|
Leopard Cat
The leopard cat (''Prionailurus bengalensis'') is a Felinae, small wild cat native to continental South Asia, South, Southeast Asia, Southeast, and East Asia. Since 2002 it has been listed as Least Concern on the IUCN Red List as it is widely distributed although threatened by habitat loss and hunting in parts of its range. Historically, the leopard cat of continental Asia was considered the same species as the Sunda leopard cat. As of 2017, the latter is recognised as a distinct species, with the Taxonomy (biology), taxonomic name ''Prionailurus javanensis''. Leopard cat subspecies differ widely in fur colour, tail length, skull shape and size of carnassials. Archaeological evidence indicates that the leopard cat was the first cat species domesticated in Neolithic China about 5,000 years ago in Shaanxi province, Shaanxi and Henan Provinces. Characteristics A leopard cat is about the size of a domestic cat, but more slender, with longer legs and well-defined webs between i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Felinae
The small cats or Felinae are a subfamily of Felidae distinguished by their bony hyoids, which let them purr but not roar. Other authors have proposed an alternative definition for this subfamily, as comprising only the living conical-toothed cat genera with two tribes, the Felini and Pantherini, and excluding the extinct sabre-toothed Machairodontinae. Characteristics The members of the Felinae have retractile claws that are protected by at least one cutaneous Lobe (anatomy), lobe. Their larynx is kept close to the base of the skull by an Ossification, ossified hyoid. They can purr owing to the vocal folds being shorter than . The cheetah ''Acinonyx'' does not have cutaneous sheaths for guarding claws. Taxonomy The term 'Felini' was first used in 1817 by Gotthelf Fischer von Waldheim, at the time for all the cat species that had been proposed as belonging to the Genus (biology), genus ''Felis''. In 1917, Reginald Innes Pocock also subordinated the following genera to the Felinae ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Parc Des Félins
Parc des Félins is a zoological park in France dedicated to the breeding and conservation of wild members of the cat family. It is located in the commune of Lumigny-Nesles-Ormeaux in Seine-et-Marne, about southeast of Paris. The park covers an area of . Of the 41 recognized species of felines in the world, the park has 30 different species and subspecies, with a total of 140 cats. The park opened to the public on October 14, 2006. Originally, the majority of the animals came from the Parc d'Aulneau, which was deemed too small to house this many animals. History *1998: The Parc d'Aulneau opens. *2005: The Parc d'Aulneau becomes too small and a new place is sought. *2006: The location of the park is chosen at the height of Fortelle at Nesles in Seine-et-Marne. *2007: The park accommodates a wildcat, two leopard cats, two sand cats, a Siberian tiger, two margays, two oncillas and two rusty-spotted cats. Visiting the park The park's philosophy is to provide for the well-bei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leopard Cat Vertical Pupils Nocturnal Ambush Predator
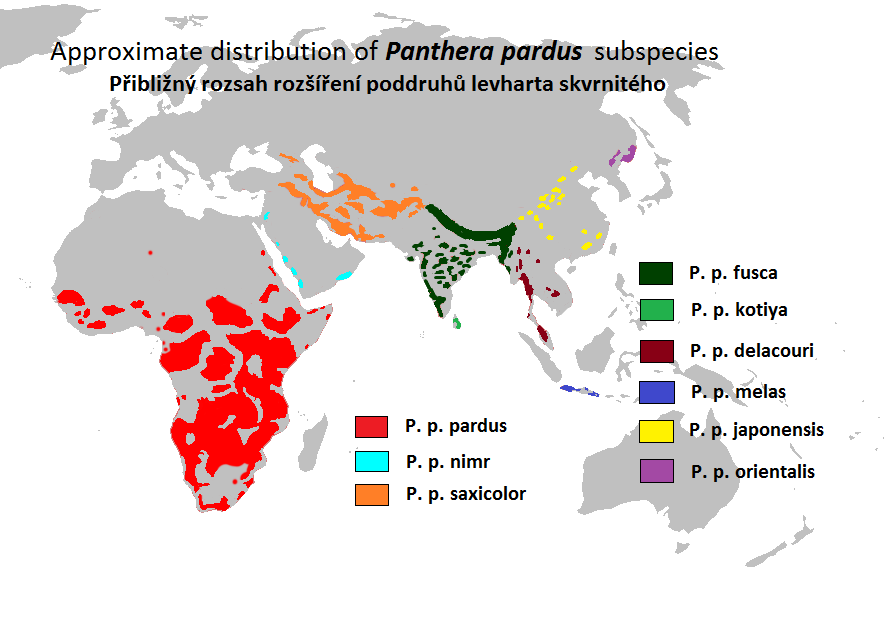
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant cat species in the genus ''Panthera''. It has a pale yellowish to dark golden fur with dark spots grouped in rosettes. Its body is slender and muscular reaching a length of with a long tail and a shoulder height of . Males typically weigh , and females . The leopard was first described in 1758, and several subspecies were proposed in the 19th and 20th centuries. Today, eight subspecies are recognised in its wide range in Africa and Asia. It initially evolved in Africa during the Early Pleistocene, before migrating into Eurasia around the Early–Middle Pleistocene transition. Leopards were formerly present across Europe, but became extinct in the region at around the end of the Late Pleistocene-early Holocene. The leopard is adapted to a variety of habitats ranging from rainforest to steppe, including arid and montane areas. It is an opportunistic predator, hunting mostly ungulates and primates. It relies on its ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Guangdong
) means "wide" or "vast", and has been associated with the region since the creation of Guang Prefecture in AD 226. The name "''Guang''" ultimately came from Guangxin ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t= , s=广信), an outpost established in Han dynasty near modern Wuzhou, whose name is a reference to an order by Emperor Wu of Han to "widely bestow favors and sow trust". Together, Guangdong and Guangxi are called ''Liangguang, Loeng gwong'' ( zh, labels=no, first=t, t=兩廣, s=两广 , p=liǎng guǎng) During the Song dynasty, the Two Guangs were formally separated as ''Guǎngnán Dōnglù'' ( zh, first=t, t=廣南東路, s=广南东路, l=East Circuit (administrative division), Circuit in Southern Guang , labels=no) and ''Guǎngnán Xīlù'' ( zh, first=t, t=廣南西路, s=广南西路, l=West Circuit (administrative division), Circuit in Southern Guang , labels=no), which became abbreviated as ''Guǎngdōng Lù'' ( zh, first=t, t=廣東路, s=广东路 , labels=no) and ''Guǎngxī Lù ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
John Edward Gray
John Edward Gray (12 February 1800 – 7 March 1875) was a British zoologist. He was the elder brother of zoologist George Robert Gray and son of the pharmacologist and botanist Samuel Frederick Gray (1766–1828). The same is used for a zoological name. Gray was keeper of zoology at the British Museum in London from 1840 until Christmas 1874, before the natural history holdings were split off to the Natural History Museum. He published several catalogues of the museum collections that included comprehensive discussions of animal groups and descriptions of new species. He improved the zoological collections to make them amongst the best in the world. Biography Gray was born in Walsall, but his family soon moved to London, where Gray studied medicine. He assisted his father in writing ''The Natural Arrangement of British Plants'' (1821). After being blackballed by the Linnean Society of London, Gray shifted his interest from botany to zoology. He began his zoological ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nicholas Aylward Vigors
Nicholas Aylward Vigors (1785 – 26 October 1840) was an Ireland, Irish zoologist and politician. He popularized the classification of birds on the basis of the quinarian system. Early life Vigors was born at Old Leighlin, County Carlow, in 1785. He was the first son of Capt. Nicholas Aylward Vigors, who served in the 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment of Foot, 29th (Worcestershire) Regiment, and his first wife, Catherine Vigors, daughter of Solomon Richards of Solsborough. He matriculated at Trinity College, Oxford, in November 1803, and was admitted at Lincoln's Inn in November 1806. Without completing his studies, he served in the army during the Peninsular War from 1809 to 1811 and was wounded in the Battle of Barrosa, Battle of Barossa on 5 March 1811. Though he had not yet completed his studies, he still published "An inquiry into the nature and extent of poetick licence" in London in 1810. He then returned to Oxford to continue his studies and achieved his Bachelor of Arts ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Thomas Horsfield
Thomas Horsfield (May 12, 1773 – July 24, 1859) was an American physician and natural history, naturalist who worked extensively in Indonesia, describing numerous species of plants and animals from the region. He was later a curator of the East India Company Museum in London. Early life Horsfield was born in Bethlehem, Pennsylvania, and studied medicine at the University of Pennsylvania. He was the grandson of Timothy Horsfield, Sr. (1708-1773), who was born in Liverpool and emigrated to New York in 1725. The Horsfield family converted from the Church of England to Moravianism, a Protestant denomination with a strong emphasis on education. In 1748, he moved his family to Bethlehem, Pennsylvania and joined them the next year. Horsfield's father was Timothy Horsfield, Jr. and he married Juliana Sarah Parsons in 1738. Thomas Horsfield was born in Bethlehem on May 12, 1773. He was educated at the Moravian schools in Bethlehem and Nazareth, Pennsylvania, Nazareth. He studied medicin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zoological Specimen
A zoological specimen is an animal or part of an animal preserved for scientific use. Various uses are: to verify the identity of a (species), to allow study, increase public knowledge of zoology. Zoological specimens are extremely diverse. Examples are bird and mammal study skins, mounted specimens, skeletal material, casts, pinned insects, dried material, animals preserved in liquid preservatives, and microscope slides. Natural history museums are repositories of zoological specimens Study skins Bird and mammal specimens are conserved as dry study skins, a form of taxidermy. The skin is removed from the animal's carcass, treated with absorbents, and filled with cotton or polyester batting (In the past plant fibres or sawdust were used). Bird specimens have a long, thin, wooden dowel wrapped in batting at their center. The dowel is often intentionally longer than the bird's body and exits at the animal's vent. This exposed dowel provides a place to handle the bird without distu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bengal
Bengal ( ) is a Historical geography, historical geographical, ethnolinguistic and cultural term referring to a region in the Eastern South Asia, eastern part of the Indian subcontinent at the apex of the Bay of Bengal. The region of Bengal proper is divided between the modern-day sovereign nation of Bangladesh and the States and union territories of India, Indian states of West Bengal, and Karimganj district of Assam. The ancient Vanga Kingdom is widely regarded as the namesake of the Bengal region. The Bengali calendar dates back to the reign of Shashanka in the 7th century CE. The Pala Empire was founded in Bengal during the 8th century. The Sena dynasty and Deva dynasty ruled between the 11th and 13th centuries. By the 14th century, Bengal was absorbed by Muslim conquests in the Indian subcontinent. An independent Bengal Sultanate was formed and became the eastern frontier of the Islamic world. During this period, Bengal's rule and influence spread to Assam, Arakan, Tri ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scientific Name
In Taxonomy (biology), taxonomy, binomial nomenclature ("two-term naming system"), also called binary nomenclature, is a formal system of naming species of living things by giving each a name composed of two parts, both of which use Latin grammar, Latin grammatical forms, although they can be based on words from other languages. Such a name is called a binomial name (often shortened to just "binomial"), a binomen, name, or a scientific name; more informally, it is also called a Latin name. In the International Code of Zoological Nomenclature (ICZN), the system is also called nomenclature, with an "n" before the "al" in "binominal", which is a typographic error, meaning "two-name naming system". The first part of the name – the ''generic name (biology), generic name'' – identifies the genus to which the species belongs, whereas the second part – the specific name or specific epithet – distinguishes the species within the genus. For example, modern humans belong to the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tsushima Cat 001
Tsushima may refer to: Places * Tsushima Island, part of Nagasaki Prefecture ** Tsushima, Nagasaki, a city in Nagasaki Prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Province, a historical province, coterminous with modern Tsushima Subprefecture ** Tsushima Subprefecture, an administrative subdivision of Nagasaki prefecture (coterminous with Tsushima Island) ** Tsushima Fuchū Domain, a feudal domain of the early modern period, largely if not entirely contiguous with the Province * Tsushima Basin, also known as Ulleung Basin, located at the juncture of the Sea of Japan and the Korea Strait * Tsushima Strait, the eastern channel of the Korea Strait * Tsushima, Aichi, a city in Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima, Ehime, a town dissolved in August 2005, formerly located in Ehime Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, Aichi Prefecture * Tsushima Shrine, located in the city of Mitoyo, Kagawa Prefecture and only accessible one day a year in early August Events * Battle of Tsushima (1 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |