|
Lesser Poland Dialect Group
The Lesser Polish dialect group () is a of dialect group of the Polish language used in Lesser Poland. The exact area is difficult to delineate due to the expansion of its features and the existence of transitional subdialects. The common traits of the Lesser Polish dialect include: *mazurzenie * regressive voicing of obstruents, including across word boundaries; e.g.: ''kot leci'' ɔd ˈlɛt͡ɕi(standard Polish: ɔt ˈlɛt͡ɕi * differentiated nasalisation (or lack thereof) of /ɔ̃/ and /ɛ̃/ in different parts of the area * merger of stop+fricative consonant clusters into affricates; e.g.: ''trzysta'' �t͡ʂɨsta(standard Polish: �tʂɨstaor �t͡ʂʂɨsta * frequent usage of initial syllable stress, also oxytonic stress in vocative case (as opposed to paroxytonic stress common in other varieties of Polish) * frequent usage of grammatical particle "że" in imperative mood ("weźże" vs. "weź" – take) List of dialects Descended from the language of the Vistulans ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, , is a country in Central Europe. Poland is divided into Voivodeships of Poland, sixteen voivodeships and is the fifth most populous member state of the European Union (EU), with over 38 million people, and the List of European countries by area, seventh largest EU country, covering a combined area of . It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordering seven countries. The territory is characterised by a varied landscape, diverse ecosystems, and Temperate climate, temperate transitional climate. The capital and List of cities and towns in Poland, largest city is Warsaw; other major cities include Kraków, Wrocław, Łódź, Poznań, and Gdańsk. Prehistory and protohistory of Poland, Humans have been present on Polish soil since the Lower Paleolithic, with continuous settlement since the end of the Last Glacial Period over 12,000 years ago. Culturally diverse throughout ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dialects Of The Polish Language
Polish dialects are regional vernacular varieties of the Polish language. Four major dialect groups are typically recognized, each primarily associated with a particular geographical region, and often further subdivided into subdialectal groups (termed ''gwara'' in Polish).Roland Sussex and Paul Cubberley (2006). ''The Slavic Languages''. Cambridge University Press. P. 530.Robert A. Rothstein (1994). "Polish". ''The Slavonic Languages'', edited by Bernard Comrie and Greville G. Corbett. Routledge. Pp. 754–756. They are: * Greater Polish, spoken in the west * Lesser Polish, spoken in the south and southeast * Masovian, spoken throughout the central and eastern parts of the country * Silesian spoken in the southwest (sometimes also considered a separate language, see comment below) The regional differences correspond mainly to old ethnic or tribal divisions from around a thousand years ago. As a result of 19th century measures taken by occupying powers, of expulsions plus o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
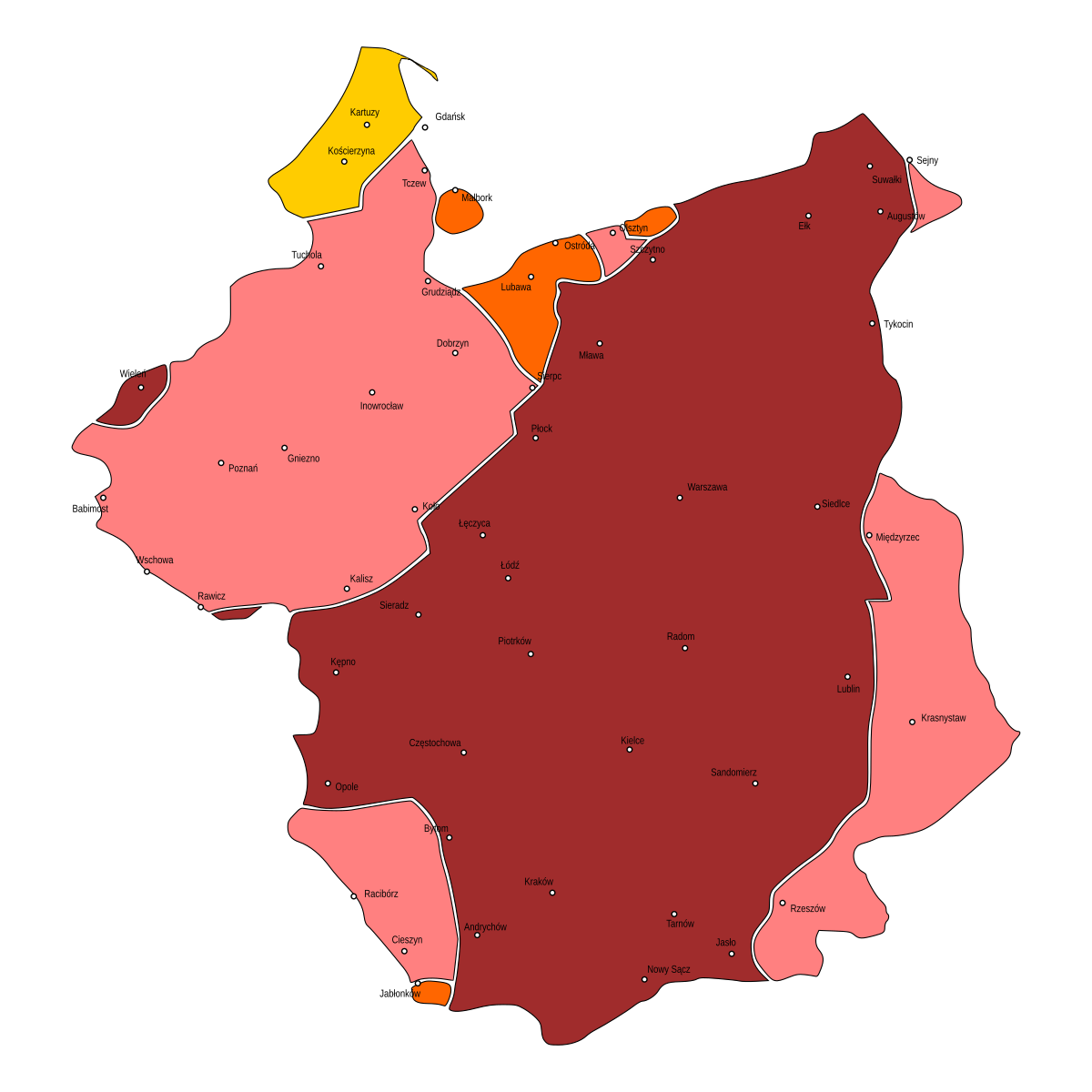
Sieradz Dialect
The Sieradz dialect () belongs to the Lesser Poland dialect group and is located in the part of Poland. It borders the Łęczyca dialect to the north, the Krakow dialect to the south, the Łęczyca dialect to the east, the Central Greater Polish dialect to the northeast, and the Eastern Greater Polish dialect to the farn northeast. The classification of the Łęczyca and Sieradz subdialects is often debated; some classify them as Lesser Polish, whereas others classify them as belonging to Greater Polish. Łęczyca and Sieradz have even been considered as one group due to the large number of similarities. This unclear categorization is the result of the land being placed under control of various administrative territories throughout history, resulting in a transitional dialect between Greater Polish, Lesser Polish, and Masovian. Furthermore, many dialectal traits of the region are fading, and Standard Polish is becoming more prevalent. Phonology Tautosyllabic -aj often shifts to -e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Łęczyca Dialect
The Łęczyca dialect () belongs to the Lesser Poland dialect group and is located in the part of Poland. It borders the Sieradz dialect to the southeast, the Kielce dialect to the southwest, the Masovian Borderland dialect to the east, the Eastern Greater Polish dialect to the northeast, and the Kujawy dialect to the far northeast. Łęczyca, along with Sieradz, occupy central Poland, which greatly affects them. The classification of the Łęczyca and Sieradz subdialects is often debated; some have classified them as Lesser Polish, whereas others as belonging to Greater Polish. Łęczyca and Sieradz have even been considered as one group due to the large number of similarities by Eugeniusz Pawłowski and others. This unclear categorization is the result of the land being placed under control of various administrative territories throughout history, resulting in a transitional dialect between Greater Polish, Lesser Polish, and Masovian. Furthermore, many dialectal traits of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vistulans
The Vistulans, or Vistulanians ( pl, Wiślanie), were an early medieval Lechitic tribe inhabiting the western part of modern Lesser Poland."The main tribe inhabiting the reaches of the Upper Vistula and its tributaries was the Vislane (Wislanie) who, by the mid-ninth century were considered by the neighbouring Moravians as "very powerful" The expansionist policy of the Christian Moravian state led to eventual conflict with the pogan Vislane. ending in the defeat of the latter and their annexation to the Great Moravian Empire between Ad 875-879" . n:''Trade and urban development in Poland: an economic geography of Cracow''. Francis W. Carter. P. 46. 1994 op. cit. L. Hajdukiewicz and M. Karaś. ''The Jagiellonian University: Traditions, The Present, The Future''. Cracow. 1978, p. 17. Etymology Their name derives from the hydronym of the river Vistula, meaning "inhabitants of Vistula"; the region is mentioned as ''Uuislane'' by the Bavarian Geographer, ''v Vislè'' and ''v Vislèh' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imperative Mood
The imperative mood is a grammatical mood that forms a command or request. The imperative mood is used to demand or require that an action be performed. It is usually found only in the present tense, second person. To form the imperative mood, use the base form of the verb. They are sometimes called ''directives'', as they include a feature that encodes directive force, and another feature that encodes modality of unrealized interpretation. An example of a verb used in the imperative mood is the English phrase "Go." Such imperatives imply a second-person subject (''you''), but some other languages also have first- and third-person imperatives, with the meaning of "let's (do something)" or "let them (do something)" (the forms may alternatively be called cohortative and jussive). Imperative mood can be denoted by the glossing abbreviation . It is one of the irrealis moods. Formation Imperative mood is often expressed using special conjugated verb forms. Like other fini ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Grammatical Particle
In grammar, the term ''particle'' (abbreviated ) has a traditional meaning, as a part of speech that cannot be inflected, and a modern meaning, as a function word associated with another word or phrase, generally in order to impart meaning. Although a particle may have an intrinsic meaning, and indeed may fit into other grammatical categories, the fundamental idea of the particle is to add context to the sentence, expressing a mood or indicating a specific action. In English, for instance, the phrase "oh well" has no purpose in speech other than to convey a mood. The word 'up' would be a particle in the phrase to 'look up' (as in the phrase ''"''look up this topic''"''), implying that one researches something, rather than literally gazing skywards. Many languages use particles, in varying amounts and for varying reasons. In Hindi, for instance, they may be used as honorifics, or to indicate emphasis or negation. In some languages they are more clearly defined, such as Chinese, whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paroxytone
Paroxytone ( el, παροξύτονος, ') is a linguistic term for a word with stress on the penultimate syllable, that is, the second last syllable, such as the English word ''potáto'', and just about all words ending in –ic such as músic, frántic, and phonétic; except for rhétoric, aríthmetic (noun) and Árabic. In Italian and Portuguese, most words have paroxytonic stress. In Polish, almost all words have paroxytonic stress, except for certain verb conjugations and a few words of foreign origin. In medieval Latin lyric poetry, a ''paroxytonic'' line or half-line is one in which the penultimate syllable is stressed, as in the second half of the verse "Estuans intrinsecus , , ira vehementi." Related terms are proparoxytone (stress on the third last syllable) and oxytone (accented on the last syllable). See also *Barytone *Oxytone *Penult * Perispomenon * Preantepenult *Proparoxytone In linguistics, a proparoxytone ( el, προπαροξύτονος, ) is a wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vocative Case
In grammar, the vocative case ( abbreviated ) is a grammatical case which is used for a noun that identifies a person (animal, object, etc.) being addressed, or occasionally for the noun modifiers ( determiners, adjectives, participles, and numerals) of that noun; the comma that should be applied in such a context is referred to as a vocative comma. The usage of vocative case in the English language (and many others where commas are used) necessitates a comma to help clarify the writer's intent; failure to strictly adhere to this rule can lead to confusion over the writer's intent. A vocative expression is an expression of direct address by which the identity of the party spoken to is set forth expressly within a sentence. For example, in the sentence "I don't know, John," ''John'' is a vocative expression that indicates the party being addressed, as opposed to the sentence "I don't know John" in which "John" is the direct object of the verb "know". In simple terms, the first ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oxytone
An oxytone (; from the grc, ὀξύτονος, ', 'sharp-sounding') is a word with the stress on the last syllable, such as the English words ''correct'' and ''reward''. (A paroxytone is stressed on the penultimate (second-last) syllable. A proparoxytone is stressed on the antepenultimate (third-last) syllable.) See also *Barytone * Paroxytone * Penult * Perispomenon * Preantepenult *Proparoxytone * Properispomenon *Ultima (linguistics) In linguistics, the ultima is the last syllable of a word, the penult is the next-to-last syllable, and the antepenult is third-from-last syllable. In a word of three syllables, the names of the syllables are antepenult-penult-ultima. Etymology ... * Stress (linguistics) Phonology Ancient Greek Stress (linguistics) {{phonology-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Affricate Consonant
An affricate is a consonant that begins as a stop and releases as a fricative, generally with the same place of articulation (most often coronal). It is often difficult to decide if a stop and fricative form a single phoneme or a consonant pair. English has two affricate phonemes, and , often spelled ''ch'' and ''j'', respectively. Examples The English sounds spelled "ch" and "j" ( broadly transcribed as and in the IPA), German and Italian ''z'' and Italian ''z'' are typical affricates, and sounds like these are fairly common in the world's languages, as are other affricates with similar sounds, such as those in Polish and Chinese. However, voiced affricates other than are relatively uncommon. For several places of articulation they are not attested at all. Much less common are labiodental affricates, such as in German and Izi, or velar affricates, such as in Tswana (written ''kg'') or in High Alemannic Swiss German dialects. Worldwide, relatively few lang ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nasalisation
In phonetics, nasalization (or nasalisation) is the production of a sound while the velum is lowered, so that some air escapes through the nose during the production of the sound by the mouth. An archetypal nasal sound is . In the International Phonetic Alphabet, nasalization is indicated by printing a tilde diacritic above the symbol for the sound to be nasalized: is the nasalized equivalent of , and is the nasalized equivalent of . A subscript diacritic , called an ogonek or ''nosinė'', is sometimes seen, especially when the vowel bears tone marks that would interfere with the superscript tilde. For example, are more legible in most fonts than . Nasal vowels Many languages have nasal vowels to different degrees, but only a minority of world languages around the world have nasal vowels as contrasting phonemes. That is the case, among others, of French, Portuguese, Hindustani, Nepali, Breton, Gheg Albanian, Hmong, Hokkien, Yoruba, and Cherokee. Those nasal vowels co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |