|
Loco, Switzerland
Loco is a village and former municipality in the canton of Ticino, Switzerland. In 2001 the municipality of Loco was merged with the neighboring municipalities Auressio and Berzona to form a new and larger municipality Isorno.Amtliches Gemeindeverzeichnis der Schweiz published by the Swiss Federal Statistical Office accessed 14 January 2010 History 
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canton Of Ticino
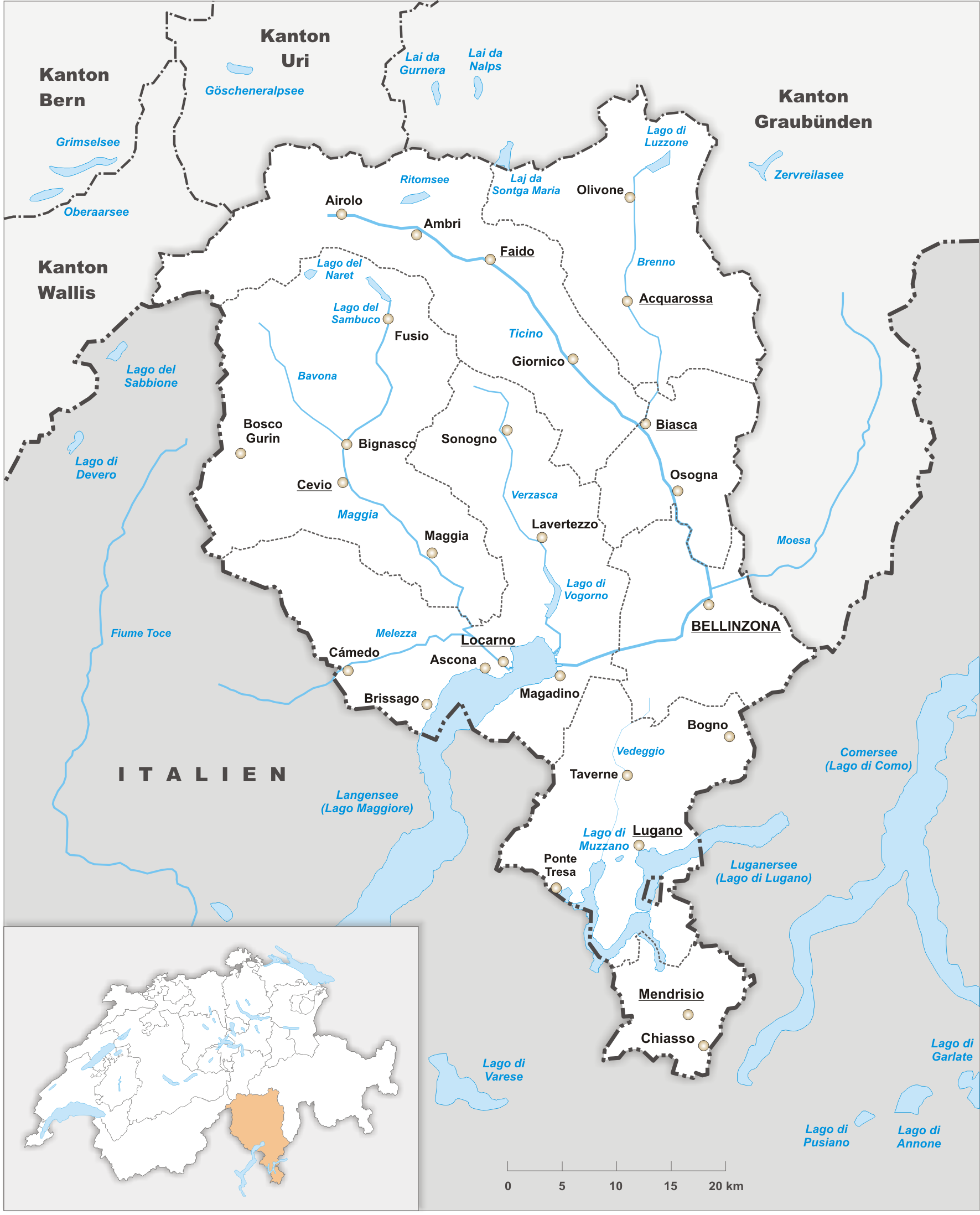
Ticino (), sometimes Tessin (), officially the Republic and Canton of Ticino or less formally the Canton of Ticino,, informally ''Canton Ticino'' ; lmo, Canton Tesin ; german: Kanton Tessin ; french: Canton du Tessin ; rm, Chantun dal Tessin . is one of the 26 cantons forming the Swiss Confederation. It is composed of eight districts and its capital city is Bellinzona. It is also traditionally divided into the Sopraceneri and the Sottoceneri, respectively north and south of Monte Ceneri. Red and blue are the colours of its flag. Ticino is the southernmost canton of Switzerland. It is one of the three large southern Alpine cantons, along with Valais and the Grisons. However, unlike all other cantons, it lies almost entirely south of the Alps, and has no natural access to the Swiss Plateau. Through the main crest of the Gotthard and adjacent mountain ranges, it borders the canton of Valais to the northwest, the canton of Uri to the north and the canton of Grisons to t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire and transitioned into the Renaissance and the Age of Discovery. The Middle Ages is the middle period of the three traditional divisions of Western history: classical antiquity, the medieval period, and the modern period. The medieval period is itself subdivided into the Early Early may refer to: History * The beginning or oldest part of a defined historical period, as opposed to middle or late periods, e.g.: ** Early Christianity ** Early modern Europe Places in the United States * Early, Iowa * Early, Texas * Early ..., High Middle Ages, High, and Late Middle Ages. Population decline, counterurbanisation, the collapse of centralized authority, invasions, and mass migrations of tribes, which had begun in late antiquity, continued i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Education In Switzerland
The education system in Switzerland is very diverse, because the constitution of Switzerland delegates the authority for the school system mainly to the cantons. The Swiss constitution sets the foundations, namely that primary school is obligatory for every child and is free in state schools and that the confederation can run or support universities. The minimum age for primary school is about six years in all cantons but Obwalden, where it is five years and three months. After primary schools, the pupils split up according to their abilities and intentions of career paths. Roughly 25% of all students attend lower and upper secondary schools leading, normally after 12 school years in total to the federal recognized matura or an academic Baccalaureate which grants access to all universities. The other students split in two or more school-types, depending on the canton, differing in the balance between theoretical and practical education. It is obligatory for all children to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Straw Plaiting
Straw plaiting is a method of manufacturing textiles by braiding straw and the industry that surrounds the craft of producing these straw manufactures. Straw is plaited to produce products including straw hats and ornaments, and the process is undertaken in a number of locations worldwide. Etymology To plait comes from late 14c., "to fold, gather in pleats," also "to braid or weave," from Old French pleir "to fold," variant of ploier, ployer "to fold, bend," from Latin plicare "to fold". Applications Straw can be plaited for a number of purposes, including: the thatching of roofs, to create a paper-making material, for ornamenting small surfaces as a "straw-mosaic", for plaiting into door and table mats, mattresses and for weaving and plaiting into light baskets and to create artificial flowers. Straw is also plaited to produce bonnets and hats. Belarus Straw weaving is an ancient folk craft of Belarus. In 2022 it was added to a UNESCO Representative List of the Intang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Baroque Architecture
Baroque architecture is a highly decorative and theatrical style which appeared in Italy in the early 17th century and gradually spread across Europe. It was originally introduced by the Catholic Church, particularly by the Jesuits, as a means to combat the Reformation and the Protestant church with a new architecture that inspired surprise and awe. It reached its peak in the High Baroque (1625–1675), when it was used in churches and palaces in Italy, Spain, Portugal, France, Bavaria and Austria. In the Late Baroque period (1675–1750), it reached as far as Russia and the Spanish and Portuguese colonies in Latin America. About 1730, an even more elaborately decorative variant called Rococo appeared and flourished in Central Europe. Baroque architects took the basic elements of Renaissance architecture, including domes and colonnades, and made them higher, grander, more decorated, and more dramatic. The interior effects were often achieved with the use of '' quadratura ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flemish Painting
Flemish painting flourished from the early 15th century until the 17th century, gradually becoming distinct from the painting of the rest of the Low Countries, especially the modern Netherlands. In the early period, up to about 1520, the painting of the whole area is (especially in the Anglophone world) typically considered as a whole, as Early Netherlandish painting. This was dominated by the Flemish south, but painters from the north were also important. Dutch and Flemish Renaissance painting, of which Antwerp became the centre, covers the period up to about 1580 or later, by the end of which the north and south Netherlands had become politically separated. Flemish Baroque painting was especially important in the first half of the 17th century, dominated by Rubens. In theory the term does not refer to modern Flanders but to the County of Flanders and neighbouring areas of the Low Countries such as the Tournaisis and Duchy of Brabant. However this distinction, well understoo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vicariate
A vicar (; Latin: ''vicarius'') is a representative, deputy or substitute; anyone acting "in the person of" or agent for a superior (compare "vicarious" in the sense of "at second hand"). Linguistically, ''vicar'' is cognate with the English prefix "vice", similarly meaning "deputy". The title appears in a number of Christian ecclesiastical contexts, but also as an administrative title, or title modifier, in the Roman Empire. In addition, in the Holy Roman Empire a local representative of the emperor, perhaps an archduke, might be styled "vicar". Roman Catholic Church The Pope uses the title ''Vicarius Christi'', meaning the ''vicar of Christ''. In Catholic canon law, ''a vicar is the representative of any ecclesiastic'' entity. The Romans had used the term to describe officials subordinate to the praetorian prefects. In the early Christian churches, bishops likewise had their vicars, such as the archdeacons and archpriests, and also the rural priest, the curate who had the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parish Church
A parish church (or parochial church) in Christianity is the church which acts as the religious centre of a parish. In many parts of the world, especially in rural areas, the parish church may play a significant role in community activities, often allowing its premises to be used for non-religious community events. The church building reflects this status, and there is considerable variety in the size and style of parish churches. Many villages in Europe have churches that date back to the Middle Ages, but all periods of architecture are represented. Roman Catholic Church Each diocese (administrative unit, headed by a Bishop) is divided into parishes. Normally, a parish comprises all Catholics living within its geographically defined area. Within a diocese, there can also be overlapping parishes for Catholics belonging to a particular rite, language, nationality, or community. Each parish has its own central church called the parish church, where religious services take p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Early Modern Switzerland
The early modern history of the Old Swiss Confederacy ('' Eidgenossenschaft'', also known as the "Swiss Republic" or ''Republica Helvetiorum'') and its constituent Thirteen Cantons encompasses the time of the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) until the French invasion of 1798. The early modern period was characterized by an increasingly aristocratic and oligarchic ruling class as well as frequent economic or religious revolts. This period came to be referred to as the ''Ancien Régime'' retrospectively, in post-Napoleonic Switzerland. The loosely organized Confederation remained generally disorganized and crippled by the religious divisions created by the Swiss Reformation. During this period the Confederation gained formal independence from the Holy Roman Empire with support from France, and had very close relations with France. The early modern period also saw the growth of French-Swiss literature, and notable authors of the Age of Enlightenment such as the mathematic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Switzerland
; rm, citad federala, links=no). Swiss law does not designate a ''capital'' as such, but the federal parliament and government are installed in Bern, while other federal institutions, such as the federal courts, are in other cities (Bellinzona, Lausanne, Lucerne, Neuchâtel, St. Gallen a.o.). , coordinates = , largest_city = Zurich , official_languages = , englishmotto = "One for all, all for one" , religion_year = 2022 , religion_ref = , religion = , demonym = , german: link=no, Schweizer/Schweizerin, french: link=no, Suisse/Suissesse, it, svizzero/svizzera or , rm, Svizzer/Svizra , government_type = Federal assembly-independent directorial republic , leader_title1 = Federal Council , leader_name1 = , leader_title2 = , leader_name2 = Viktor Rossi , legislature = Federal Assembly , upper_house = Counci ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |