|
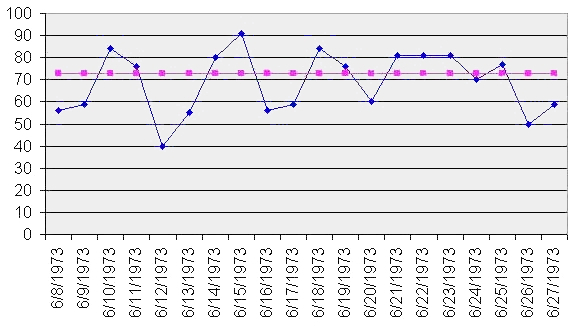
Line Chart
A line chart or line graph, also known as curve chart, is a type of chart that displays information as a series of data points called 'markers' connected by straight wikt:line, line segments. It is a basic type of chart common in many fields. It is similar to a scatter plot except that the measurement points are ordered (typically by their x-axis value) and joined with straight line segments. A line chart is often used to visualize a trend in data over intervals of time – a time series – thus the line is often drawn chronologically. In these cases they are known as run charts. History Some of the earliest known line charts are generally credited to Francis Hauksbee, Nicolaus Samuel Cruquius, Johann Heinrich Lambert and the Scottish engineer William Playfair. Line charts often display time as a variable on the x-axis. Playfair was one of the first to visualize data this way. In 1786, he plotted ten years of money spent by the Royal Navy. He supplemented the chart with a det ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pushkin Population History
Alexander Sergeyevich Pushkin () was a Russian poet, playwright, and novelist of the Romantic era.Basker, Michael. Pushkin and Romanticism. In Ferber, Michael, ed., ''A Companion to European Romanticism''. Oxford: Blackwell, 2005. He is considered by many to be the greatest Russian poet,Short biography from University of Virginia . Retrieved 24 November 2006.Allan Reid, "Russia's Greatest Poet/Scoundrel" Retrieved 2 September 2006. as well as the founder of modern Russian literature.Maxim Gorky [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dwiggins Graph
Dwiggins is a surname. Notable people with the surname include: * Clare Victor Dwiggins (1874–1958), American cartoonist * Don Dwiggins (1913–1988), American aviation journalist and author * Sue Dwiggins (1914–2011), American writer and production assistant * William Addison Dwiggins (1880–1956), American type designer, calligrapher, and book designer See also * Diggins (other) * Wiggins (surname) {{surname ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Quality Control Tools
Quality may refer to: Concepts *Quality (business), the ''non-inferiority'' or ''superiority'' of something *Quality (philosophy), an attribute or a property * Quality (physics), in response theory * Energy quality, used in various science disciplines * Logical quality, philosophical categorization of statements * Service quality, comparison of expectations with performance in a service *Vapor quality, in thermodynamics, the ratio of mass of vapor to that of vapor and liquid *Data quality, refers to the condition of a set of values of qualitative or quantitative variables Practices *Quality assurance (QA) *Quality control (QC) *Quality management system (QMS) *Quality Management (QM) Places *Quality, Kentucky, an unincorporated community Brands and enterprises *Quality Comics, an American comic book publisher between 1939 and 1956 *Quality Communications, a British comic book publisher between 1982 and 2008 *Quality Records, a Canadian entertainment company Music * ''Quality'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Run Chart
A run chart, also known as a run-sequence plot is a graph that displays observed data in a time sequence. Often, the data displayed represent some aspect of the output or performance of a manufacturing or other business process. It is therefore a form of line chart. Overview Run sequence plots are an easy way to graphically summarize a univariate data set. A common assumption of univariate data sets is that they behave like:NIST/SEMATECH (2003)"Run-Sequence Plot"In: ''e-Handbook of Statistical Methods'' 6/01/2003 (Date created). * random drawings; * from a fixed distribution; * with a common location; and * with a common scale. With run sequence plots, shifts in location and scale are typically quite evident. Also, outliers can easily be detected. Examples could include measurements of the fill level of bottles filled at a bottling plant or the water temperature of a dishwashing machine each time it is run. Time is generally represented on the horizontal (x) axis and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Information Graphics Software
This is a list of software to create any kind of information graphics: * either includes the ability to create one or more infographics from a provided data set * either it is provided specifically for information visualization Vector graphics Vector graphics software can be used for manual graphing or for editing the output of another program; see: * :Vector graphics editors * Comparison of vector graphics editors A few online editors using vector graphics for specific needs have been created. This kind of creative Interface (computing), interfaces work well together with data visualization tools like the ones above. See also * :Diagramming software * Comparison of numerical-analysis software * List of graphical methods * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Information Graphics Software Comparisons of mathematical software Graphics software Infographics Lists of software Plotting software, Statistical software, Statistics-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Data And Information Visualization
Data and information visualization (data viz/vis or info viz/vis) is the practice of designing and creating graphic or visual representations of a large amount of complex quantitative and qualitative data and information with the help of static, dynamic or interactive visual items. Typically based on data and information collected from a certain domain of expertise, these visualizations are intended for a broader audience to help them visually explore and discover, quickly understand, interpret and gain important insights into otherwise difficult-to-identify structures, relationships, correlations, local and global patterns, trends, variations, constancy, clusters, outliers and unusual groupings within data (''exploratory visualization''). When intended for the general public (mass communication) to convey a concise version of known, specific information in a clear and engaging manner (''presentational'' or ''explanatory visualization''), it is typically called information gra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
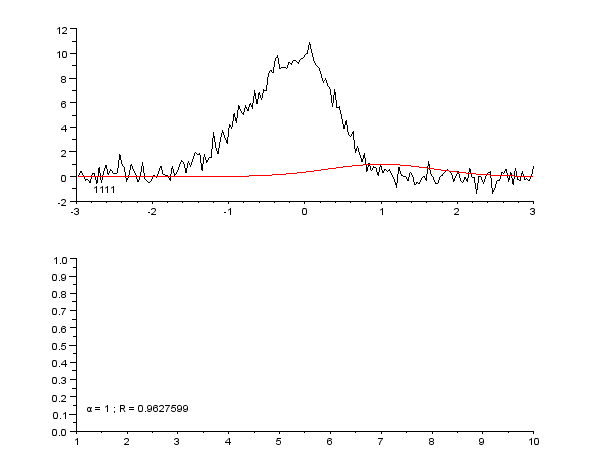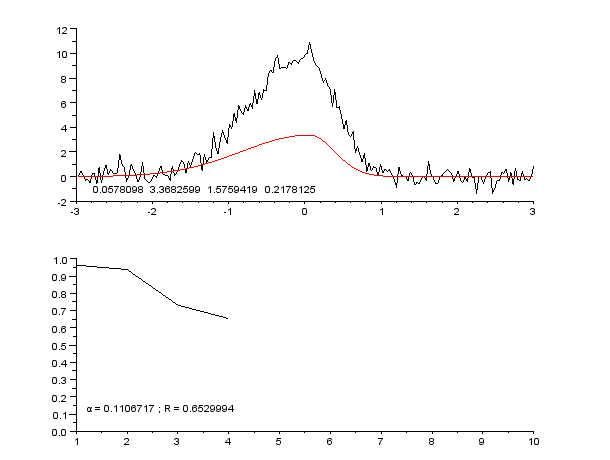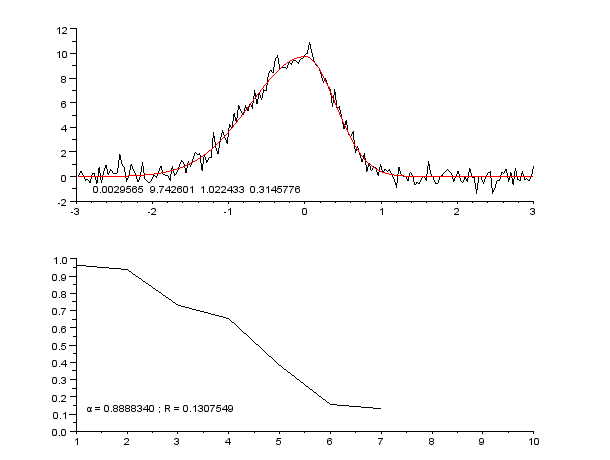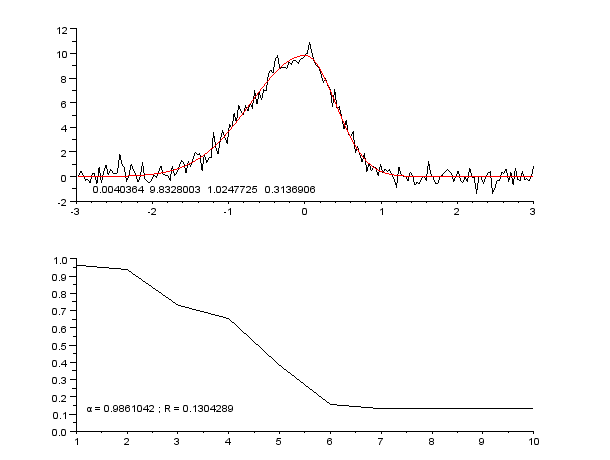
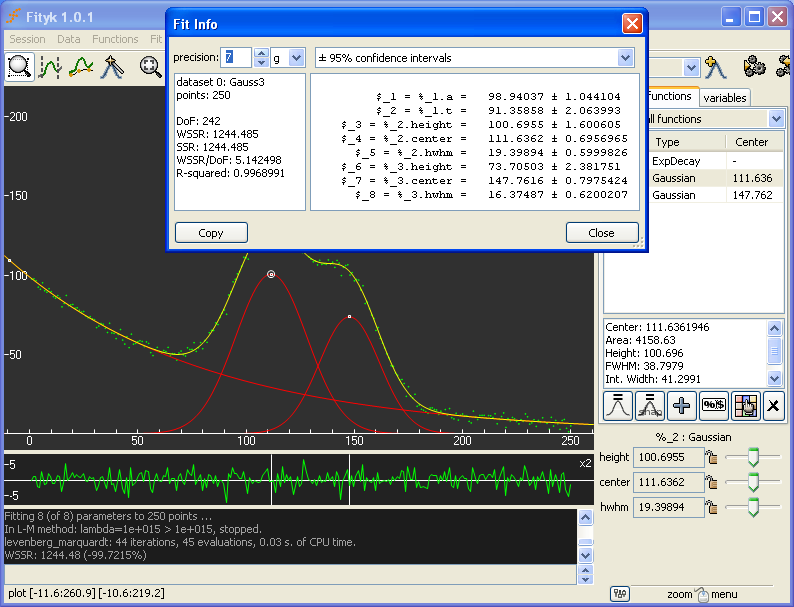
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fitted to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linear Equation
In mathematics, a linear equation is an equation that may be put in the form a_1x_1+\ldots+a_nx_n+b=0, where x_1,\ldots,x_n are the variables (or unknowns), and b,a_1,\ldots,a_n are the coefficients, which are often real numbers. The coefficients may be considered as parameters of the equation and may be arbitrary expressions, provided they do not contain any of the variables. To yield a meaningful equation, the coefficients a_1, \ldots, a_n are required to not all be zero. Alternatively, a linear equation can be obtained by equating to zero a linear polynomial over some field, from which the coefficients are taken. The solutions of such an equation are the values that, when substituted for the unknowns, make the equality true. In the case of just one variable, there is exactly one solution (provided that a_1\ne 0). Often, the term ''linear equation'' refers implicitly to this particular case, in which the variable is sensibly called the ''unknown''. In the case of two ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spreadsheet
A spreadsheet is a computer application for computation, organization, analysis and storage of data in tabular form. Spreadsheets were developed as computerized analogs of paper accounting worksheets. The program operates on data entered in cells of a table. Each cell may contain either numeric or text data, or the results of formulas that automatically calculate and display a value based on the contents of other cells. The term ''spreadsheet'' may also refer to one such electronic document. Spreadsheet users can adjust any stored value and observe the effects on calculated values. This makes the spreadsheet useful for "what-if" analysis since many cases can be rapidly investigated without manual recalculation. Modern spreadsheet software can have multiple interacting sheets and can display data either as text and numerals or in graphical form. Besides performing basic arithmetic and mathematical functions, modern spreadsheets provide built-in functions for common financial ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Graphing Software
This is a list of software to create any kind of information graphics: * either includes the ability to create one or more infographics from a provided data set * either it is provided specifically for information visualization Vector graphics Vector graphics software can be used for manual graphing or for editing the output of another program; see: * :Vector graphics editors * Comparison of vector graphics editors A few online editors using vector graphics for specific needs have been created. This kind of creative Interface (computing), interfaces work well together with data visualization tools like the ones above. See also * :Diagramming software * Comparison of numerical-analysis software * List of graphical methods * References {{DEFAULTSORT:Information Graphics Software Comparisons of mathematical software Graphics software Infographics Lists of software Plotting software, Statistical software, Statistics-related lists ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Curve Fitting
Curve fitting is the process of constructing a curve, or mathematical function, that has the best fit to a series of data points, possibly subject to constraints. Curve fitting can involve either interpolation, where an exact fit to the data is required, or smoothing, in which a "smooth" function is constructed that approximately fits the data. A related topic is regression analysis, which focuses more on questions of statistical inference such as how much uncertainty is present in a curve that is fitted to data observed with random errors. Fitted curves can be used as an aid for data visualization, to infer values of a function where no data are available, and to summarize the relationships among two or more variables. Extrapolation refers to the use of a fitted curve beyond the range of the observed data, and is subject to a degree of uncertainty since it may reflect the method used to construct the curve as much as it reflects the observed data. For linear-algebraic ana ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Gradient
In vector calculus, the gradient of a scalar-valued differentiable function f of several variables is the vector field (or vector-valued function) \nabla f whose value at a point p gives the direction and the rate of fastest increase. The gradient transforms like a vector under change of basis of the space of variables of f. If the gradient of a function is non-zero at a point p, the direction of the gradient is the direction in which the function increases most quickly from p, and the magnitude of the gradient is the rate of increase in that direction, the greatest absolute directional derivative. Further, a point where the gradient is the zero vector is known as a stationary point. The gradient thus plays a fundamental role in optimization theory, where it is used to minimize a function by gradient descent. In coordinate-free terms, the gradient of a function f(\mathbf) may be defined by: df=\nabla f \cdot d\mathbf where df is the total infinitesimal change in f for a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |