|
Library Linked Data
Library linked data (LLD) is the use of linked data standards by libraries. These standards are usually applied to bibliographic and authority data sets, with the hope of decreasing redundant cataloging work; and increasing visibility of library resources and interoperability with non-library systems. Use cases In 2010, Byrne and Goddard have written that the "killer ibrary linked dataexample isn't out there yet," and warned that implementation work will be hampered if clear use cases don't exist. Many groups have examined this issue, including the W3C Library Linked Data Incubator Group, the Bibliographic Framework Initiative, and the LD4L project. Conferences * The Hochschulbibliothekszentrum des Landes Nordrhein-Westfalen and the German National Library of Economics sponsor the annual international Semantic Web in Libraries (SWIB) conference See also * BIBFRAME * Resource Description and Access and RDA vocabularies * Universal Bibliographic Control Universal Bibliographic Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linked Data
In computing, linked data is structured data which is interlinked with other data so it becomes more useful through semantic queries. It builds upon standard Web technologies such as HTTP, RDF and URIs, but rather than using them to serve web pages only for human readers, it extends them to share information in a way that can be read automatically by computers. Part of the vision of linked data is for the Internet to become a global database. Tim Berners-Lee, director of the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C), coined the term in a 2006 design note about the Semantic Web project. Linked data may also be open data, in which case it is usually described as Linked Open Data. Principles In his 2006 "Linked Data" note, Tim Berners-Lee outlined four principles of linked data, paraphrased along the following lines: #Uniform Resource Identifiers (URIs) should be used to name and identify individual things. #HTTP URIs should be used to allow these things to be looked up, interpreted, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bibliographic Record
A bibliographic record is an entry in a bibliographic index (or a library catalog) which represents and describes a specific resource. A bibliographic record contains the data elements necessary to help users identify and retrieve that resource, as well as additional supporting information, presented in a formalized bibliographic format. Additional information may support particular database functions such as search, or browse (e.g., by keywords), or may provide fuller presentation of the content item (e.g., the article's abstract). Bibliographic records are usually retrievable from bibliographic indexes (e.g., contemporary bibliographic databases) by author, title, index term, or keyword. Bibliographic records can also be referred to as ''surrogate records'' or metadata. Bibliographic records can represent a wide variety of published contents, including traditional paper, digitized, or born-digital publications. The process of creation, exchange, and preservation of bibliograph ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
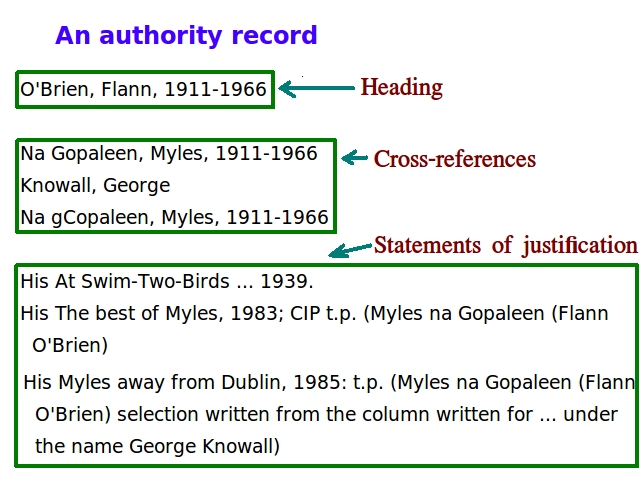
Authority Control
In information science, authority control is a process that organizes information, for example in library catalogs, by using a single, distinct spelling of a name (heading) or an identifier (generally persistent and alphanumeric) for each topic or concept. The word ''authority'' in ''authority control'' derives from the idea that the names of people, places, things, and concepts are ''authorized,'' i.e., they are established in one particular form. Note: root words for both ''author'' and ''authority'' are words such as ''auctor'' or ''autor'' and ''autorite'' from the 13th century. These one-of-a-kind headings or identifiers are applied consistently throughout catalogs which make use of the respective authority file, and are applied for other methods of organizing data such as linkages and cross references. Each controlled entry is described in an authority ''record'' in terms of its scope and usage, and this organization helps the library staff maintain the catalog and make ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
BIBFRAME
BIBFRAME (Bibliographic Framework) is a data model for bibliographic description. BIBFRAME was designed to replace the MARC standards, and to use linked data principles to make bibliographic data more useful both within and outside the library community. History The MARC Standards, which BIBFRAME seeks to replace, were developed by Henriette Avram at the U.S. Library of Congress during the 1960s. By 1971, MARC formats had become the national standard for dissemination of bibliographic data in the United States, and the international standard by 1973. In a provocatively titled 2002 article, library technologist Roy Tennant argued that "MARC Must Die", noting that the standard was old; used only within the library community; and designed to be a display, rather than a storage or retrieval format. A 2008 report from the Library of Congress wrote that MARC is "based on forty-year old techniques for data management and is out of step with programming styles of today." In 2012, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
German National Library Of Economics
The National Library of Economics (, "ZBW – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics", formerly: ''Deutsche Zentralbibliothek für Wirtschaftswissenschaften'') is the world's largest research infrastructure for economic literature, online as well as offline. The ZBW is a member of the Leibniz Association and has been a foundation under public law since 2007. Several times the ZBW received the international LIBER Award for its innovative work in librarianship. The ZBW allows for access of millions of documents and research on economics, partnering with over 40 research institutions to create a connective Open Access portal and social web of research. Through its EconStor and EconBiz, researchers and students have accessed millions of datasets and thousands of articles. The ZBW also edits two journals: '' Wirtschaftsdienst'' and '' Intereconomics''. History The German National Library of Economics – Leibniz Information Centre for Economics (ZBW) was founded on 1 February 19 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource Description And Access
Resource Description and Access (RDA) is a standard for descriptive cataloging initially released in June 2010, providing instructions and guidelines on formulating bibliographic data. Intended for use by libraries and other cultural organizations such as museums and archives, RDA is the successor to ''Anglo-American Cataloguing Rules, Second Edition'' (AACR2). Background RDA emerged from the International Conference on the Principles & Future Development of AACR held in Toronto in 1997. It is published jointly by the American Library Association, the Canadian Federation of Library Associations, and the Chartered Institute of Library and Information Professionals (CILIP) in the United Kingdom. Maintenance of RDA is the responsibility of the RDA Steering Committee (RSC). As of 2015, RSC is undergoing a transition to an international governance structure, expected to be in place in 2019. RDA instructions and guidelines are available through RDA Toolkit, an online subscription serv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Universal Bibliographic Control
Universal Bibliographic Control (UBC) was a concept championed by the International Federation of Library Associations and Institutions (IFLA). Under the theoretical UBC, any document would only be cataloged once in its country of origin, and that record would then be available for the use of any library in the world. Current UBC practice is developed by IFLA's Bibliography Section. During the 1970s, IFLA established an office for Universal Bibliographic Control. Dunsire, Hillman, Phipps, and Willer have suggested that Semantic Web technologies, including BIBFRAME BIBFRAME (Bibliographic Framework) is a data model for bibliographic description. BIBFRAME was designed to replace the MARC standards, and to use linked data principles to make bibliographic data more useful both within and outside the library c ... may allow UBC. See also * * * * * References {{library-stub Library cataloging and classification Library cooperation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Library Cataloging And Classification
A library is a collection of books, and possibly other materials and media, that is accessible for use by its members and members of allied institutions. Libraries provide physical (hard copies) or digital (soft copies) materials, and may be a physical location, a virtual space, or both. A library's collection normally includes printed materials which may be borrowed, and usually also includes a reference section of publications which may only be utilized inside the premises. Resources such as commercial releases of films, television programmes, other video recordings, radio, music and audio recordings may be available in many formats. These include DVDs, Blu-rays, CDs, cassettes, or other applicable formats such as microform. They may also provide access to information, music or other content held on bibliographic databases. In addition, some libraries offer creation stations for makers which offer access to a 3D printing station with a 3D scanner. Libraries can vary wid ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metadata
Metadata (or metainformation) is "data that provides information about other data", but not the content of the data itself, such as the text of a message or the image itself. There are many distinct types of metadata, including: * Descriptive metadata – the descriptive information about a resource. It is used for discovery and identification. It includes elements such as title, abstract, author, and keywords. * Structural metadata – metadata about containers of data and indicates how compound objects are put together, for example, how pages are ordered to form chapters. It describes the types, versions, relationships, and other characteristics of digital materials. * Administrative metadata – the information to help manage a resource, like resource type, and permissions, and when and how it was created. * Reference metadata – the information about the contents and quality of Statistical data type, statistical data. * Statistical metadata – also called process data, may ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Semantic Web
The Semantic Web, sometimes known as Web 3.0, is an extension of the World Wide Web through standards set by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The goal of the Semantic Web is to make Internet data machine-readable. To enable the encoding of semantics with the data, technologies such as Resource Description Framework (RDF) and Web Ontology Language (OWL) are used. These technologies are used to formally represent metadata. For example, Ontology (information science), ontology can describe concepts, relationships between Entity–relationship model, entities, and categories of things. These embedded semantics offer significant advantages such as reasoning engine, reasoning over data and operating with heterogeneous data sources. These standards promote common data formats and exchange protocols on the Web, fundamentally the RDF. According to the W3C, "The Semantic Web provides a common framework that allows data to be shared and reused across application, enterprise, and commu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |