|
Lichun
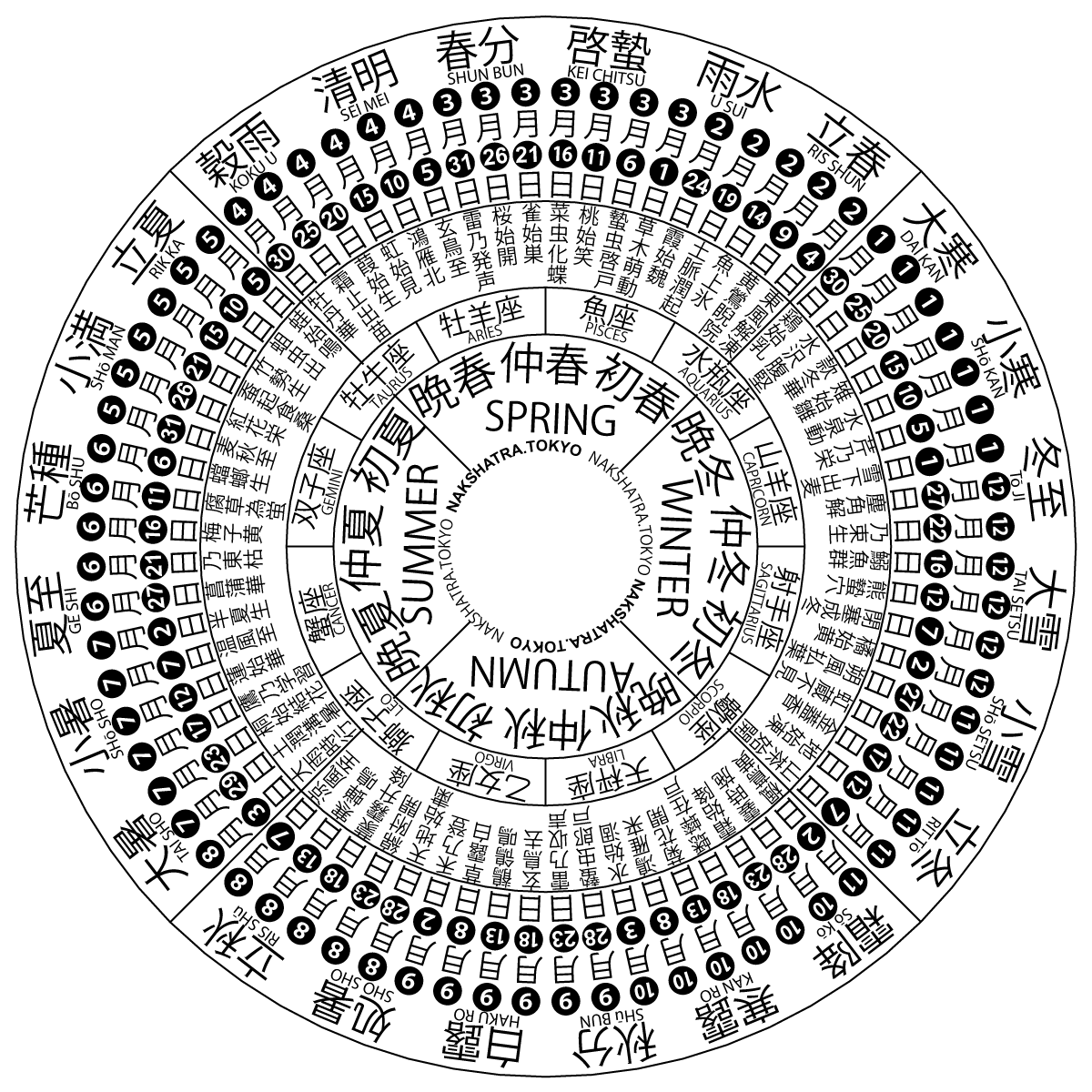
The traditional Chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms. The first one is known as in Chinese, in Japanese, in Korean, and in Vietnamese. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 315° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 330°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 315°. In the Gregorian calendar, it usually begins around February 4 and ends around February 18 (February 19 East Asia time). It is also the beginning of a sexagenary cycle. Lichun signifies the beginning of spring in East Asian cultures. Pentads Each solar term can be divided into 3 pentads (候). They are: first pentad (初候), second pentad (次候) and last pentad (末候). Pentads in Lichun include: ; China * First pentad: Dōng Fēng Jiě Dòng () *: '' Yuè Lìng Qī Shí Èr Hòu Jí Jiě'' (月令七十二候集解) explains the name of this pentad:It is not called the 'winter ice meets the spring win ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chūnbǐng
The spring pancake ( zh , s = 春饼 , t = 春餅 , p = chūnbǐng ) is a traditional Chinese food unique to the northern regions. The pancake is prepared by rubbing oil between two thin layers of leavened dough; after steaming, the pancake can be peeled apart to add fillings. People eat spring pancakes during Lichun to celebrate the beginning spring. History The spring pancake took its rise from the Jin dynasty and has prospered since the Tang dynasty. The Lichun was valued by both Chinese ancient kings and civilians. Unlike kings’ great celebrations, civilians celebrated the Lichun by eating spring pancakes wrapped around fresh vegetables and meat, which is called bite-the-spring. Bite-the-spring implies that civilians are praying for a good harvest year by eating fresh vegetables and meat at the beginning of spring. In the Qing dynasty, spring pancakes became a fried pancake wrapped around a filling that included ham, chicken, pork, black dates, scallions, walnuts and suga ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Egg Of Li Chun
Egg balancing is a traditional Chinese practice of standing eggs on their ends that has also been popularized in the United States. Although the irregular shape of eggs makes this somewhat difficult, eggshells typically have many textural variations such that the vast majority can be balanced on their broad ends with minimal effort. Folklore holds that eggs can be balanced in this way only at a particular time of year: the lunar new year in China, the Dragon Boat Festival in Taiwan, or the vernal equinox in the United States. It is also said that eggs can be balanced on the heads of nails at the equator. In reality, eggs will balance anywhere at any time of year, and the practice has no connection to the gravitational force of the moon or sun. History Lichun egg Egg balancing has been connected with Lichun, the solar term beginning ''Chinese'' spring () on February 4 or 5 when the sun is at the celestial longitude of 315°. On this day, fresh chicken eggs were balanced on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sexagenary Cycle
The sexagenary cycle, also known as the gānzhī (干支) or stems-and-branches, is a cycle of sixty terms, each corresponding to one year, thus amounting to a total of sixty years every cycle, historically used for recording time in China and the rest of the East Asian cultural sphere, as well as in Southeast Asia. It appears as a means of recording days in the first Chinese written texts, the oracle bones of the late second millennium BC Shang dynasty. Its use to record years began around the middle of the 3rd century BC. The cycle and its variations have been an important part of the traditional calendrical systems in Chinese-influenced Asian states and territories, particularly those of Japan, Korea, and Vietnam, with the old Chinese system still in use in Taiwan, and in Mainland China. In India, the Ahom people (descendants of the Dai people of Yunnan who migrated to Assam in the 13th century) also used the sexagenary cycle known as Lak-Ni. This traditional metho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solar Terms
A solar term (or ''jiéqì'', zh, t=節氣, s=节气) is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the ''Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient type of sundial called (). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; not until the Taichu Calendar of 104 BC were all twenty-four solar terms officially included in the Chinese c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
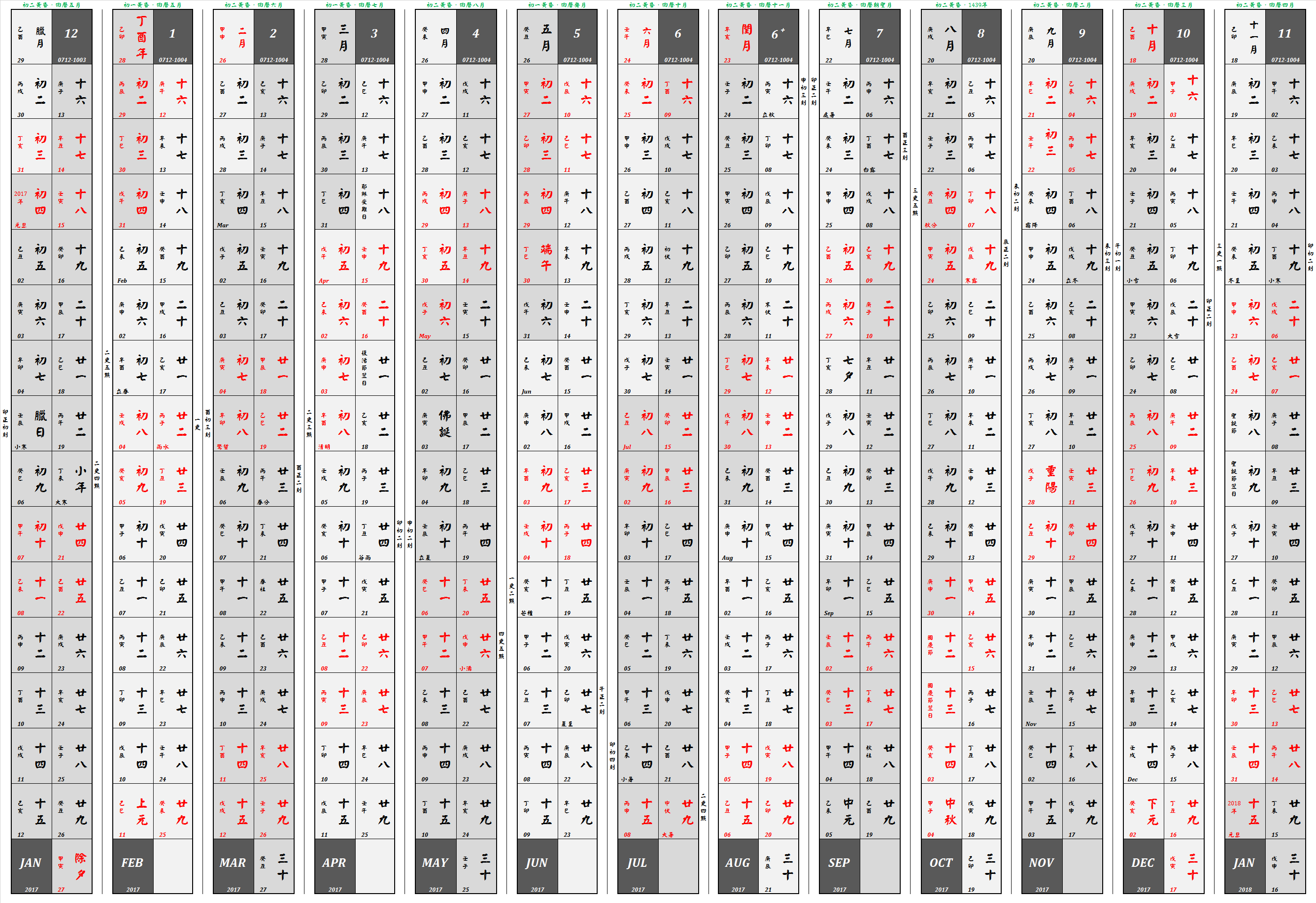
Chinese Calendar
The traditional Chinese calendar, dating back to the Han dynasty, is a lunisolar calendar that blends solar, lunar, and other cycles for social and agricultural purposes. While modern China primarily uses the Gregorian calendar for official purposes, the traditional calendar remains culturally significant. It determines the timing of Chinese New Year with traditions like the twelve animals of the Chinese zodiac, Chinese Zodiac still widely observed. The traditional Chinese calendar uses the Sexagenary cycle, sexagenary cycle, a repeating system of Heavenly Stems and Earthly Branches, to mark years, months, and days. This system, along with astronomical observations and mathematical calculations, was developed to align solar and lunar cycles, though some approximations are necessary due to the natural differences between these cycles. Over centuries, the calendar was refined through advancements in astronomy and horology, with dynasties introducing variations to improve accu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Solar Term
A solar term (or ''jiéqì'', zh, t=節氣, s=节气) is any of twenty-four periods in traditional Chinese lunisolar calendars that matches a particular astronomical event or signifies some natural phenomenon. The points are spaced 15° apart along the ecliptic and are used by lunisolar calendars to stay synchronized with the seasons, which is crucial for agrarian societies. The solar terms are also used to calculate intercalary months; which month is repeated depends on the position of the sun at the time. According to the '' Book of Documents'', the first determined term was Dongzhi (Winter Solstice) by Dan, the Duke of Zhou, while he was trying to locate the geological center of the Western Zhou dynasty, by measuring the length of the sun's shadow on an ancient type of sundial called (). Then four terms of seasons were set, which were soon evolved as eight terms; not until the Taichu Calendar of 104 BC were all twenty-four solar terms officially included in the Chinese ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Dahan (solar Term)
The traditional Chinese calendar divides a year into 24 solar terms. ''Dàhán'', ''Daikan'', ''Daehan'', or ''Đại hàn'' () is the 24th solar term. It begins when the Sun reaches the celestial longitude of 300° and ends when it reaches the longitude of 315°. It more often refers in particular to the day when the Sun is exactly at the celestial longitude of 300°. In the Gregorian calendar The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in October 1582 following the papal bull issued by Pope Gregory XIII, which introduced it as a modification of, and replacement for, the Julian cale ..., it usually begins around 20 January and ends around 4 February. Date and time Customs There are many important folk customs during the period from Dahan to Lichun, such as getting rid of the old and bringing in the new, preserving meat, and the year-end festival. Weiya ( :zh:做牙) is the year-end festival. Glutinous rice, steamed ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Setsubun
is the day before the beginning of spring in the old calendar in Japan. The name literally means 'seasonal division', referring to the day just before the first day of spring in the traditional calendar, known as ; though previously referring to a wider range of possible dates, is now typically held on February 3 (in 2021 and 2025 it was on 2nd February), with the day after – the first day of spring in the old calendar – known as . Both and are celebrated yearly as part of the Spring Festival () in Japan. was accompanied by a number of rituals and traditions held at various levels to drive away the previous year's bad fortunes and evil spirits for the year to come. History has its origins in , a Chinese custom introduced to Japan in the 8th century. It was quite different from the known today. According to the Japanese history book , was first held in Japan in 706, and it was an event to ward off evil spirits held at the court on the last day of the year accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Chinese Zodiac
The Chinese zodiac is a traditional classification scheme based on the Chinese calendar that assigns an animal and its reputed attributes to each year in a repeating twelve-year (or duodenary) cycle. The zodiac is very important in traditional Chinese culture and exists as a reflection of Chinese philosophy and Chinese culture, culture. Chinese folkways held that one's personality is related to the attributes of their zodiac animal. Originating from China, the zodiac and its variations remain popular in many East Asian and Southeast Asian Sovereign state, countries, such as Japan, South Korea, Vietnam, Singapore, Nepal, Bhutan, Cambodia, and Thailand. Identifying this scheme as a "''zodiac''" reflects superficial similarities to the western astrology, Western zodiac: both divide time cycles into twelve parts, label the majority of those parts with animals, and are used to ascribe a person's personality or events in their life to the person's particular relationship to the cycle. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Imbolc
Imbolc or Imbolg (), also called Saint Brigid's Day (; ; ), is a Gaels, Gaelic traditional festival on 1 February. It marks the beginning of Spring (season), spring, and in Christianity, it is the calendar of saints, feast day of Brigid of Kildare, Saint Brigid, Ireland's patroness saint. Historically, its many Folk Catholicism, folk traditions were widely observed throughout Ireland, Scotland and the Isle of Man. Imbolc falls about halfway between the winter solstice and the spring equinox (Northern Hemisphere), spring equinoxMcNeill, F. Marian (1959, 1961) ''The Silver Bough'', Vol. 1–4. William MacLellan, Glasgow; Vol. 2, pp. 11–42 and is one of Quarter days, the four Gaelic seasonal festivals, along with Bealtaine, Lughnasadh and Samhain. Imbolc is mentioned in early Irish literature, although less often than the other seasonal festivals. Historians suggest that Imbolc was originally a pre-Christian (or Ancient Celtic religion, pagan) festival associated with t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |