|
Leísmo
''Leísmo'' ("using ''le''") is a dialectal variation in the Spanish language that occurs largely in Spain. It involves using the indirect object pronouns ''le'' and ''les'' in place of the (generally standard) direct object pronouns ''lo'', ''la'', ''los'', and ''las'', especially when the direct object refers to a male person or people. ''Leísmo'' with animate objects is both common and prescriptively accepted in many dialects spoken in Spain, but uncommon in most others. It thus typically correlates with the use of the preposition ''a'' for animate direct objects (for this "personal a", see Spanish prepositions). ''Leísmo'' is always rejected in linguistic prescription when the direct object to which it refers is not an animate object. For example: :' ("I see the boy") → ''Lo veo'' (standard Spanish, with ''lo'') :' ("I see the boy") → ''Le veo'' (''leísmo'', common in Spain; other regions prefer ''lo veo'') :' ("I see the tree") → ''Le veo'' (not accepted in ling ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Loísmo
''Loísmo'', with its feminine counterpart ''laísmo'', is a feature of certain dialects of Spanish consisting of the use of the pronouns ', ', ', and ' (which are normally used for direct objects) in place of the pronouns ''le'' and ''les'' (which are used for indirect objects). ''Loísmo'' and ''laísmo'' are almost entirely restricted to some dialects in central Spain; they are virtually absent from formal and written language. In practice ''laísmo'' is much more frequent than ''loísmo''. A simple example would be saying ''lo hablé'' (lit. "I spoke him"), ''la hablé'' (lit. "I spoke her"), ''los hablé'' (lit. "I spoke them asculine), or ''las hablé'' (lit. "I spoke them eminine) where a speaker of a dialect without ''loísmo'' would say ''le(s) hablé'' ("I spoke to him/her/them"). This effectively means the loss of a declensional case marker. The difference between ''lo'' (accusative case) and ''le'' (dative case) are holdovers from Latin declension. The general trend ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
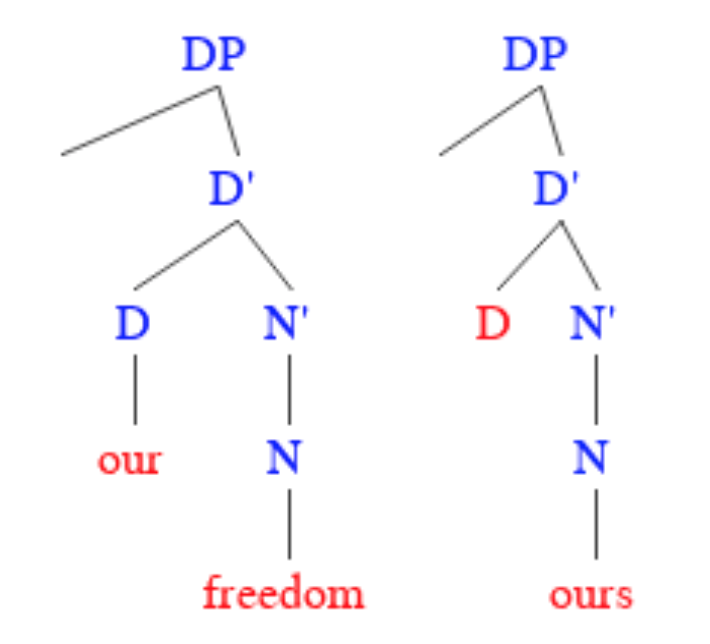
Spanish Object Pronouns
Spanish object pronouns are Spanish personal pronouns that take the function of the object in the sentence. Object pronouns may be both clitic and non-clitic, with non-clitic forms carrying greater emphasis. When used as clitics, object pronouns are generally proclitic, i.e. they appear before the verb of which they are the object; enclitic pronouns (i.e. pronouns attached to the end of the verb) appear with positive imperatives, infinitives, and gerunds. Non-clitic forms, by contrast, can appear anywhere in the sentence but can rarely be used without their clitic counterparts. When used together, clitic pronouns cluster in specific orders based primarily on person, and clitic doubling is often found as well. In many dialects in Central Spain, including that of Madrid, there exists the phenomenon of ''leísmo'', which is using the indirect object pronoun ''le'' as the direct object pronoun where most other dialects would use ''lo'' (masculine) or ''la'' (feminine). History As ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Language
Spanish ( or , Castilian) is a Romance languages, Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from colloquial Latin spoken on the Iberian peninsula. Today, it is a world language, global language with more than 500 million native speakers, mainly in the Americas and Spain. Spanish is the official language of List of countries where Spanish is an official language, 20 countries. It is the world's list of languages by number of native speakers, second-most spoken native language after Mandarin Chinese; the world's list of languages by total number of speakers, fourth-most spoken language overall after English language, English, Mandarin Chinese, and Hindustani language, Hindustani (Hindi-Urdu); and the world's most widely spoken Romance languages, Romance language. The largest population of native speakers is in Mexico. Spanish is part of the Iberian Romance languages, Ibero-Romance group of languages, which evolved from several dialects of Vulgar Latin in I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Object (grammar)
In linguistics, an object is any of several types of arguments. In subject-prominent, nominative-accusative languages such as English, a transitive verb typically distinguishes between its subject and any of its objects, which can include but are not limited to direct objects, indirect objects, and arguments of adpositions ( prepositions or postpositions); the latter are more accurately termed ''oblique arguments'', thus including other arguments not covered by core grammatical roles, such as those governed by case morphology (as in languages such as Latin) or relational nouns (as is typical for members of the Mesoamerican Linguistic Area). In ergative-absolutive languages, for example most Australian Aboriginal languages, the term "subject" is ambiguous, and thus the term " agent" is often used instead to contrast with "object", such that basic word order is often spoken of in terms such as Agent-Object-Verb (AOV) instead of Subject-Object-Verb (SOV). Topic-prominent l ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pronouns
In linguistics and grammar, a pronoun (abbreviated ) is a word or a group of words that one may substitute for a noun or noun phrase. Pronouns have traditionally been regarded as one of the parts of speech, but some modern theorists would not consider them to form a single class, in view of the variety of functions they perform cross-linguistically. An example of a pronoun is "you", which can be either singular or plural. Subtypes include personal and possessive pronouns, reflexive and reciprocal pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, relative and interrogative pronouns, and indefinite pronouns. The use of pronouns often involves anaphora, where the meaning of the pronoun is dependent on an antecedent. For example, in the sentence ''That poor man looks as if he needs a new coat'', the meaning of the pronoun ''he'' is dependent on its antecedent, ''that poor man''. The name of the adjective that belongs with a "pronoun" is called a "pronominal". A pronominal is also a word or phras ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Linguistic Prescription
Linguistic prescription, or prescriptive grammar, is the establishment of rules defining preferred usage of language. These rules may address such linguistic aspects as spelling, pronunciation, vocabulary, syntax, and semantics. Sometimes informed by linguistic purism, such normative practices often suggest that some usages are incorrect, inconsistent, illogical, lack communicative effect, or are of low aesthetic value, even in cases where such usage is more common than the prescribed usage. They may also include judgments on socially proper and politically correct language use. Linguistic prescriptivism may aim to establish a standard language, teach what a particular society or sector of a society perceives as a correct or proper form, or advise on effective and stylistically felicitous communication. If usage preferences are conservative, prescription might appear resistant to language change; if radical, it may produce neologisms. Prescriptive approaches to language ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spanish Prepositions
Prepositions in the Spanish language, like those in other languages, are a set of connecting words (such as ''con'', ''de'' or ''para'') that serve to indicate a relationship between a content word (noun, verb, or adjective) and a following noun phrase (or noun, or pronoun), which is known as the object of the preposition. The relationship is typically spatial or temporal, but prepositions express other relationships as well. As implied by the name, Spanish "prepositions" (like those of English) are positioned ''before'' their objects. Spanish does not place these function words ''after'' their objects, which would be postpositions. Spanish prepositions can be classified as either "simple", consisting of a single word, or "compound", consisting of two or three words. The prepositions of Spanish form a closed class and so they are a limited set to which new items are rarely added. Many Spanish school pupils memorize the following list: ''a, ante, bajo, cabe, con, contra, de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Epicene
Epicenity is the lack of gender distinction, often reducing the emphasis on the masculine to allow the feminine. It includes androgyny – having both masculine and feminine characteristics. The adjective ''gender-neutral'' may describe epicenity (and both terms are associated with the terms '' gender-neutral language'', '' gender-neutral pronoun'', ''gender-blind'', and ''unisex''). Specialized uses In linguistics, an ''epicene'' word has the same form for male and for female referents. In some cases, the term ''common gender'' is also used, but should not be confused with ''common'' or ''appellative'' as a contrary to ''proper'' (as in proper noun). In English, for example, the epicene (or common) nouns ''cousin'' and ''violinist'' can refer to a man or a woman, and so can the epicene (or common) pronoun ''one''. The noun ''stewardess'' and the third-person singular pronouns ''he'' and ''she'' on the other hand are not epicene (or common). [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Real Academia Española
The Royal Spanish Academy ( es, Real Academia Española, generally abbreviated as RAE) is Spain's official royal institution with a mission to ensure the stability of the Spanish language. It is based in Madrid, Spain, and is affiliated with national language academies in 22 other Hispanophone nations through the Association of Academies of the Spanish Language. The RAE's emblem is a fiery crucible, and its motto is ("It purifies, it fixes, and it dignifies"). The RAE dedicates itself to language planning by applying linguistic prescription aimed at promoting linguistic unity within and between various territories, to ensure a common standard. The proposed language guidelines are shown in a number of works. History The Royal Spanish Academy was founded in 1713, modeled after the Accademia della Crusca (1582), of Italy, and the Académie Française (1635), of France, with the purpose "to fix the voices and vocabularies of the Spanish language with propriety, elegance ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Benito Jerónimo Feijóo Y Montenegro
Friar Benito Jerónimo Feijóo y Montenegro (; 8 October 167626 September 1764) was a Spanish monk and scholar who led the Age of Enlightenment in Spain. He was an energetic popularizer noted for encouraging scientific and empirical thought in an effort to debunk myths and superstitions. Biography He joined the Benedictine order at the age of 14, and had taken classes in Galicia, León, and Salamanca. He later taught theology and philosophy at the University, where he earned a professorship in theology. He was appalled by the superstition and ignorance of his time, and his works aimed at combating the situation. His fame spread quickly throughout Europe. His revelations excited considerable opposition in certain quarters in Spain, for example from Salvador José Mañer and others; but the opposition was futile, and Feijóo's services to the cause of education and knowledge were universally recognized long before his death in Oviedo. A century later Alberto Lista said that a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |