|
Lodewijk Van Heiden
Lodewijk Sigismund Vincent Gustaaf Reichsgraf van Heiden (; ; 6 September 1773 – 17 October 1850) was a Dutch naval officer and Orangism (Dutch Republic), Orangist who went into exile from the Batavian Republic and served in the Russian Navy. He ultimately became a Russian admiral and commanded a squadron of the Imperial Russian Navy in the Battle of Navarino (1827). He was the father of Fyodor Logginovich van Heiden. Personal life Born in Zuidlaren, in the northeast of the Netherlands, Van Heiden was the second son of Sigismund Pieter Alexander Reichsgraf van Heiden, Lord of Reinestein and Laarwoud, Landdrost, Drost of Drenthe, and Marie Frederique Freiin van Reede. He is the only Dutch naval hero to have come from the landlocked province of Drenthe. Van Heiden married Anne-Marie Akeleye, daughter of Captain Johannes Akeleye, a Danish people, Danish-born sea officer in Russian service. They had four children, including their sons Fyodor Geyden, Friedrich Moritz and Ludw ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sigismund Gustaaf Graaf Van Heiden Reinestein2
Sigismund (variants: Sigmund (given name), Sigmund, :de:Siegmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it ''Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of the High German word "Sieg" (victory): ''sigis'', obviously Gothic and an inferred Germanic form, and there is a younger form: ''sigi'', which is Old Saxon or Old High German ''sigu'' (both from about 9th century). A 5th century Prince of Burgundy was known both as ''Sigismund'' and ''Sigimund'' (see Ernst Förstemann, ''Altdeutsche Personennamen'', 1906; Henning Kaufmann, ''Altdeutsche Personennamen'', Ergänzungsband, 1968). Its Hungarian equivalent is Zsigmond. A Lithuanian name Žygimantas, meaning "wealth of (military) campaign", from Lithuanian language, Lithuanian ''žygis'' "campaign, march" + ''manta'' "goods, wealth", has been a substitution of the name ''Sigismund'' in the Lithuanian language, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dutch Colonial Empire
The Dutch colonial empire () comprised overseas territories and trading posts under some form of Dutch control from the early 17th to late 20th centuries, including those initially administered by Dutch chartered companies—primarily the Dutch East India Company (1602–1799) and Dutch West India Company (1621–1792)—and subsequently governed by the Dutch Republic (1581–1795) and modern Kingdom of the Netherlands (1815–1975). Following the ''de facto'' independence of the Dutch Republic from the Spanish Empire in the late 16th century, various trading companies known as '' voorcompagnie'' led maritime expeditions overseas in search of commercial opportunities. By 1600, Dutch traders and mariners had penetrated the lucrative Asian spice trade but lacked the capital or manpower to secure or expand their ventures; this prompted the States General in 1602 to consolidate several trading enterprises into the semi-state-owned Dutch East India Company (, VOC), which was gr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archipelago Fleet
The archipelago fleet (), officially the "fleet of the army" (), was a Navy, maritime branch of the Swedish Armed Forces which existed between 1756 and 1823. Its purpose was to protect the coasts of Sweden, which was surrounded by a natural barrier of archipelagoes (or skerry, skerries). Throughout its existence, the fleet was a largely independent arm of the Swedish Army, separate from the Swedish Navy, with the exception of a few years in the late 1760s. In a number of respects, it was a precursor of the Swedish Coastal Artillery and its coastal fleet. The fleet's vessels consisted of traditional Mediterranean-style galleys, Pram (ship), prams, gunboats and specially designed Broadside (naval), broadside-armed "archipelago frigates". All types had the ability to operate under oars and a small draft (hull), draft, enabling them to navigate the shallow and often treacherous inshore waters. The archipelago fleet was active in several wars from 1757 to 1814, such as the Seven Years' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Swedish Navy
The Swedish Navy () is the maritime service branch of the Swedish Armed Forces. It is composed of surface and submarine naval units – the Fleet (), formally sometimes referred to as the Royal Navy () – as well as marine units, the Amphibious Corps (). Founded under King Gustav Vasa in 1522, the Swedish navy is one of the oldest continuously serving navies in the world, celebrating its 500th anniversary in 2022. History Early Swedish kings ( 9th–14th centuries) organised a Swedish Navy along the coastline through . This involved combined rowing and sailing ships (without artillery). This system became obsolete with the development of society and changes in military technology. No later than in the 14th century, the duty to serve in was replaced by a tax. In 1427, when Sweden was part of the Kalmar Union (with Denmark and Norway), Swedish warships did however participate in the naval battle of Öresund against the Hanseatic League. It is unclear how this force was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Finnish War
The Finnish War (; ; ) was fought between the Gustavian era, Kingdom of Sweden and the Russian Empire from 21 February 1808 to 17 September 1809 as part of the Napoleonic Wars. As a result of the war, the eastern third of Sweden was established as the autonomous Grand Duchy of Finland within the Russian Empire. Other notable effects were the Riksdag of the Estates, Swedish parliament's adoption of a Instrument of Government (1809), new constitution and the establishment of the House of Bernadotte, the new Swedish Act of Succession, Swedish royal house, in 1818. Background After the Russian Emperor Alexander I of Russia, Alexander I concluded the 1807 Treaty of Tilsit with Napoleon, Alexander, in his letter on 24 September 1807 to the Swedish King Gustav IV Adolf, informed the king that the peaceful relations between Russia and Sweden depended on Swedish agreement to abide by the limitations of the Treaty of Tilsit which in practice meant that Sweden would have been required ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vyborg
Vyborg (; , ; , ; , ) is a town and the administrative center of Vyborgsky District in Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It lies on the Karelian Isthmus near the head of Vyborg Bay, northwest of St. Petersburg, east of the Finnish capital Helsinki, and south of Russia's border with Finland, where the Saimaa Canal enters the Gulf of Finland. The most recent census population of Vyborg is Vyborg was founded as a medieval fortress in Finland under Swedish rule during the Third Swedish Crusade. After numerous wars between the Russians and Swedes, the Treaty of Nöteborg in 1323 defined the border of eastern Finland, and would separate the two cultures. Vyborg remained under Swedish rule until it was captured by the Russians during the Great Northern War. Under Russian rule, Vyborg was the seat of Vyborg Governorate until it was incorporated into the newly established Grand Duchy of Finland, an autonomous part of the Russian Empire. Finland declared its independence from R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain 1st Rank
Captain 1st rank () is a rank used by the Russian Navy and a number of List of communist states#Former communist states, former communist states. The rank is the most senior rank in the staff officers' career group. The rank is equivalent to Colonel (Eastern Europe), colonel in armies and air forces. Within NATO forces, the rank is rated as OF-5 and is equivalent to Captain (naval), captain in English-speaking navies. Russia The rank was introduced in Russia by Peter the Great in 1713. By decision of the so-called ''Military Navy Commission'' (ru: ''Воинская морскaя комиссия'') in 1732 the sequence of Kapitan ranks was abolished. However, until 1752 the grade rank ''Kapitan 1st rank'' was corresponding to ''Fleet kapitan'' (ru: флота капитан). Finally, the ''Kapitan ranks'' were reintroduced September 5 (16), 1751. The Red Army introduced the ''Kapitan 1st rank'' rank in 1935, together with a number of other former Russian ranks, and it continues ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Captain 2nd Rank
Captain 2nd rank () is a rank used by the Russian Navy and a number of List of communist states#Former communist states, former communist states. The rank is the middle rank in the staff officer's career group. The rank is equivalent to lieutenant colonel (Eastern Europe), lieutenant colonel in armies and air forces. Within NATO forces, the rank is rated as OF-4 and is equivalent to commander in English-speaking navies. Russia Russian Empire The rank was introduced in Russia by Peter the Great in 1722. From the introduction of the History of Russian military ranks, Russian table of ranks to the abolishment in 1917 ''Captain 2nd rank'' was quoted to rank positioned VII, and until 1856 it was privileged by hereditary nobility. In the Russian Empire Navy it was the second highest rank of the stab-ofizer (derived from German ''Stabsoffizier'') career group. Soviet Navy and Russian Federation The first equivalent rank in the Soviet Navy (from 1918 to 1935) was ''Starpom of the ship ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
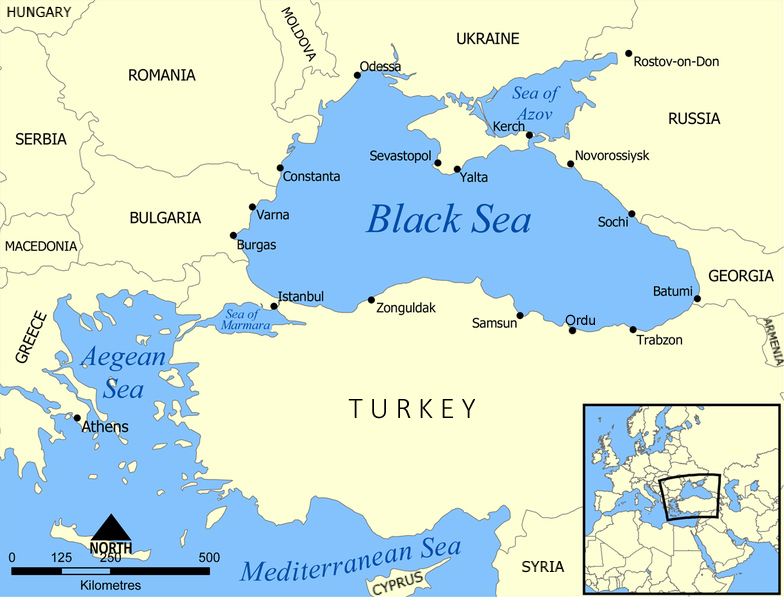
Black Sea Fleet
The Black Sea Fleet () is the Naval fleet, fleet of the Russian Navy in the Black Sea, the Sea of Azov and the Mediterranean Sea. The Black Sea Fleet, along with other Russian ground and air forces on the Crimea, Crimean Peninsula, are subordinate to the Southern Military District of the Russian Armed Forces. The fleet traces its history to its founding by Grigory Potemkin, Prince Potemkin on 13 May 1783 as part of the Imperial Russian Navy. The Russian Soviet Federative Socialist Republic, Russian SFSR inherited the fleet in 1918; with the founding of the Soviet Union in 1922, it became part of the Soviet Navy. Following the Dissolution of the Soviet Union, collapse of the Soviet Union in 1991, the Black Sea Fleet was partitioned between the Russia, Russian Federation and Ukraine in 1997, with Russia receiving title to 82% of the vessels. The Black Sea Fleet has its official primary headquarters and facilities at the Sevastopol Naval Base, Crimea, which Annexation of Crimea by ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire that spanned most of northern Eurasia from its establishment in November 1721 until the proclamation of the Russian Republic in September 1917. At its height in the late 19th century, it covered about , roughly one-sixth of the world's landmass, making it the list of largest empires, third-largest empire in history, behind only the British Empire, British and Mongol Empire, Mongol empires. It also Russian colonization of North America, colonized Alaska between 1799 and 1867. The empire's 1897 census, the only one it conducted, found a population of 125.6 million with considerable ethnic, linguistic, religious, and socioeconomic diversity. From the 10th to 17th centuries, the Russians had been ruled by a noble class known as the boyars, above whom was the tsar, an absolute monarch. The groundwork of the Russian Empire was laid by Ivan III (), who greatly expanded his domain, established a centralized Russian national state, and secured inde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jean-Charles Pichegru
Jean-Charles Pichegru (; 16 February 1761 – 5 April 1804) was a French general of the Revolutionary Wars. Under his command, French troops overran Belgium and the Netherlands before fighting on the Rhine front. His royalist positions led to his loss of power and imprisonment in Cayenne, French Guiana during the Coup of 18 Fructidor in 1797. After escaping into exile in London and joining the staff of Alexander Korsakov, he returned to France and planned the Pichegru Conspiracy to remove Napoleon from power, which led to his arrest and death. Despite his defection, his surname is one of the names inscribed under the Arc de Triomphe, on Column 3. Early life and career Pichegru was born in a peasant family at Arbois (or, according to Charles Nodier, at Les Planches-près-Arbois, near Lons-le-Saulnier), in the then Franche-Comté (now in the Jura department of France). The friars of Arbois were entrusted with his education, and sent him to the military school of Brienne-l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |