|
Legal System Of Macau
Macau law is broadly based on law of Portugal, Portuguese law, and therefore part of the civil law (legal system), civil law tradition of continental European legal systems. Portuguese law is itself highly influenced by German law. However, many other influences are present, including Chinese law, Italian law, and some narrow aspects of common law. Macau's legal code is written in Portuguese; therefore law students at University of Macau take their classes in Portuguese. Constitutional law The apex of the legal system is the Basic Law of the Macau SAR, a Chinese law approved in accordance with and due to the Sino-Portuguese Joint Declaration on the Question of Macau (an international treaty that is officially deposited at the UN) and with article 31 of the Constitution of the PRC. Within Macau, the Basic Law has constitutional rank. The Basic Law of Macau is modelled upon the Basic Law of Hong Kong, although it is not totally equal, as it namely is influenced by the Portuguese Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leal Senado Building
The Leal Senado Building was the seat of Portuguese Macau's government ( Legislative Assembly of Macau and Municipal Council of Macau). It is located at one end of the Senado Square in São Lourenço, Macau, China. It currently houses Macau's Municipal Affairs Bureau. Name The title ''Leal Senado'' () was bestowed on Macau's government in 1810 by Portugal's prince regent João, who later became King John VI of Portugal. This was a reward for Macau's loyalty to Portugal, which refused to recognise Spain’s sovereignty during the Philippine Dynasty that it occupied Portugal, between 1580 and 1640. A plaque ordered by the king commemorating this can still be seen inside the entrance hall. History A Chinese-style Pavilion used to stand on the site of Leal Senado building. That building was then a meeting place for the Portuguese and the Chinese officials, and where the Ming dynasty government would announce regulations to Macau. The Portuguese planned to buy the pavilion as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judiciary Of Portugal
The judiciary of Portugal is a system of courts that together constitute one of the four organs of Sovereignty as defined by the Portuguese Constitution. The courts are independent from the other three Portuguese organs of Sovereignty (President of Portugal, President of the Republic, Government of Portugal, Government and Assembly of the Republic (Portugal), Assembly of the Republic). The Portuguese courts are divided by four independent orders, each of which corresponds to the separate Constitutional, Judicial, Administrative and Auditors jurisdictions. The public prosecution and the representation of the State before the courts is assured by an independent body of magistrates, known as Public Ministry. The Ministry of Justice is the Ministry (government department), Government department responsible for the administration of the Judiciary system. Orders of courts The Portuguese judiciary system is not unitary, but it is instead divided in four independent categories or ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
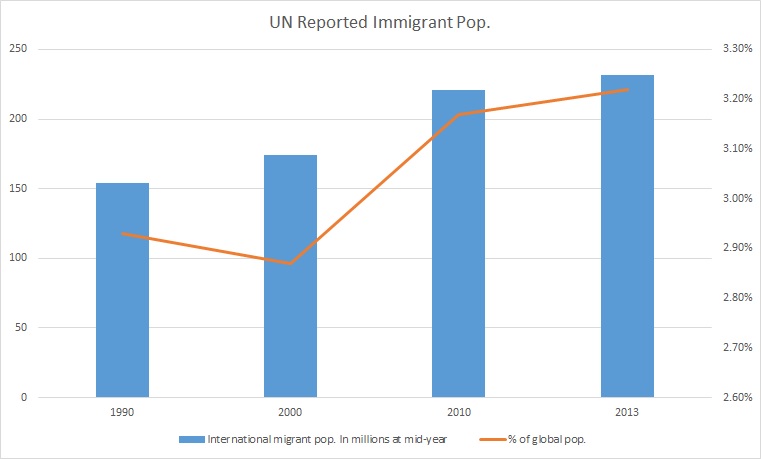
Immigration To Macau
Immigration is the international movement of people to a destination country of which they are not usual residents or where they do not possess nationality in order to settle as permanent residents. Commuters, tourists, and other short-term stays in a destination country do not fall under the definition of immigration or migration; seasonal labour immigration is sometimes included, however. Economically, research suggests that migration can be beneficial both to the receiving and sending countries. The academic literature provides mixed findings for the relationship between immigration and crime worldwide. Research shows that country of origin matters for speed and depth of immigrant assimilation, but that there is considerable assimilation overall for both first- and second-generation immigrants. Discrimination based on nationality is legal in most countries. Extensive evidence of discrimination against foreign-born persons in criminal justice, business, the econo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Code
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property law, property, family law, family, and law of obligations, obligations. A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure. In some jurisdictions with a civil code, a number of the core areas of private law that would otherwise typically be codified in a civil code may instead be codified in a commercial code (law), commercial code. History The history of Codification (law), codification dates back to ancient Babylon. The earliest surviving civil code is the Code of Ur-Nammu, written around 2100–2050 BC. The Corpus Juris Civilis, a codification of Roman law produced between 529 and 534 AD by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor Justinian I, forms the basis of Civil law (legal system), civil law legal systems that would rule over Continental Europe. Other codified laws used since ancient times include various texts used in religious law, such as the Manu Smriti, Law of Manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Law (legal System)
Civil law is a legal system rooted in the Roman Empire and was comprehensively codified and disseminated starting in the 19th century, most notably with France's Napoleonic Code (1804) and Germany's (1900). Unlike common law systems, which rely heavily on judicial precedent, civil law systems are characterized by their reliance on legal codes that function as the primary source of law. Today, civil law is the world's most common legal system, practiced in about 150 countries. The civil law system is often contrasted with the common law system, which originated in medieval England. Whereas the civil law takes the form of legal codes, the common law comes from uncodified case law that arises as a result of judicial decisions, recognising prior court decisions as legally binding precedent. Historically, a civil law is the group of legal ideas and systems ultimately derived from the '' Corpus Juris Civilis'', but heavily overlain by Napoleonic, Germanic, canonical, feuda ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Legal Systems Of The World
The contemporary national legal systems are generally based on one of four major legal traditions: civil law, common law, customary law, religious law or combinations of these. However, the legal system of each country is shaped by its unique history and so incorporates individual variations. The science that studies law at the level of legal systems is called comparative law. Both ''civil'' (also known as ''Roman'') and ''common'' law systems can be considered the most widespread in the world: civil law because it is the most widespread by landmass and by population overall, and common law because it is employed by the greatest number of people compared to any single civil law system. Civil law The source of law that is recognized as authoritative is codifications in a constitution or statute passed by legislature, to amend a code. While the concept of codification dates back to the Code of Hammurabi in Babylon ca. 1790 BC, civil law systems derive from the Roman Empire and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Macau Gaming Law
Gambling in Macau, a special administrative region of China, is the only place in China where casinos are legal. Gambling has been legal since the 1850s when the Portuguese government legalised the activity in the autonomous colony. After the handover of Macau from Portugal to China, Macau and the business has grown at an astounding pace since 2001, when the government ended the four-decade gambling monopoly of the Hong Kong billionaire Stanley Ho. With the entry of large foreign casinos from Las Vegas and Australia, Macau overtook the Las Vegas Strip in gambling revenues in 2007. Since then, Macau has become known worldwide as the "gambling capital of the world", grossing the highest amount of gambling/gaming revenue and greatly dwarfing all the other gambling centers/cities. Gambling tourism is Macau's biggest source of revenue, making up about 50% of the economy. Visitors are largely from mainland China and Hong Kong. History In an attempt to generate revenues fo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Commercial Code (law)
In law, a commercial code is a codification of private law relating to merchants, trade, business entities (especially companies), commercial contracts and other matters such as negotiable instruments. Many civil law legal systems have codifications of commercial law. See also * Civil code * Civil law (legal system) * Commercial law Commercial law (or business law), which is also known by other names such as mercantile law or trade law depending on jurisdiction; is the body of law that applies to the rights, relations, and conduct of Legal person, persons and organizations ... References Civil law (legal system) {{Law-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Civil Code
A civil code is a codification of private law relating to property law, property, family law, family, and law of obligations, obligations. A jurisdiction that has a civil code generally also has a code of civil procedure. In some jurisdictions with a civil code, a number of the core areas of private law that would otherwise typically be codified in a civil code may instead be codified in a commercial code (law), commercial code. History The history of Codification (law), codification dates back to ancient Babylon. The earliest surviving civil code is the Code of Ur-Nammu, written around 2100–2050 BC. The Corpus Juris Civilis, a codification of Roman law produced between 529 and 534 AD by the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor Justinian I, forms the basis of Civil law (legal system), civil law legal systems that would rule over Continental Europe. Other codified laws used since ancient times include various texts used in religious law, such as the Manu Smriti, Law of Manu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Final Appeal Of Macau
The Court of Final Appeal of Macau (; ) is the court with the final adjudication power on laws of Macau. Prior to 1999, the highest court was the Higher Court of Justice of Macau and prior to that the Court of Appeal of the Judiciary District of Lisbon in Portugal. Under the Basic Law of Macau, which is the constitutional document of the region, Macau remains the previous legal jurisdiction. On the other hand, the power of interpretation of the Basic Law itself, being part of the national law, is vested in the Standing Committee of the National People's Congress of China (NPCSC) in accordance with the Basic Law. However, the same Article delegates such power to the courts of Macau for interpretation while handling court cases. Judges As of December 2024, the judges of the court include the following: * Song Man Lei (President) * José Maria Dias Azedo Sam Hou Fai, who has been serving as the President of the Court of Final Appeal of Macau since its establishment, has res ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Reuters
Reuters ( ) is a news agency owned by Thomson Reuters. It employs around 2,500 journalists and 600 photojournalists in about 200 locations worldwide writing in 16 languages. Reuters is one of the largest news agencies in the world. The agency was established in London in 1851 by Paul Reuter. The Thomson Corporation of Canada acquired the agency in a 2008 corporate merger, resulting in the formation of the Thomson Reuters Corporation. In December 2024, Reuters was ranked as the 27th most visited news site in the world, with over 105 million monthly readers. History 19th century Paul Julius Reuter worked at a book-publishing firm in Berlin and was involved in distributing radical pamphlets at the beginning of the Revolutions of 1848. These publications brought much attention to Reuter, who in 1850 developed a prototype news service in Aachen using homing pigeons and electric telegraphy from 1851 on, in order to transmit messages between Brussels and Aachen, in what today is Aa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Court Of Second Instance
A court is an institution, often a government entity, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and administer justice in civil, criminal, and administrative matters in accordance with the rule of law. Courts generally consist of judges or other judicial officers, and are usually established and dissolved through legislation enacted by a legislature. Courts may also be established by constitution or an equivalent constituting instrument. The practical authority given to the court is known as its jurisdiction, which describes the court's power to decide certain kinds of questions, or petitions put to it. There are various kinds of courts, including trial courts, appellate courts, administrative courts, international courts, and tribunals. Description A court is any person or institution, often as a government institution, with the authority to adjudicate legal disputes between parties and carry out the administration of justice in civil, criminal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |