|
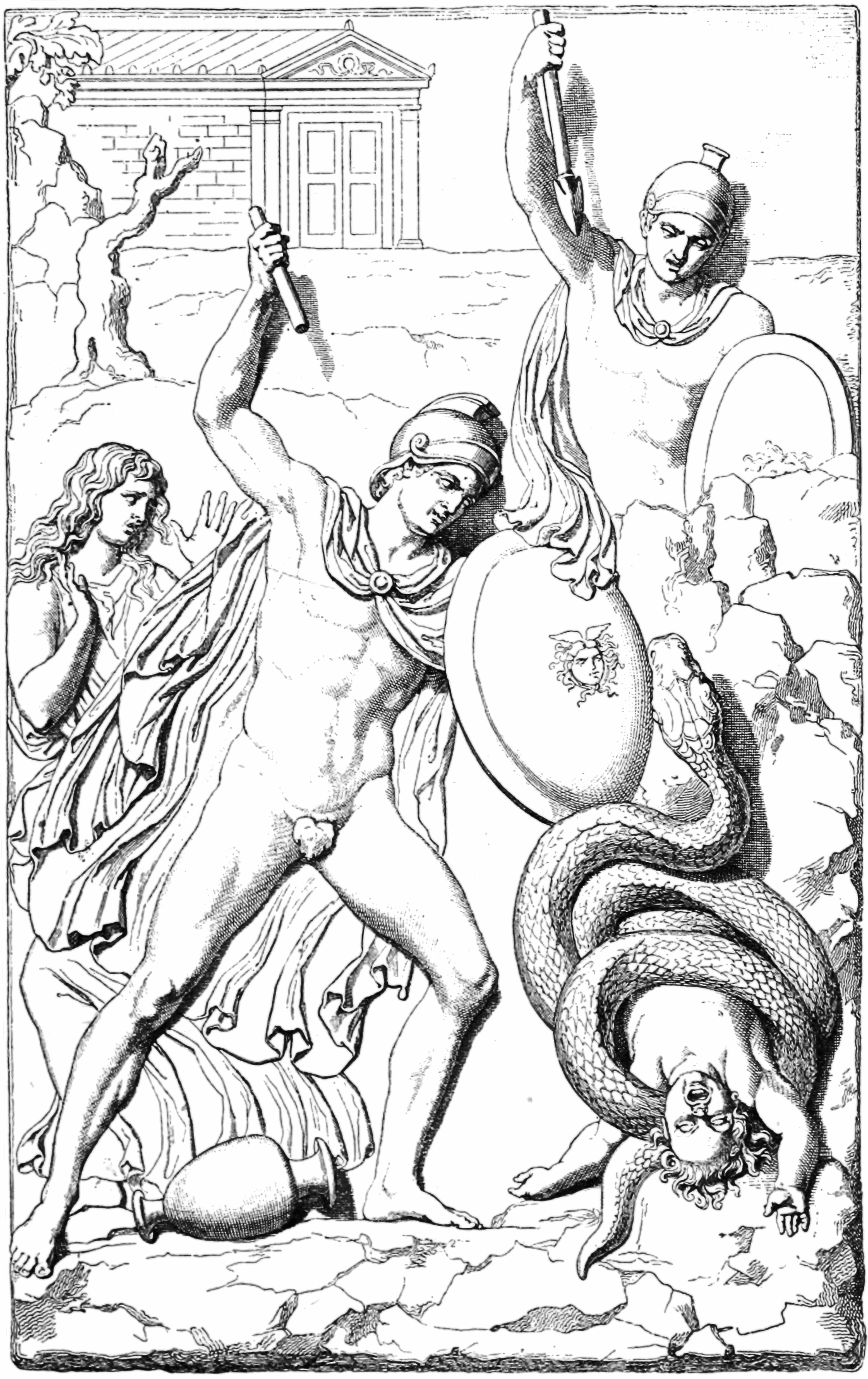
Linus (Argive)
In Greek mythology, Linus (Ancient Greek: Λῖνος ''Linos'' "flax"), son of Apollo and Psamathe, daughter of King Crotopus of Argos. Mythology When Psamathe had given birth to Linus, fearing her father she thus exposed the child. Linus was found by shepherds, who brought him up but the child after reaching adulthood was torn to pieces by the shepherd's dogs. Psamathe's grief at the occurrence betrayed her misfortune to her father, who would not believe that she had had intercourse with a god rather than a mortal, and thus condemned her to death. Apollo, in his indignation at the father's cruelty, visited Argos with a child-killing plague and when his oracle was consulted about the means of averting the plague, he answered that the Argives must propitiate Psamathe and Linus. This was attempted by means of sacrifices, and matrons and virgins sang dirges which were called ''linoi'', and the month in which this solemnity was celebrated was called ''arneios'', and the festival it ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greek Mythology
Greek mythology is the body of myths originally told by the Ancient Greece, ancient Greeks, and a genre of ancient Greek folklore, today absorbed alongside Roman mythology into the broader designation of classical mythology. These stories concern the ancient Greek religion's view of the Cosmogony, origin and Cosmology#Metaphysical cosmology, nature of the world; the lives and activities of List of Greek deities, deities, Greek hero cult, heroes, and List of Greek mythological creatures, mythological creatures; and the origins and significance of the ancient Greeks' cult (religious practice), cult and ritual practices. Modern scholars study the myths to shed light on the religious and political institutions of ancient Greece, and to better understand the nature of mythmaking itself. The Greek myths were initially propagated in an oral tradition, oral-poetic tradition most likely by Minoan civilization, Minoan and Mycenaean Greece, Mycenaean singers starting in the 18th century&n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Greek
Ancient Greek (, ; ) includes the forms of the Greek language used in ancient Greece and the classical antiquity, ancient world from around 1500 BC to 300 BC. It is often roughly divided into the following periods: Mycenaean Greek (), Greek Dark Ages, Dark Ages (), the Archaic Greece, Archaic or Homeric Greek, Homeric period (), and the Classical Greece, Classical period (). Ancient Greek was the language of Homer and of fifth-century Athens, fifth-century Athenian historians, playwrights, and Ancient Greek philosophy, philosophers. It has contributed many words to English vocabulary and has been a standard subject of study in educational institutions of the Western world since the Renaissance. This article primarily contains information about the Homeric Greek, Epic and Classical periods of the language, which are the best-attested periods and considered most typical of Ancient Greek. From the Hellenistic period (), Ancient Greek was followed by Koine Greek, which is regar ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apollo
Apollo is one of the Twelve Olympians, Olympian deities in Ancient Greek religion, ancient Greek and Ancient Roman religion, Roman religion and Greek mythology, Greek and Roman mythology. Apollo has been recognized as a god of archery, music and dance, truth and prophecy, healing and diseases, the Sun and light, poetry, and more. One of the most important and complex of the Greek gods, he is the son of Zeus and Leto, and the twin brother of Artemis, goddess of the hunt. He is considered to be the most beautiful god and is represented as the ideal of the ''kouros'' (ephebe, or a beardless, athletic youth). Apollo is known in Greek-influenced Etruscan mythology as ''Apulu''. As the patron deity of Delphi (''Apollo Pythios''), Apollo is an oracular god—the prophetic deity of the Pythia, Delphic Oracle and also the deity of ritual purification. His oracles were often consulted for guidance in various matters. He was in general seen as the god who affords help and wards off e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Psamathe (Crotopus)
In Greek mythology, Psamathe () was the daughter of King Crotopus of Argos, who became the lover of the god Apollo. Mythology In one version (Conon), Psamathe abandoned the child, and although shepherds reared the foundling who was then named Linus, the child was torn apart by the shepherd's dogs. In the interim, Psamathe was ordered to be killed by her father. Apollo avenged her murder by sending a plague to Argos. When consulted, Apollo demanded that Psamathe and Linus be propitiated with due honors and festivities. The Argives complied but the plague persisted. And by oracular decree, the king was forced to leave in order to found the city of Tripodiscium near Megara, where he would live out his life. In an alternate version ( Pausanias), Psamathe exposed the unnamed child, which was torn apart by the king's sheepdogs. Apollo then sent Poena (Greek: Poinē), the personification of punishment, upon the city. Poine would steal children from their mothers until Coroebus killed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Crotopus
Crotopus or Krotopos (), in Greek mythology, was the eighth king of Argos.Eusebius''. Praeparatio evangelica10.9.8; 10.11.2, 10.12.1-3 Chronography66' Family Crotopus was the son of Agenor and father of Psamathe and Sthenelus, Sthenelas. Mythology According to myth, Crotopus condemned to death his own daughter Psamathe, after she gave birth to a child who was Apollo 's son. Crotopus's city of Argos was consequently punished by Apollo with a plague. There are various versions, but it is in Conon (mythographer), Conon's account that the king must expiate this himself by self-exile: Crotopus was a terrifying father to Psamathe, and she exposed the child, but the child was found and grew up as a shepherd's boy named Linus of Argos, Linus, until Crotopus's sheepdogs tore the boy apart. As Psamathe grieved over the loss of her child, Crotopus discovered about the secret child, and under the assumption she had acted like a harlot and was lying about Apollo, sentenced her to death. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Argos, Peloponnese
Argos (; ; ) is a city and former municipality in Argolis, Peloponnese (region), Peloponnese, Greece and is one of the List of oldest continuously inhabited cities, oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, and the oldest in Europe. It is the largest city in Argolis and a major center in the same prefecture, having nearly twice the population of the prefectural capital, Nafplio. Since the 2011 local government reform it has been part of the municipality of Argos-Mykines, of which it is a municipal unit. The municipal unit has an area of 138.138 km2. It is from Nafplion, which was its historic harbour. A settlement of great antiquity, Argos has been continuously inhabited as at least a substantial village for the past 7,000 years. A resident of the city of Argos is known as an Argive ( , ; ). However, this term is also used to refer to those ancient Greeks generally who assaulted the city of Troy during the Trojan War; the term is more widely applied by the Hom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pausanias (geographer)
Pausanias ( ; ; ) was a Greek traveler and geographer of the second century AD. He is famous for his '' Description of Greece'' (, ), a lengthy work that describes ancient Greece from his firsthand observations. ''Description of Greece'' provides crucial information for making links between classical literature and modern archaeology, which is providing evidence of the sites and cultural details he mentions although knowledge of their existence may have become lost or relegated to myth or legend. Biography Nothing is known about Pausanias apart from what historians can piece together from his own writing. However, it is probable that he was born into a Greek family and was probably a native of Lydia in Asia Minor. From until his death around 180, Pausanias travelled throughout the mainland of Greece, writing about various monuments, sacred spaces, and significant geographical sites along the way. In writing his '' Description of Greece'', Pausanias sought to put together ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Statius
Publius Papinius Statius (Greek language, Greek: Πόπλιος Παπίνιος Στάτιος; , ; ) was a Latin poetry, Latin poet of the 1st century CE. His surviving poetry includes an epic in twelve books, the ''Thebaid (Latin poem), Thebaid''; a collection of occasional poetry, the ''Silvae''; and an unfinished epic, the ''Achilleid''. He is also known for his appearance as a guide in the ''Purgatorio, Purgatory'' section of Dante Alighieri, Dante's epic poem, the ''Divine Comedy''. Life Family background The poet's father (whose name is unknown) was a native of Velia but later moved to Naples and spent time in Rome where he taught with marked success. From boyhood to adulthood, Statius's father proved himself a champion in the poetic contests at Naples in the Augustalia and in the Nemean, Pythian Games, Pythian, and Isthmian Games, Isthmian games, which served as important events to display poetic skill during the early empire. Statius declares in his lament for his fath ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thebaid (Latin Poem)
The ''Thebaid'' (; ) is a Latin epic poem written by the Roman poet Statius. Published in the early 90s AD, it contains 9748 lines arranged in 12 books, and recounts the clash of two brothers, Eteocles and Polynices, over the throne of the Greek city of Thebes, Greece, Thebes. After Polynices is sent into exile, he forges an alliance of Seven against Thebes, seven Greek princes and embarks on a military campaign against his brother. Although its source material derives predominantly from the Ancient Greek literature, Greek literary tradition, the ''Thebaid'' has close ties with other Latin texts such as Virgil's ''Aeneid'' and Senecan tragedy, the tragedies of Seneca the Younger. The poem's central themes include the relationship between politics and the family, civil war, and the amoral acts to which it gives rise. Critics have also noted the poem's innovative depiction of Roman mythology. Following in the footsteps of Ovid, Ovid's ''Metamorphoses'', Statius used an episodic w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Conon (mythographer)
Conon (, ''gen''.: Κόνωνος) was a Greek grammarian and mythographer of the age of Augustus (who lived 63 BC – 14 AD), the author of a work titled (Narrations), addressed to Archelaus Philopator, king of Cappadocia. It was a collection of fifty narratives relating to the mythical and heroic period, and especially the foundation of colonies. An epitome of the work was preserved in the '' Bibliotheca'' of Photius, the 9th-century patriarch of Constantinople Constantinople (#Names of Constantinople, see other names) was a historical city located on the Bosporus that served as the capital of the Roman Empire, Roman, Byzantine Empire, Byzantine, Latin Empire, Latin, and Ottoman Empire, Ottoman empire .... Photius commends Conon's Attic style, and remarks that Nicolaus Damascenus borrowed much from him. There are separate editions of this abstract by Gale, by Teucher, and Kanne. Dion ChrysostomOr. xviii. torn. i. p. 480. mentions a rhetorician of this name, who may pos ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dirge
A dirge () is a somber song or lament expressing mourning or grief, such as may be appropriate for performance at a funeral. Often taking the form of a brief hymn, dirges are typically shorter and less meditative than elegy, elegies. Dirges are often slow and bear the character of funeral marches. Poetic dirges may be dedicated to a specific individual or otherwise Death and culture, thematically refer to death. The English word ''dirge'' is etymology, derived from the Latin ''Dirige, Domine, Deus meus, in conspectu tuo viam meam'' ("Direct my way in your sight, O Lord my God"), the first words of the first antiphon (a short chant in Christian liturgy) in the Matins of the Office of the Dead, Office for the Dead, based on Psalm 5. The original meaning of ''dirge'' in English referred to this office, particularly as it appeared within breviary, breviaries and primer (prayer book), primer prayer books. History In the late Medieval period, it was common for Western Christian laity� ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |