|
Linkage (linguistics)
In historical linguistics, a linkage is a network of related dialects or languages that formed from a gradual diffusion and differentiation of a proto-language. The term was introduced by Malcolm Ross in his study of Western Oceanic languages . It is contrasted with a family, which arises when the proto-language speech community separates into groups that remain isolated from each other and do not form a network. Principle Linkages are formed when languages emerged historically from the diversification of an earlier dialect continuum. Its members may have diverged despite sharing subsequent innovations, or such dialects may have come into contact and so converged. In any dialect continuum, innovations are shared between neighbouring dialects in intersecting patterns. The patterns of intersecting innovations continue to be evident as the dialect continuum turns into a linkage. According to the comparative method, a group of languages that exclusively shares a set of innovat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Historical Linguistics
Historical linguistics, also known as diachronic linguistics, is the scientific study of how languages change over time. It seeks to understand the nature and causes of linguistic change and to trace the evolution of languages. Historical linguistics involves several key areas of study, including the reconstruction of ancestral languages, the classification of languages into families, ( comparative linguistics) and the analysis of the cultural and social influences on language development. This field is grounded in the uniformitarian principle, which posits that the processes of language change observed today were also at work in the past, unless there is clear evidence to suggest otherwise. Historical linguists aim to describe and explain changes in individual languages, explore the history of speech communities, and study the origins and meanings of words ( etymology). Development Modern historical linguistics dates to the late 18th century, having originally grown o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
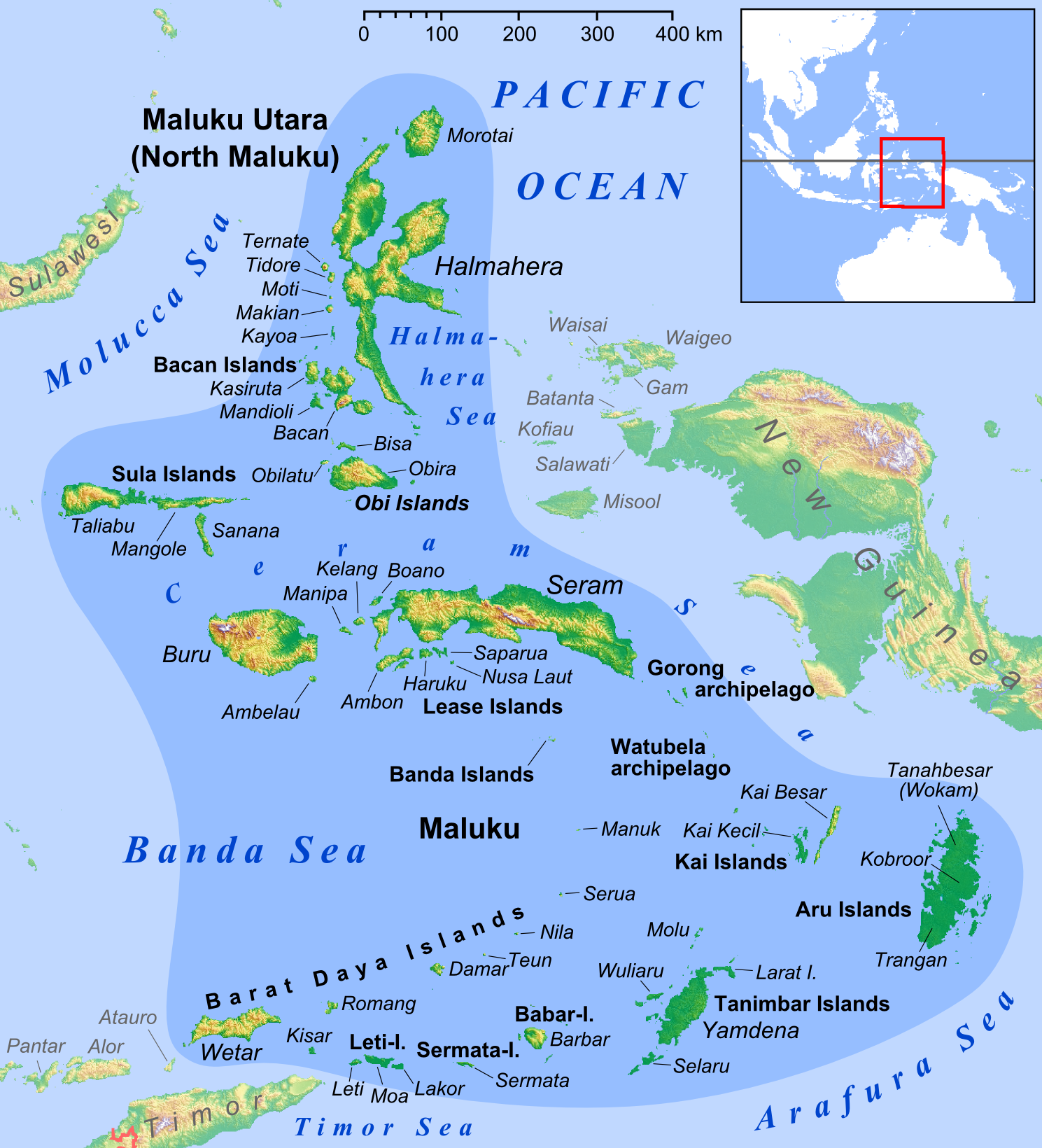
Banda Sea
The Banda Sea (, , ) is one of four seas that surround the Maluku Islands of Indonesia, connected to the Pacific Ocean, but surrounded by hundreds of islands, including Timor, as well as the Halmahera Sea, Halmahera and Ceram Seas. It is about 1000 km (600 mi) east to west, and about 500 km (300 mi) north to south. Extent The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) defines the Banda Sea as being one of the waters of the East Indian Archipelago. The IHO defines its limits as follows: ''On the North'' The Southern limits of the Molucca Sea, Molukka Sea and the Western and Southern limits of the Ceram Sea. ''On the East.'' From Tg Borang, the Northern point of Noehoe Tjoet [Kai Besar], through this island to its Southern point, thence a line to the Northeast point of Fordata, through this island and across to the Northeast point of Larat, Tanimbar Islands (), down the East coast of Jamdena [Yamdena] Island to its Southern point, thence through Anggarma ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indo-European Languages
The Indo-European languages are a language family native to the northern Indian subcontinent, most of Europe, and the Iranian plateau with additional native branches found in regions such as Sri Lanka, the Maldives, parts of Central Asia (e.g., Tajikistan and Afghanistan), Armenia, and areas of southern India. Historically, Indo-European languages were also spoken in Anatolia. Some European languages of this family—English language, English, French language, French, Portuguese language, Portuguese, Russian language, Russian, Spanish language, Spanish, and Dutch language, Dutch—have expanded through colonialism in the modern period and are now spoken across several continents. The Indo-European family is divided into several branches or sub-families, including Albanian language, Albanian, Armenian language, Armenian, Balto-Slavic, Celtic languages, Celtic, Germanic languages, Germanic, Hellenic languages, Hellenic, Indo-Iranian languages, Indo-Iranian, and Italic languages, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sinitic Languages
The Sinitic languages (), often synonymous with the Chinese languages, are a language group, group of East Asian analytic languages that constitute a major branch of the Sino-Tibetan language family. It is frequently proposed that there is a primary split between the Sinitic languages and the rest of the family (the Tibeto-Burman languages). This view is rejected by some researchers but has found phylogenetic support among others. The Macro-Bai languages, whose classification is difficult, may be an offshoot of Old Chinese and thus Sinitic; otherwise, Sinitic is defined only by the many varieties of Chinese unified by a shared historical background, and usage of the term "Sinitic" may reflect the linguistic view that Chinese language, Chinese constitutes a family of distinct languages, rather than variants of a single language. Population Over 91% of the Chinese population speaks a Sinitic language, of whom about three-quarters speak a Mandarin variety. Estimates of the number ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semitic Languages
The Semitic languages are a branch of the Afroasiatic languages, Afroasiatic language family. They include Arabic, Amharic, Tigrinya language, Tigrinya, Aramaic, Hebrew language, Hebrew, Maltese language, Maltese, Modern South Arabian languages and numerous other ancient and modern languages. They are spoken by more than 330 million people across much of Western Asia, West Asia, North Africa, the Horn of Africa, Malta, and in large Immigration, immigrant and Expatriate, expatriate communities in North America, Europe, and Australasia. The terminology was first used in the 1780s by members of the Göttingen school of history, who derived the name from Shem, one of the three Generations of Noah, sons of Noah in the Book of Genesis. Semitic languages List of languages by first written account, occur in written form from a very early historical date in West Asia, with East Semitic languages, East Semitic Akkadian language, Akkadian (also known as Ancient Assyrian language, Assyrian ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Athabaskan Languages
Athabaskan ( ; also spelled ''Athabascan'', ''Athapaskan'' or ''Athapascan'', and also known as Dene) is a large branch of the Na-Dene languages, Na-Dene language family of North America, located in western North America in three areal language groups: Northern, Pacific Coast and Southern (or Apachean). Kari and Potter (2010:10) place the total territory of the 53 Athabaskan languages at . Chipewyan language, Chipewyan is spoken over the largest area of any North American native language, while Navajo language, Navajo is spoken by the largest number of people of any native language north of Mexico. The word ''Athabaskan'' is an Anglicisation, anglicized version of a Cree language name for Lake Athabasca ( '[where] there are reeds one after another') in Canada. Cree is one of the Algonquian languages and therefore not itself an Athabaskan language. The name was assigned by Albert Gallatin in his 1836 (written 1826) classification of the languages of North America. He acknowledged ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Polynesian Languages
The Polynesian languages form a genealogical group of languages, itself part of the Oceanic branch of the Austronesian family. There are 38 Polynesian languages, representing 7 percent of the 522 Oceanic languages, and 3 percent of the Austronesian family. While half of them are spoken in geographical Polynesia (the Polynesian triangle), the other half – known as Polynesian outliers – are spoken in other parts of the Pacific: from Micronesia to atolls scattered in Papua New Guinea, the Solomon Islands or Vanuatu. The most prominent Polynesian languages, by number of speakers, are Samoan, Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Hawaiian. The ancestors of modern Polynesians were Lapita navigators, who settled in the Tonga and Samoa areas about 3,000 years ago. Linguists and archaeologists estimate that this first population went through common development over approximately 1,000 years, giving rise to Proto-Polynesian, the linguistic ancestor of all modern Polynesian l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Pacific Languages
The Central Pacific languages, also known as Fijian–Polynesian languages, are a branch of the Oceanic languages spoken in Fiji and Polynesia Polynesia ( , ) is a subregion of Oceania, made up of more than 1,000 islands scattered over the central and southern Pacific Ocean. The indigenous people who inhabit the islands of Polynesia are called Polynesians. They have many things in .... Classification Ross et al. (2002) classify the languages as a linkage. Lynch, John, Malcolm Ross & Terry Crowley. 2002. ''The Oceanic languages.'' Richmond, Surrey: Curzon Press. *Central Pacific **Western *** Rotuman ***Western Fijian linkage **** Namosi-Naitasiri-Serua **** Western Fijian (Nadroga, Waya) **East Central Pacific linkage ***Eastern Fijian linkage **** Bauan (standard Fijian) **** Gone Dau **** Lauan **** Lomaiviti *** Polynesian family The West Fijian languages are more closely related to Rotuman, and East Fijian to Polynesian, than they are to each other, but subse ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Languages Of Vanuatu
The Republic of Vanuatu has the world's highest linguistic density per capita. Despite being a country with a Demographics of Vanuatu, population of less than 300,000, Vanuatu is home to 138 indigenous Oceanic languages, Oceanic languages. The country's three official languages are of foreign origin: English language, English, French language, French, and Bislama, an English-based creole languages, English-based creole language.Constitution of Vanuatu Article 3 Additional languages are also spoken as a result of recent migrations (e.g. Samoan language, Samoan, Hakka Chinese, Mandarin Chinese). The linguistic situation in Vanuatu Indigenous languages There are over one hundred local languages spread over the archipelago (#List_of_Vanuatu’s_indigenous_languages, listed below), all of them belonging to the Austronesian languages, Austronesian family of languages. Vanuatu is the country with the highest density of languages per capita in the world: it currently shows an average o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Languages
The approximately 450 Oceanic languages are a branch of the Austronesian languages. The area occupied by speakers of these languages includes Polynesia, as well as much of Melanesia and Micronesia. Though covering a vast area, Oceanic languages are spoken by only two million people. The largest individual Oceanic languages are Eastern Fijian with over 600,000 speakers, and Samoan with an estimated 400,000 speakers. The Gilbertese (Kiribati), Tongan, Tahitian, Māori and Tolai (Gazelle Peninsula) languages each have over 100,000 speakers. The common ancestor which is reconstructed for this group of languages is called Proto-Oceanic (abbr. "POc"). Classification The Oceanic languages were first shown to be a language family by Sidney Herbert Ray in 1896 and, besides Malayo-Polynesian, they are the only established large branch of Austronesian languages. Grammatically, they have been strongly influenced by the Papuan languages of northern New Guinea, but they retain a rema ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eastern Malayo-Polynesian Languages
Eastern or Easterns may refer to: Transportation Airlines *China Eastern Airlines, a current Chinese airline based in Shanghai * Eastern Air, former name of Zambia Skyways * Eastern Air Lines, a defunct American airline that operated from 1926 to 1991 * Eastern Air Lines (2015), an American airline that began operations in 2015 * Eastern Airlines, LLC, previously Dynamic International Airways, a U.S. airline founded in 2010 * Eastern Airways, an English/British regional airline * Eastern Provincial Airways, a defunct Canadian airline that operated from 1949 to 1986 Roads * Eastern Avenue (other), various roads * Eastern Parkway (other), various parkways * Eastern Freeway, Melbourne, Australia * Eastern Freeway Mumbai, Mumbai, India Other * Eastern Railway (other), various railroads *, a cargo liner in service 1946-65 Education * Eastern University (other) * Eastern College (other) Sports * Easterns (cricket team), South ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |