|
London–Brabant Massif
The London–Brabant Massif or London–Brabant Platform is, in the tectonic structure of Europe, a structural high or massif that stretches from the Rhineland in western Germany across northern Belgium (in the province of Brabant) and the North Sea to the sites of East Anglia and the middle Thames in southern England. The massif also occurs in the Belgian subsurface, where it is bounded to the northeast by the Roer Valley Graben that runs diagonally through Dutch Limburg. The Midlands Microcraton (southeastern Wales and part of western England) is often considered part of the massif and to reflect this the names Wales–Brabant Massif, Wales–London–Brabant Massif and Wales–Brabant High are sometimes used. This massif was also formerly referred to, at least in part, as St George's Land. The London–Brabant Massif is part of the former microcontinent Avalonia. To the south it borders the Rhenohercynian Zone of the Hercynian orogeny. To the northeast it is flanked by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tectonics
Tectonics ( via Latin ) are the processes that result in the structure and properties of the Earth's crust and its evolution through time. The field of ''planetary tectonics'' extends the concept to other planets and moons. These processes include those of orogeny, mountain-building, the growth and behavior of the strong, old cores of continents known as cratons, and the ways in which the relatively rigid tectonic plate, plates that constitute the Earth's outer shell interact with each other. Principles of tectonics also provide a framework for understanding the earthquake and volcanic belts that directly affect much of the global population. Tectonic studies are important as guides for economic geology, economic geologists searching for fossil fuels and ore deposits of metallic and nonmetallic resources. An understanding of tectonic principles can help geomorphology, geomorphologists to explain Erosion and tectonics, erosion patterns and other Earth-surface features. Ma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hercynian Orogeny
The Variscan orogeny, or Hercynian orogeny, was a geologic mountain-building event caused by Late Paleozoic continental collision between Euramerica (Laurussia) and Gondwana to form the supercontinent of Pangaea. Nomenclature The name ''Variscan'' comes from the Medieval Latin name for the district '' Variscia'', the home of a Germanic tribe, the Varisci; Eduard Suess, professor of geology at the University of Vienna, coined the term in 1880. ( Variscite, a rare green mineral first discovered in the Vogtland district of Saxony in Germany, which is in the Variscan belt, has the same etymology.) ''Hercynian'', on the other hand, derives from the Hercynian Forest. Both words were descriptive terms of strike directions observed by geologists in the field, ''variscan'' for southwest to northeast, ''hercynian'' for northwest to southeast. The ''variscan'' direction reflected the direction of ancient fold belts cropping out throughout Germany and adjacent countries and the meaning shi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silurian
The Silurian ( ) is a geologic period and system spanning 23.5 million years from the end of the Ordovician Period, at million years ago ( Mya), to the beginning of the Devonian Period, Mya. The Silurian is the third and shortest period of the Paleozoic Era, and the third of twelve periods of the Phanerozoic Eon. As with other geologic periods, the rock beds that define the period's start and end are well identified, but the exact dates are uncertain by a few million years. The base of the Silurian is set at a series of major Ordovician–Silurian extinction events when up to 60% of marine genera were wiped out. One important event in this period was the initial establishment of terrestrial life in what is known as the Silurian-Devonian Terrestrial Revolution: vascular plants emerged from more primitive land plants, dikaryan fungi started expanding and diversifying along with glomeromycotan fungi, and three groups of arthropods ( myriapods, arachnids and hexapods) ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Caledonian Orogeny
The Caledonian orogeny was a mountain-building cycle recorded in the northern parts of the British Isles, the Scandinavian Caledonides, Svalbard, eastern Greenland and parts of north-central Europe. The Caledonian orogeny encompasses events that occurred from the Ordovician to Early Devonian, roughly 490–390 million years ago ( Ma). It was caused by the closure of the Iapetus Ocean when the Laurentia and Baltica continents and the Avalonia microcontinent collided. The orogeny is named for Caledonia, the Latin name for Scotland. The term was first used in 1885 by Austrian geologist Eduard Suess for an episode of mountain building in northern Europe that predated the Devonian period. Geologists like Émile Haug and Hans Stille saw the Caledonian event as one of several episodic phases of mountain building that had occurred during Earth's history.McKerrow ''et al.'' (2002) Current understanding has it that the Caledonian orogeny encompasses a number of tectonic phases th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ediacaran
The Ediacaran ( ) is a geological period of the Neoproterozoic geologic era, Era that spans 96 million years from the end of the Cryogenian Period at 635 Million years ago, Mya to the beginning of the Cambrian Period at 538.8 Mya. It is the last period of the Proterozoic geologic eon, Eon as well as the last of the so-called "Precambrian supereon", before the beginning of the subsequent Cambrian Period marks the start of the Phanerozoic Eon, where recognizable fossil evidence of life becomes common. The Ediacaran Period is named after the Ediacara Hills of South Australia, where trace fossils of a diverse community of previously unrecognized lifeforms (later named the Ediacaran biota) were first discovered by geologist Reg Sprigg in 1946. Its status as an official geological period was ratified in 2004 by the International Union of Geological Sciences (IUGS), making it the first new geological period declared in 120 years. Although the period took namesake from the Ediacara Hills ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphism
Metamorphism is the transformation of existing Rock (geology), rock (the protolith) to rock with a different mineral composition or Texture (geology), texture. Metamorphism takes place at temperatures in excess of , and often also at elevated pressure or in the presence of chemically active fluids, but the rock remains mostly solid during the transformation. Metamorphism is distinct from weathering or diagenesis, which are changes that take place at or just beneath Earth's surface. Various forms of metamorphism exist, including Regional metamorphism, regional, Contact metamorphism, contact, Hydrothermal metamorphism, hydrothermal, Shock metamorphism, shock, and Dynamic metamorphism, dynamic metamorphism. These differ in the characteristic temperatures, pressures, and rate at which they take place and in the extent to which reactive fluids are involved. Metamorphism occurring at increasing pressure and temperature conditions is known as ''prograde metamorphism'', while decreasin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
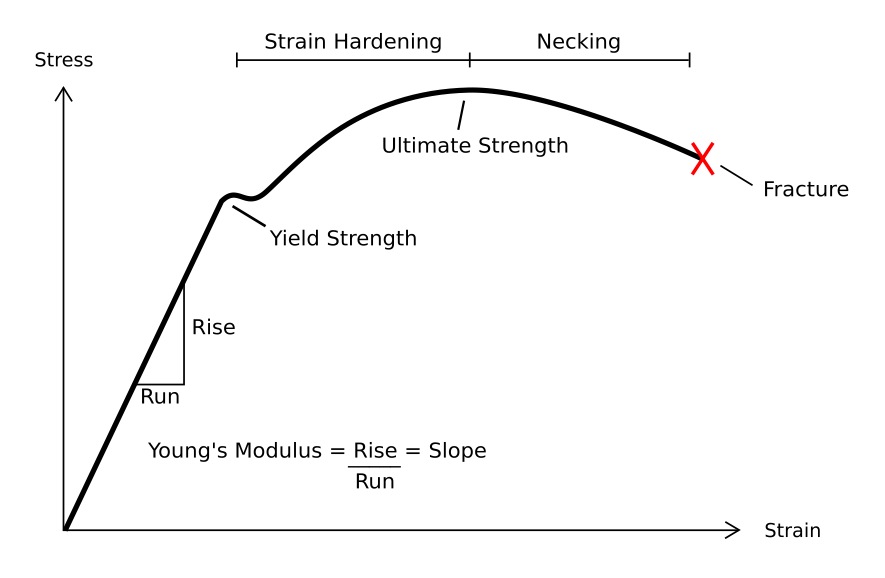
Deformation (geology)
In engineering, deformation (the change in size or shape of an object) may be ''elastic'' or ''plastic''. If the deformation is negligible, the object is said to be ''rigid''. Main concepts Occurrence of deformation in engineering applications is based on the following background concepts: * ''Displacements'' are any change in position of a point on the object, including whole-body translations and rotations (rigid transformations). * ''Deformation'' are changes in the relative position between internals points on the object, excluding rigid transformations, causing the body to change shape or size. * ''Strain'' is the ''relative'' ''internal'' deformation, the dimensionless change in shape of an infinitesimal cube of material relative to a reference configuration. Mechanical strains are caused by mechanical stress, ''see stress-strain curve''. The relationship between stress and strain is generally linear and reversible up until the yield point and the deformation is e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paleozoic
The Paleozoic ( , , ; or Palaeozoic) Era is the first of three Era (geology), geological eras of the Phanerozoic Eon. Beginning 538.8 million years ago (Ma), it succeeds the Neoproterozoic (the last era of the Proterozoic Eon) and ends 251.9 Ma at the start of the Mesozoic Era. The Paleozoic is subdivided into six period (geology), geologic periods (from oldest to youngest), Cambrian, Ordovician, Silurian, Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. Some geological timescales divide the Paleozoic informally into early and late sub-eras: the Early Paleozoic consisting of the Cambrian, Ordovician and Silurian; the Late Paleozoic consisting of the Devonian, Carboniferous and Permian. The name ''Paleozoic'' was first used by Adam Sedgwick (1785–1873) in 1838 to describe the Cambrian and Ordovician periods. It was redefined by John Phillips (geologist), John Phillips (1800–1874) in 1840 to cover the Cambrian to Permian periods. It is derived from the Ancient Greek, Greek ''palaiós'' (π� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Proterozoic
The Proterozoic ( ) is the third of the four geologic eons of Earth's history, spanning the time interval from 2500 to 538.8 Mya, and is the longest eon of Earth's geologic time scale. It is preceded by the Archean and followed by the Phanerozoic, and is the most recent part of the Precambrian "supereon". The Proterozoic is subdivided into three geologic eras (from oldest to youngest): the Paleoproterozoic, Mesoproterozoic and Neoproterozoic. It covers the time from the appearance of free oxygen in Earth's atmosphere to just before the proliferation of complex life on the Earth during the Cambrian Explosion. The name ''Proterozoic'' combines two words of Greek origin: meaning "former, earlier", and , meaning "of life". Well-identified events of this eon were the transition to an oxygenated atmosphere during the Paleoproterozoic; the evolution of eukaryotes via symbiogenesis; several global glaciations, which produced the 300 million years-long Huronian glaciation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Igneous Rock
Igneous rock ( ), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or lava. The magma can be derived from partial melts of existing rocks in either a planet's mantle or crust. Typically, the melting is caused by one or more of three processes: an increase in temperature, a decrease in pressure, or a change in composition. Solidification into rock occurs either below the surface as intrusive rocks or on the surface as extrusive rocks. Igneous rock may form with crystallization to form granular, crystalline rocks, or without crystallization to form natural glasses. Igneous rocks occur in a wide range of geological settings: shields, platforms, orogens, basins, large igneous provinces, extended crust and oceanic crust. Geological significance Igneous and metamorphic rocks make up 90–95% of the top of the Earth's crust by volume. Igneous rock ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metamorphic Rock
Metamorphic rocks arise from the transformation of existing rock to new types of rock in a process called metamorphism. The original rock ( protolith) is subjected to temperatures greater than and, often, elevated pressure of or more, causing profound physical or chemical changes. During this process, the rock remains mostly in the solid state, but gradually recrystallizes to a new texture or mineral composition. The protolith may be an igneous, sedimentary, or existing metamorphic rock. Metamorphic rocks make up a large part of the Earth's crust and form 12% of the Earth's land surface. They are classified by their protolith, their chemical and mineral makeup, and their texture. They may be formed simply by being deeply buried beneath the Earth's surface, where they are subject to high temperatures and the great pressure of the rock layers above. They can also form from tectonic processes such as continental collisions, which cause horizontal pressure, friction, and dist ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |