|
List Of Trigonometry Topics
The following outline is provided as an overview of and topical guide to trigonometry: Trigonometry – branch of mathematics that studies the relationships between the sides and the angles in triangles. Trigonometry defines the trigonometric functions, which describe those relationships and have applicability to cyclical phenomena, such as waves. Basics * Geometry – mathematics concerned with questions of shape, size, the relative position of figures, and the properties of space. Geometry is used extensively in trigonometry. * Angle – the angle is the figure formed by two rays, called the sides of the angle, sharing a common endpoint, called the vertex of the angle. Angles formed by two rays lie in a plane, but this plane does not have to be a Euclidean plane. * Ratio – a ratio indicates how many times one number contains another Content of trigonometry * Trigonometry * Trigonometric functions * Trigonometric identities * Euler's formula Schola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus Of Samos
Aristarchus of Samos (; , ; ) was an ancient Greek astronomer and mathematician who presented the first known heliocentric model that placed the Sun at the center of the universe, with the Earth revolving around the Sun once a year and rotating about its axis once a day. He also supported the theory of Anaxagoras according to which the Sun was just another star. He likely moved to Alexandria, and he was a student of Strato of Lampsacus, who later became the third head of the Peripatetic school in Greece. According to Ptolemy, he observed the summer solstice of 280 BC. Along with his contributions to the heliocentric model, as reported by Vitruvius, he created two separate sundials: one that is a flat disc; and one hemispherical. Aristarchus estimated the sizes of the Sun and Moon as compared to Earth's size. He also estimated the distances from the Earth to the Sun and Moon. His estimate that the Sun was 7 times larger than Earth (while inaccurate by an order of magnitu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Astronomy
Astronomy has a long history in the Indian subcontinent, stretching from History of India, pre-historic to History of India (1947–present), modern times. Some of the earliest roots of Indian astronomy can be dated to the period of Indus Valley civilisation or earlier. Astronomy later developed as a discipline of Vedanga, or one of the "auxiliary disciplines" associated with the study of the Vedas dating 1500 BCE or older. The oldest known text is the ''Vedanga Jyotisha'', dated to 1400–1200 BCE (with the extant form possibly from 700 to 600 BCE). Indian astronomy was influenced by Greek astronomy beginning in the 4th century BCEHighlights of Astronomy, Volume 11B: As presented at the XXIIIrd General Assembly of the IAU, 1997. Johannes Andersen Springer, 31 January 1999 – Science – 616 pages. p. 72/ref>Babylon to Voyager and Beyond: A History of Planetary Astronomy. David Leverington. Cambridge University Press, 29 May 2010 – Science – 568 pages. p. 4/ref>Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
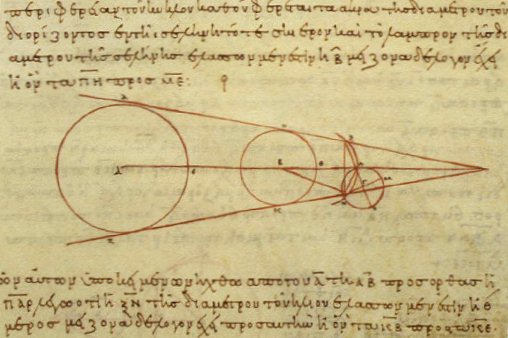
Greek Astronomy
Ancient Greek astronomy is the astronomy written in the Greek language during classical antiquity. Greek astronomy is understood to include the Ancient Greece, Ancient Greek, Hellenistic period, Hellenistic, Roman Empire, Greco-Roman, and Late antiquity, late antique eras. Ancient Greek astronomy can be divided into three phases, with ''Classical Greek astronomy'' being practiced during the 5th and 4th centuries BC, ''Hellenistic period, Hellenistic astronomy'' from the 3rd century BC until the formation of the Roman Empire in the late 1st century BC, and ''Greco-Roman astronomy'' continuing the tradition in the Roman world. During the Hellenistic era and onwards, Greek astronomy expanded beyond the geographic region of Greece as the Greek language had become the language of scholarship throughout the Hellenistic world, in large part delimited by the boundaries of the Macedonian Empire established by Alexander the Great. The most prominent and influential practitione ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aristarchus's Inequality
Aristarchus's inequality (after the Greek astronomer and mathematician Aristarchus of Samos; c. 310 – c. 230 BCE) is a law of trigonometry which states that if ''α'' and ''β'' are acute angles (i.e. between 0 and a right angle) and ''β'' < ''α'' then : used the first of these inequalities while constructing his table of chords. Proof The proof is a consequence of the more widely known inequalities :, : and :.Proof of the first inequality Using these inequalities we can ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regiomontanus
Johannes Müller von Königsberg (6 June 1436 – 6 July 1476), better known as Regiomontanus (), was a mathematician, astrologer and astronomer of the German Renaissance, active in Vienna, Buda and Nuremberg. His contributions were instrumental in the development of Copernican heliocentrism in the decades following his death. Regiomontanus wrote under the Latinized name of ''Ioannes de Monteregio'' (or ''Monte Regio''; ''Regio Monte''); the toponym ''Regiomontanus'' was first used by Philipp Melanchthon in 1534. He is named after Königsberg in Lower Franconia, not the larger Königsberg (modern Kaliningrad) in Prussia. Life Although little is known of Regiomontanus' early life, it is believed that at eleven years of age, he became a student at the University of Leipzig, Saxony. In 1451 he continued his studies at Alma Mater Rudolfina, the university in Vienna, in the Duchy of Austria, where he became a pupil and friend of Georg von Peuerbach. In 1452 he was awarded hi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos (; BC) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher, polymath, and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His political and religious teachings were well known in Magna Graecia and influenced the philosophies of Plato, Aristotle, and, through them, Western philosophy. Modern scholars disagree regarding Pythagoras's education and influences, but most agree that he travelled to Croton in southern Italy around 530 BC, where he founded a school in which initiates were allegedly sworn to secrecy and lived a communal, ascetic lifestyle. In antiquity, Pythagoras was credited with mathematical and scientific discoveries, such as the Pythagorean theorem, Pythagorean tuning, the five regular solids, the theory of proportions, the sphericity of the Earth, the identity of the morning and evening stars as the planet Venus, and the division of the globe into five climatic zones. He was reputedly the first man to call himself a philosopher ("lover of wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; , ; ; – 160s/170s AD) was a Greco-Roman mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were important to later Byzantine science, Byzantine, Islamic science, Islamic, and Science in the Renaissance, Western European science. The first was his astronomical treatise now known as the ''Almagest'', originally entitled ' (, ', ). The second is the ''Geography (Ptolemy), Geography'', which is a thorough discussion on maps and the geographic knowledge of the Greco-Roman world. The third is the astrological treatise in which he attempted to adapt horoscopic astrology to the Aristotelian physics, Aristotelian natural philosophy of his day. This is sometimes known as the ' (, 'On the Effects') but more commonly known as the ' (from the Koine Greek meaning 'four books'; ). The Catholic Church promoted his work, which included the only mathematically sound geocentric model of the Sola ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Madhava Of Sangamagrama
Mādhava of Sangamagrāma (Mādhavan) Availabl/ref> () was an Indian mathematician and astronomer who is considered to be the founder of the Kerala school of astronomy and mathematics in the Late Middle Ages. Madhava made pioneering contributions to the study of infinite series, calculus, trigonometry, geometry and algebra. He was the first to use infinite series approximations for a range of trigonometric functions, which has been called the "decisive step onward from the finite procedures of ancient mathematics to treat their limit-passage to infinity". Biography Little is known about Madhava's life with certainty. However, from scattered references to Madhava found in diverse manuscripts, historians of Kerala school have pieced together information about the mathematician. In a manuscript preserved in the Oriental Institute, Baroda, Madhava has been referred to as ''Mādhavan vēṇvārōhādīnām karttā ... Mādhavan Ilaññippaḷḷi Emprān''. It has been noted that th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hipparchus
Hipparchus (; , ; BC) was a Ancient Greek astronomy, Greek astronomer, geographer, and mathematician. He is considered the founder of trigonometry, but is most famous for his incidental discovery of the precession of the equinoxes. Hipparchus was born in Nicaea, Bithynia, and probably died on the island of Rhodes, Greece. He is known to have been a working astronomer between 162 and 127 BC. Hipparchus is considered the greatest ancient astronomical observer and, by some, the greatest overall astronomer of classical antiquity, antiquity. He was the first whose quantitative and accurate models for the motion of the Sun and Moon survive. For this he certainly made use of the observations and perhaps the mathematical techniques accumulated over centuries by the Babylonians and by Meton of Athens (fifth century BC), Timocharis, Aristyllus, Aristarchus of Samos, and Eratosthenes, among others. He developed trigonometry and constructed trigonometric tables, and he solved se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Euclid
Euclid (; ; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the '' Elements'' treatise, which established the foundations of geometry that largely dominated the field until the early 19th century. His system, now referred to as Euclidean geometry, involved innovations in combination with a synthesis of theories from earlier Greek mathematicians, including Eudoxus of Cnidus, Hippocrates of Chios, Thales and Theaetetus. With Archimedes and Apollonius of Perga, Euclid is generally considered among the greatest mathematicians of antiquity, and one of the most influential in the history of mathematics. Very little is known of Euclid's life, and most information comes from the scholars Proclus and Pappus of Alexandria many centuries later. Medieval Islamic mathematicians invented a fanciful biography, and medieval Byzantine and early Renaissance scholars mistook him for the earlier philo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |