|
Lincoln, Ontario
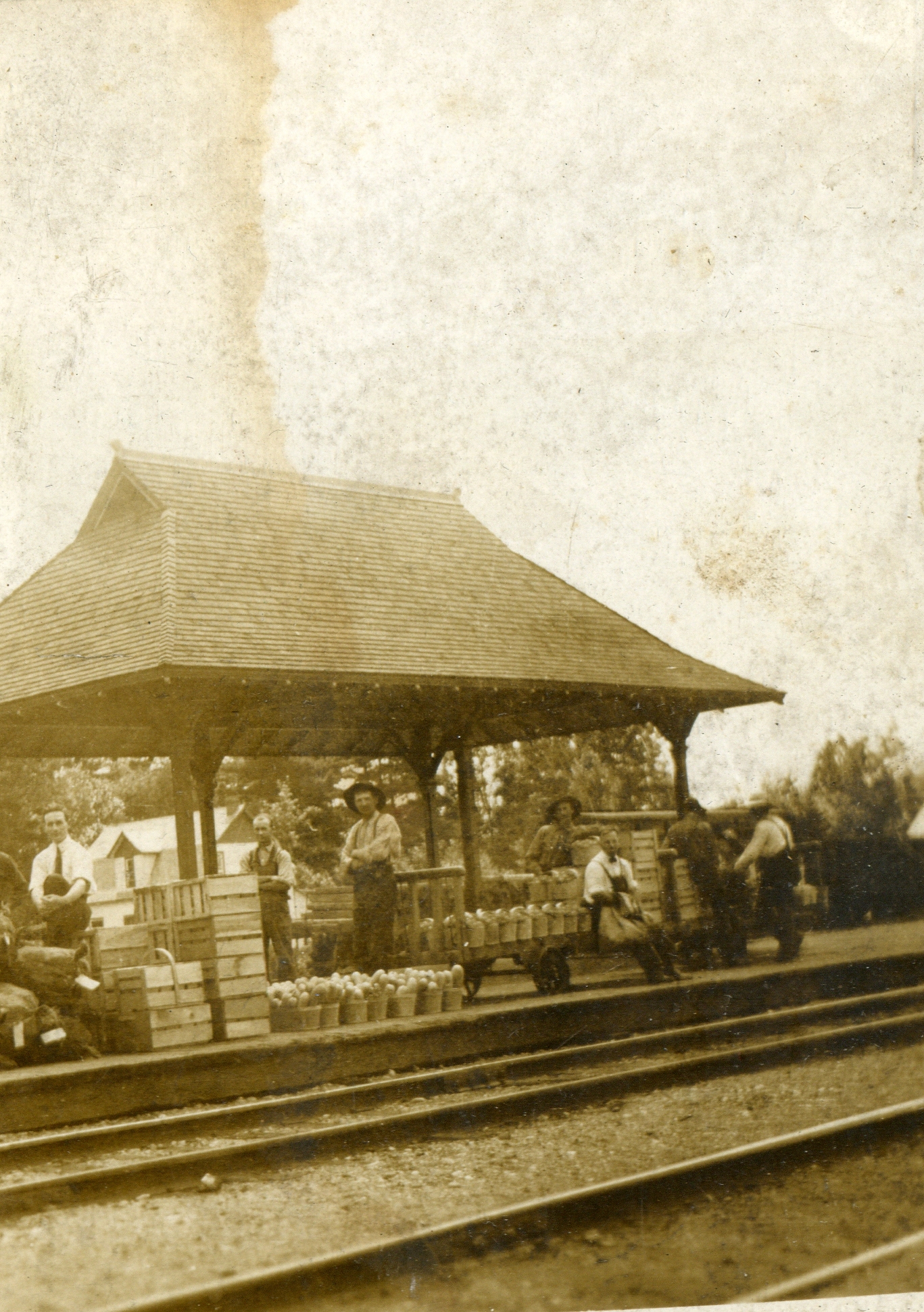
Lincoln is a town on Lake Ontario in the Niagara Region, Ontario, Canada. The town's administrative and commercial centre is in the community of Beamsville. Geography Lincoln's location between the southern shore of Lake Ontario and the Niagara Escarpment provides for a moderate climate with mild winters. The area is known in Canada for its orchards, vineyards, wineries and restaurants that feature local produce and wines. Fruit crops grown in Lincoln include cherries, peaches, apples and pears, and during the summer attract many tourists from all over Ontario, particularly Toronto. Since November 2017, the town has been served by the "uLinc" bus network, which runs three routes. GO Transit also serves the town. Communities The township comprises the communities of Beamsville, Campden, Jordan, Jordan Station, Rockway, Tintern, Vineland and Vineland Station. History Lincoln's earliest known inhabitants was the Neutral Confederacy, also called the Attawandaron. Archaeologists from ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns In Ontario
A town is a sub-type of municipalities in the Canadian province of Ontario. A town can have the municipal status of either a single-tier or lower-tier municipality. Ontario has 89 towns that had a cumulative population of 1,813,458 and an average population of 22,316 in the 2016 Census. Ontario's largest and smallest towns are Oakville and Latchford with populations of 193,832 and 313 respectively. History Under the former ''Municipal Act, 1990'', a town was both an urban and a local municipality. Under this former legislation, a locality with a population of 2,000 or more could have been incorporated as a town by Ontario's Municipal Board upon review of an application from 75 or more residents of the locality. It also enabled the Municipal Board to change the status of a village or township to a town if it had a population of 2,000 upon review of an application from the village or township. In the transition to the ''Municipal Act, 2001'', these ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Orchards
An orchard is an intentional plantation of trees or shrubs that is maintained for food production. Orchards comprise fruit- or nut-producing trees which are generally grown for commercial production. Orchards are also sometimes a feature of large gardens, where they serve an aesthetic as well as a productive purpose. A fruit garden is generally synonymous with an orchard, although it is set on a smaller non-commercial scale and may emphasize berry shrubs in preference to fruit trees. Most temperate-zone orchards are laid out in a regular grid, with a grazed or mown grass or bare soil base that makes maintenance and fruit gathering easy. Most modern commercial orchards are planted for a single variety of fruit. While the importance of introducing biodiversity is recognized in forest plantations, it would seem to be beneficial to introduce some genetic diversity in orchard plantations as well by interspersing other trees through the orchard. Genetic diversity in an orchard would ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to the French as the Iroquois League, and later as the Iroquois Confederacy. The English called them the Five Nations, comprising the Mohawk, Oneida, Onondaga, Cayuga, and Seneca (listed geographically from east to west). After 1722, the Iroquoian-speaking Tuscarora people from the southeast were accepted into the confederacy, which became known as the Six Nations. The Confederacy came about as a result of the Great Law of Peace, said to have been composed by Deganawidah the Great Peacemaker, Hiawatha, and Jigonsaseh the Mother of Nations. For nearly 200 years, the Six Nations/Haudenosaunee Confederacy were a powerful factor in North American colonial policy, with some scholars arguing for the concept of the Middle Ground, in that Eu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Royal Ontario Museum
The Royal Ontario Museum (ROM) is a museum of art, world culture and natural history in Toronto, Ontario, Canada. It is one of the largest museums in North America and the largest in Canada. It attracts more than one million visitors every year, making the ROM List of most-visited museums by region, the most-visited museum in Canada. The museum is north of Queen's Park (Toronto), Queen's Park, in the University of Toronto district, with its main entrance on Bloor Street, Bloor Street West. Museum station (Toronto), Museum subway station is named after the ROM and, since a 2008 renovation, is decorated to resemble the institution's collection at the platform level. Established on April 16, 1912, and opened on March 19, 1914, the museum has maintained close relations with the University of Toronto throughout its history, often sharing expertise and resources. The museum was under the direct control and management of the University of Toronto until 1968, when it became an independe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
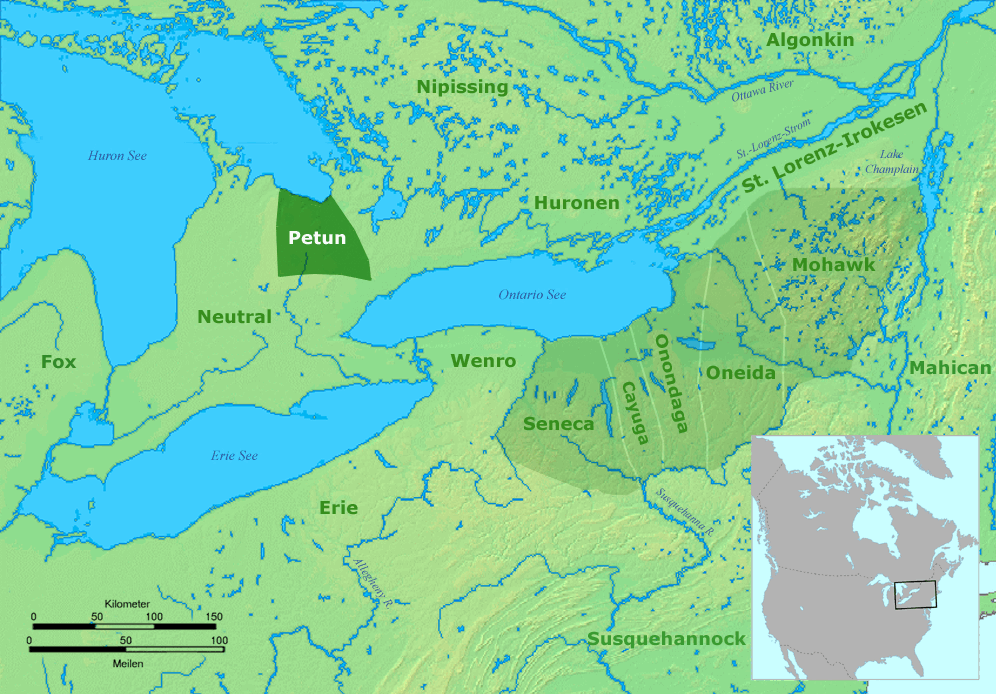
Neutral Nation
The Neutral Confederacy (also Neutral Nation, Neutral people, or ''Attawandaron'' by neighbouring tribes) were an Iroquoian people who lived in what is now southwestern and south-central Ontario in Canada, North America. They lived throughout the area bounded by the southern half of Lake Huron, the entire northern shoreline of Lake Erie, from the Detroit River in the west to the Niagara River in the east, plus northward around the western end of Lake Ontario. Their territory was southwest of the Petun and west of the southern area of the Huron people, or Wendat territory. They were related to other Iroquoian-language speakers: the Huron people, the Petun (who later merged with the Huron), the Wenro to their east, and the Five Nations of the Iroquois Confederation further to the east, as well as to the Erie people of the south shore of Lake Erie, and the Susquehannock of Central Pennsylvania. Like others of Iroquoian language and culture, the tribes would raid and feud wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vineland, Ontario
Vineland is an unincorporated community within the Town of Lincoln in Niagara Region. Located in the Canadian province of Ontario, it is bordered by the Twenty Mile Creek and Jordan to the east, Lake Ontario to the north, Beamsville to the west, and Pelham to the south. Vineland is primarily an agricultural community and is home to many tender fruit farms and wineries. As the second-largest community in the Town of Lincoln, Vineland's small commercial centre along King Street serves the surrounding communities of Campden and Jordan. The post office was established in 1894. Agriculture Its location between the southern shore of Lake Ontario and the Niagara Escarpment provides for a moderate climate with mild winters. Vineland and the surrounding area is known in Canada for its orchards, vineyards, wineries and restaurants that feature local produce and wines. There are also a large number of greenhouses and farms in the vicinity that are a major economic driver. Vinel ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jordan, Ontario
Jordan is a community located on the eastern edge of the Town of Lincoln, in the Niagara Region. Jordan is bordered by the Twenty Mile Creek and Vineland to the west, Lake Ontario to the north, St. Catharines to the east, and Pelham to the south. Lying roughly 100 km from Toronto and 65 km from Buffalo by road, Jordan is located along a major transportation corridor between Canada and the United States. In January 2014, Jordan was brought to international attention when Al-Qaeda-directed terrorists were arrested for plotting to derail a passenger train traveling from Toronto to New York on a rail-bridge crossing the Jordan Harbour. Jordan is home to many wineries due to its climatically advantageous grape-growing conditions in the Niagara Region, and is one of the premier icewine-producing destinations in Canada. Also located in Jordan is the Ball's Falls Conservation Area, which is maintained by the Niagara Peninsula Conservation Authority, and the home of the se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
GO Transit
GO Transit is a regional public transit system serving the Greater Golden Horseshoe region of Ontario, Canada. With its hub at Union Station in Toronto, GO Transit's green-and-white trains and buses serve a population of more than seven million across an area over stretching from London in the west to Peterborough in the east, and from Barrie in the north to Niagara Falls in the south. In , the system had a ridership of . GO Transit operates diesel-powered double-decker trains and coach buses, on routes that connect with all local and some long-distance inter-city transit services in its service area. GO Transit began regular passenger service on May 23, 1967, as a part of the Ontario Ministry of Transportation. Since then, it has grown from a single train line to seven lines, and expanded to include complementary bus service. GO Transit has been constituted in a variety of public-sector configurations. Today, it is an operating division of Metrolinx, a provincial Crown a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Toronto
Toronto ( ; or ) is the capital city of the Provinces and territories of Canada, Canadian province of Ontario. With a recorded population of 2,794,356 in 2021, it is the List of the largest municipalities in Canada by population, most populous city in Canada and the List of North American cities by population, fourth most populous city in North America. The city is the anchor of the Golden Horseshoe, an urban agglomeration of 9,765,188 people (as of 2021) surrounding the western end of Lake Ontario, while the Greater Toronto Area proper had a 2021 population of 6,712,341. Toronto is an international centre of business, finance, arts, sports and culture, and is recognized as one of the most multiculturalism, multicultural and cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan cities in the world. Indigenous peoples in Canada, Indigenous peoples have travelled through and inhabited the Toronto area, located on a broad sloping plateau interspersed with Toronto ravine system, rivers, deep ravines, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
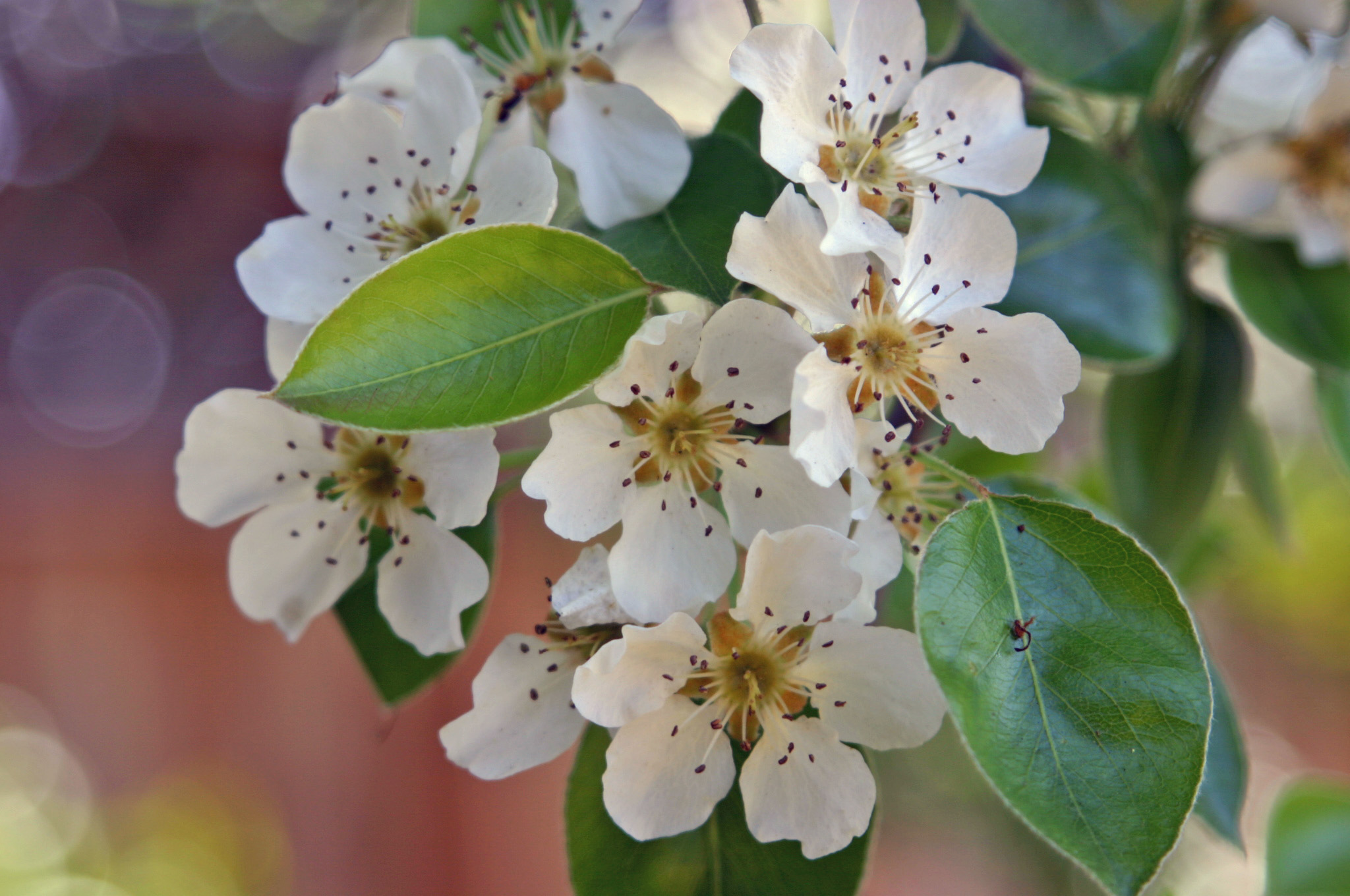
Pear
Pears are fruits produced and consumed around the world, growing on a tree and harvested in the Northern Hemisphere in late summer into October. The pear tree and shrub are a species of genus ''Pyrus'' , in the family Rosaceae, bearing the pomaceous fruit of the same name. Several species of pears are valued for their edible fruit and juices, while others are cultivated as trees. The tree is medium-sized and native to coastal and mildly temperate regions of Europe, North Africa, and Asia. Pear wood is one of the preferred materials in the manufacture of high-quality woodwind instruments and furniture. About 3,000 known varieties of pears are grown worldwide, which vary in both shape and taste. The fruit is consumed fresh, canned, as juice, or dried. Etymology The word ''pear'' is probably from Germanic ''pera'' as a loanword of Vulgar Latin ''pira'', the plural of ''pirum'', akin to Greek ''apios'' (from Mycenaean ''ápisos''), of Semitic origin (''pirâ''), meaning "fru ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Apple
An apple is an edible fruit produced by an apple tree (''Malus domestica''). Apple trees are cultivated worldwide and are the most widely grown species in the genus '' Malus''. The tree originated in Central Asia, where its wild ancestor, '' Malus sieversii'', is still found today. Apples have been grown for thousands of years in Asia and Europe and were brought to North America by European colonists. Apples have religious and mythological significance in many cultures, including Norse, Greek, and European Christian tradition. Apples grown from seed tend to be very different from those of their parents, and the resultant fruit frequently lacks desired characteristics. Generally, apple cultivars are propagated by clonal grafting onto rootstocks. Apple trees grown without rootstocks tend to be larger and much slower to fruit after planting. Rootstocks are used to control the speed of growth and the size of the resulting tree, allowing for easier harvesting. There ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peach
The peach (''Prunus persica'') is a deciduous tree first domesticated and cultivated in Zhejiang province of Eastern China. It bears edible juicy fruits with various characteristics, most called peaches and others (the glossy-skinned, non-fuzzy varieties), nectarines. The specific name ''persica'' refers to its widespread cultivation in Persia (modern-day Iran), from where it was transplanted to Europe. It belongs to the genus '' Prunus'', which includes the cherry, apricot, almond, and plum, in the rose family. The peach is classified with the almond in the subgenus '' Amygdalus'', distinguished from the other subgenera by the corrugated seed shell ( endocarp). Due to their close relatedness, the kernel of a peach stone tastes remarkably similar to almond, and peach stones are often used to make a cheap version of marzipan, known as persipan. Peaches and nectarines are the same species, though they are regarded commercially as different fruits. The skin of nectarine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |