Paleorrota. It was first named by Marco Aurélio G. França, Jorge Ferigolo and Max C. Langer in 2011 and the type species is ''Decuriasuchus quartacolonia''. The generic name means "unit of ten crocodiles" in Latin and Greek in reference to the ten known specimens and the animal's possible group behavior. The specific name refers to the Quarta Colonia region where the fossils were collected. Description ''Decuriasuchus'' is known from ten specimens, including nine articulated and associated skeletons, three of which have nearly complete skulls. The holotype MCN PV10105a consists of an articulated partial skeleton, lacking scapular girdle and limbs. Eight specimens associated with the holotype, MCN PV10105b-i, and the tenth specimen (MCN PV10004), consists of cranial remains from a different spot in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Prestosuchidae
Prestosuchidae (in its widest usage) is a polyphyletic grouping of carnivorous archosaurs that lived during the Triassic. They were large active terrestrial apex predators, ranging from around in length. They succeeded the Erythrosuchidae as the largest archosaurs of their time. While resembling erythrosuchids in size and some features of the skull and skeleton, they were more advanced in their erect posture and crocodile-like ankle, indicating more efficient gait. "Prestosuchids" flourished throughout the whole of the middle, and the early part of the late Triassic, and fossils are so far known from Europe, India, Africa (Tanzania), Argentina, and Paleorrota in Brazil. However, for a long time experts disagree regarding the phylogenetic relationships of the group, what genera should be included, and whether indeed the "Prestosuchidae" constitute a distinct family. In 2011, Prestosuchidae in its broadest definition was determined to be a poorly-diagnosed and obsolete polyphylet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fasolasuchus
''Fasolasuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan. Fossils have been found in the Los Colorados Formation of the Ischigualasto-Villa Unión Basin in northwestern Argentina that date back to the Norian stage of the Late Triassic, making it one of the last "rauisuchians" to have existed before the order became extinct at the end of the Triassic. Description ''Fasolasuchus'' is likely the largest known "rauisuchian", with an estimated length of to . This would make ''Fasolasuchus'' the largest terrestrial predator to have ever existed save for large theropods, surpassing the Cenozoic '' Barinasuchus'', the "rauisuchian" counterpart '' Saurosuchus'' at , and many medium sized theropods as large as ''Ceratosaurus''. Like ''Saurosuchus'', it had only a single row of caudal osteoderms, unusual among "rauisuchians". It also had a hyposphene-hypantrum articulation that gave the vertebral column extra rigidity. This feature is also seen in several other "rauisuchians" such as '' Post ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dagasuchus
''Dagasuchus'' is an extinct genus of pseudosuchian archosaur from the Late Triassic (Carnian) of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil, represented by the type species ''Dagasuchus santacruzensis''. ''D. santacruzensis'' was named in 2015 on the basis of specimen UFRGS-PV-1244-T and UFRGS-PV-1245-T, a partial hip (one ilium (bone), ilium and a pair of ischium, ischia) found in an exposure of the Santa Maria Formation in the Paraná Basin, near the city of Santa Cruz do Sul. ''Dagasuchus'' is an early member of a large evolutionary group called Loricata, which originated in the Triassic and includes modern crocodylians and their ancestors. Features of its hip closely resemble those of other early loricatans such as ''Stagonosuchus'' and ''Saurosuchus''. ''Dagasuchus'' is notable for being the first loricatan found in the ''Santacruzodon'' assemblage zone of the Santa Maria Formation; previously loricatans were only known from the older ''Dinodontosaurus'' assemblage zone and the younger ''Hyp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Arganasuchus
''Arganasuchus'' is an extinct genus of " rauisuchian" (loricatan) archosaur. It is known from a single species, ''Arganasuchus dutuiti''. Fossils of this genus have been found in Upper Triassic rocks of the Argana Basin, Morocco. Though its remains were initially referred to ''Ticinosuchus'' when discovered during the 1970s'','' in 2007 it was identified as a distinct genus with unique features of the pubis and maxilla. ''Arganasuchus'' also had several anatomical details in common with ''Batrachotomus'', ''Fasolasuchus'', and ''Postosuchus,'' though its relations with other loricatans remains unresolved. ''Arganasuchus'' is considered a carnivore due to its large, knife-shaped teeth. Discovery Fossils of ''Arganasuchus'' were first reported by Jean-Michel Dutuit in 1979, who referred a maxilla, dentary, femur, and fibula to ''Ticinosuchus''. These fossils were found in the lower part of unit T5 (the Irohalene Member) of the Timezgadiouine Formation. This geological format ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apatosuchus
''Apatosuchus'' is an extinct genus of non-crocodylomorph loricatan pseudosuchian known from the Late Triassic of Germany. It is known from a partial holotype skull from the middle Stubensandstein (a deposit that dates back to the Norian stage and is part of the Löwenstein Formation) in Baden-Württemberg. The type species is ''Halticosaurus orbitoangulatus.'' ''A. orbitoangulatus'' was first described by German paleontologist Friedrich von Huene in 1932,Huene, F. von. (1932). ''Die fossile Reptil-Ordnung Saurischia, ihre Entwicklung und Geschichte. Monogr. Geol. Pal.'' 4 (1) pts. 1 and 2, viii + 361 pp. who considered it a species of the theropod dinosaur '' Halticosaurus''. Some later studies proposed that it was an early crocodylomorph or "sphenosuchian" like ''Saltoposuchus'', another pseudosuchian from the middle Stubensandstein of Baden-Württemberg. The name ''Apatosuchus'', "deceptive crocodile", was erected for ''H. orbitoangulatus'' by Hans-Dieter Sues and Rainer R. S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Batrachotomus
''Batrachotomus'' is a genus of prehistoric archosaur. Fossils of this animal have been found in southern Germany and dated from the Ladinian stage of the Middle Triassic period, around 242 to 237 million years ago. ''Batrachotomus'' was described by palaeontologist David J. Gower 22 years after its discovery. The locality where ''Batrachotomus'' lived was a swampy region and the name comes from the Greek ''batrachos/βάτραχος'' (frog) and ''tome/τομή'' (cutting, slicing), which refers to its preying on the large amphibian ''Mastodonsaurus''.Gower (1999), p. 6. In contrast with sprawling reptiles, like crocodiles, this large carnivore was very agile with locomotor superiority due to its erect stance. A remarkable feature seen on its back was a row of paired, flattened bony plates. ''Batrachotomus'' was possibly an early relative of '' Postosuchus'',Gower (1999), p. 1. which lived during the dawn of the dinosaurs. Description ''Batrachotomus'' was a heavily buil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Etjosuchus
''Etjosuchus'' is an Extinction, extinct genus of carnivorous "rauisuchian" (loricatan) archosaur from the Triassic of Namibia. It is known from a Monotypic taxon, single species, ''Etjosuchus recurvidens'', which is based on a partial skeleton from the Ladinian to Carnian-aged Omingonde Formation. Discovery and history The holotype of ''Etjosuchus'', GSN F382, was discovered in the early 1990s by Thomas Löffler in outcrops of the Omingonde Formation in the bed of the Omingonde River near Mount Etjo. The specimen comprises a partially complete skeleton, preserving most of the vertebral column in articulation, a coracoid, both partial humeri, articulated cervical ribs, disarticulated dorsal ribs, partial gastralia, many articulated and disarticulated osteoderms, and both lateral halves of the skull and jaws, which are split in half in the sagittal plane. The specimen was figured and provisionally identified as ''Erythrosuchus africanus'' by Martin Pickford in 1995, and excavated ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
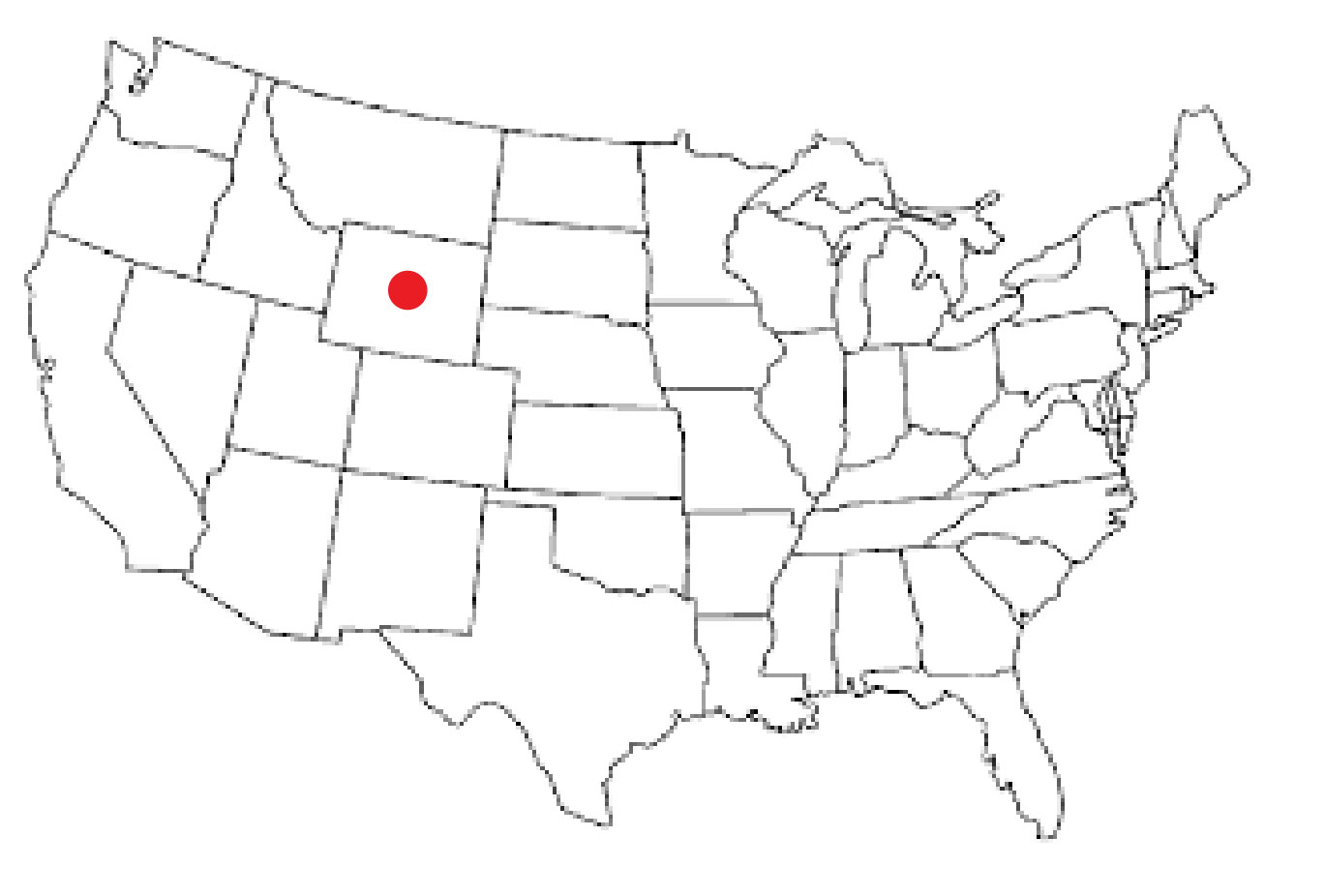
Heptasuchus
''Heptasuchus'' is an extinct genus of loricatan pseudosuchian known from the Middle Triassic, Middle or Late Triassic upper Chugwater Group of Wyoming, United States. It contains a single species, ''Heptasuchus clarki'', the first formally recognized "rauisuchian" or loricatan pseudosuchian from North America. Discovery and history Collected in the summer of 1977 at the newly discovered Clark locality northwest of Casper, Wyoming, Casper Wyoming, the specimens assigned to ''H. clarki'' were described in a brief article and two master's theses at Wayne State University, Detroit. ''Heptasuchus'' was first formally described and named by Robert M. Dawley, John M. Zawiskie and J. W. Cosgriff in 1979 in paleontology, 1979 and the type species is ''Heptasuchus clarki''. The name of a biological genus, generic name is derived from ''epta'' (ἑπτά), "seven" in Ancient Greek, and ''suchus'' (συχος) which is the Latinised form of the Ancient Greek word for the crocodile god of an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |