|
Leeuwin Current
The Leeuwin Current is a warm ocean current which flows southwards near the western coast of Australia. It rounds Cape Leeuwin to enter the waters south of Australia where its influence extends as far as Tasmania. Discovery The existence of the current was first suggested by William Saville-Kent in 1897. Saville-Kent noted the presence of warm tropical water offshore in the Houtman Abrolhos, making the water there in winter much warmer than inshore at the adjacent coast. The existence of the current was confirmed over the years, but not characterised and named until Cresswell and Golding did so in the 1980s. Track The West Australian Current and Southern Australian Countercurrent, which are produced by the West Wind Drift on the southern Indian Ocean and at Tasmania, respectively, flow in the opposite direction, producing one of the most interesting oceanic current systems in the world. The ‘core’ of the Leeuwin Current can generally be detected as a peak in the surfac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Leeuwin Current 2
Leeuwin (Dutch for "lioness") may refer to: Places * Leeuwin, Western Australia, a locality in Western Australia * Cape Leeuwin, the most south-westerly point of Australia ** Cape Leeuwin Lighthouse ** Cape Leeuwin water wheel * Leeuwin-Naturaliste National Park, the national park in which Cape Leeuwin is located * Leeuwin Barracks, formerly HMAS ''Leeuwin'' (naval base), a Royal Australian Navy shore base in North Fremantle Ships * ''Leeuwin'' (galleon), Dutch galleon that encountered south-west Australia in 1622 * HMAS ''Leeuwin'' (A 245), a hydrographic survey ship ** ''Leeuwin'' class survey vessel, the class of HMAS ''Leeuwin'' * STS ''Leeuwin II'', a Western Australian sail training ship Other uses * Leeuwin Current, a warm ocean current flowing down the west coast of Australia * Leeuwin triplefin (''Norfolkia leeuwin''), a species of small fish of the family Tripterygiidae * ''Leeuwin'' (journal), a short-lived literary journal published in Western Australia by Wil ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Western Australia
Western Australia (WA) is the westernmost state of Australia. It is bounded by the Indian Ocean to the north and west, the Southern Ocean to the south, the Northern Territory to the north-east, and South Australia to the south-east. Western Australia is Australia's largest state, with a land area of , and is also the List of country subdivisions by area, second-largest subdivision of any country on Earth. Western Australia has a diverse range of climates, including tropical conditions in the Kimberley (Western Australia), Kimberley, deserts in the interior (including the Great Sandy Desert, Little Sandy Desert, Gibson Desert, and Great Victoria Desert) and a Mediterranean climate on the south-west and southern coastal areas. the state has 2.965 million inhabitants—10.9 percent of the national total. Over 90 percent of the state's population live in the South-West Land Division, south-west corner and around 80 percent live in the state capital Perth, leaving the remainder ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Physical Oceanography
Physical oceanography is the study of physical conditions and physical processes within the ocean, especially the motions and physical properties of ocean waters. Physical oceanography is one of several sub-domains into which oceanography is divided. Others include biological, chemical and geological oceanography. Physical oceanography may be subdivided into ''descriptive'' and ''dynamical'' physical oceanography. Descriptive physical oceanography seeks to research the ocean through observations and complex numerical models, which describe the fluid motions as precisely as possible. Dynamical physical oceanography focuses primarily upon the processes that govern the motion of fluids with emphasis upon theoretical research and numerical models. These are part of the large field of Geophysical Fluid Dynamics (GFD) that is shared together with meteorology. GFD is a sub field of Fluid dynamics describing flows occurring on spatial and temporal scales that are greatly influenced ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Oceanic Gyres
In oceanography, a gyre () is any large system of ocean current, ocean surface currents moving in a circular fashion driven by wind movements. Gyres are caused by the Coriolis effect; planetary vorticity, horizontal friction and vertical friction determine the circulatory patterns from the ''wind stress Curl (mathematics), curl'' (torque). ''Gyre'' can refer to any type of vortex in an planetary atmosphere, atmosphere or a Planetary ocean, sea, even one that is human-created, but it is most commonly used in terrestrial oceanography to refer to the major ocean systems. Gyre formation The largest ocean gyres are wind-driven, meaning that their locations and dynamics are controlled by the prevailing Prevailing winds, global wind patterns: Trade winds, easterlies at the tropics and westerlies at the midlatitudes. These wind patterns result in a wind stress curl that drives Ekman transport#Ekman pumping, Ekman pumping in the subtropics (resulting in downwelling) and Ekman transport# ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Ocean Current
An ocean current is a continuous, directed movement of seawater generated by a number of forces acting upon the water, including wind, the Coriolis effect, breaking waves, cabbeling, and temperature and salinity differences. Depth contours, shoreline configurations, and interactions with other currents influence a current's direction and strength. Ocean currents move both horizontally, on scales that can span entire oceans, as well as vertically, with vertical currents (upwelling and downwelling) playing an important role in the movement of nutrients and gases, such as carbon dioxide, between the surface and the deep ocean. Ocean currents flow for great distances and together they create the global conveyor belt, which plays a dominant role in determining the climate of many of Earth's regions. More specifically, ocean currents influence the temperature of the regions through which they travel. For example, warm currents traveling along more temperate coasts increase the temper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Canary Current
The Canary Current is a wind-driven surface current that is part of the North Atlantic Gyre. This eastern boundary current branches south from the North Atlantic Current and flows southwest about as far as Senegal where it turns west and later joins the Atlantic North Equatorial Current. The current is named after the Canary Islands. The archipelago partially blocks the flow of the Canary Current (Gyory, 2007). This wide and slow moving current is thought to have been exploited in the early Phoenician navigation and settlement along the coast of western Morocco and Old Spanish Sahara. The ancient Phoenicians not only exploited numerous fisheries within this current zone, but also established a factory at Iles Purpuraires off present day Essaouira for extracting a Tyrian purple dye from a marine gastropod murex species. The current heavily influences the weather of the Canaries and coastal Morocco and Western Sahara, cooling down shoreline temperatures for much of the year and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
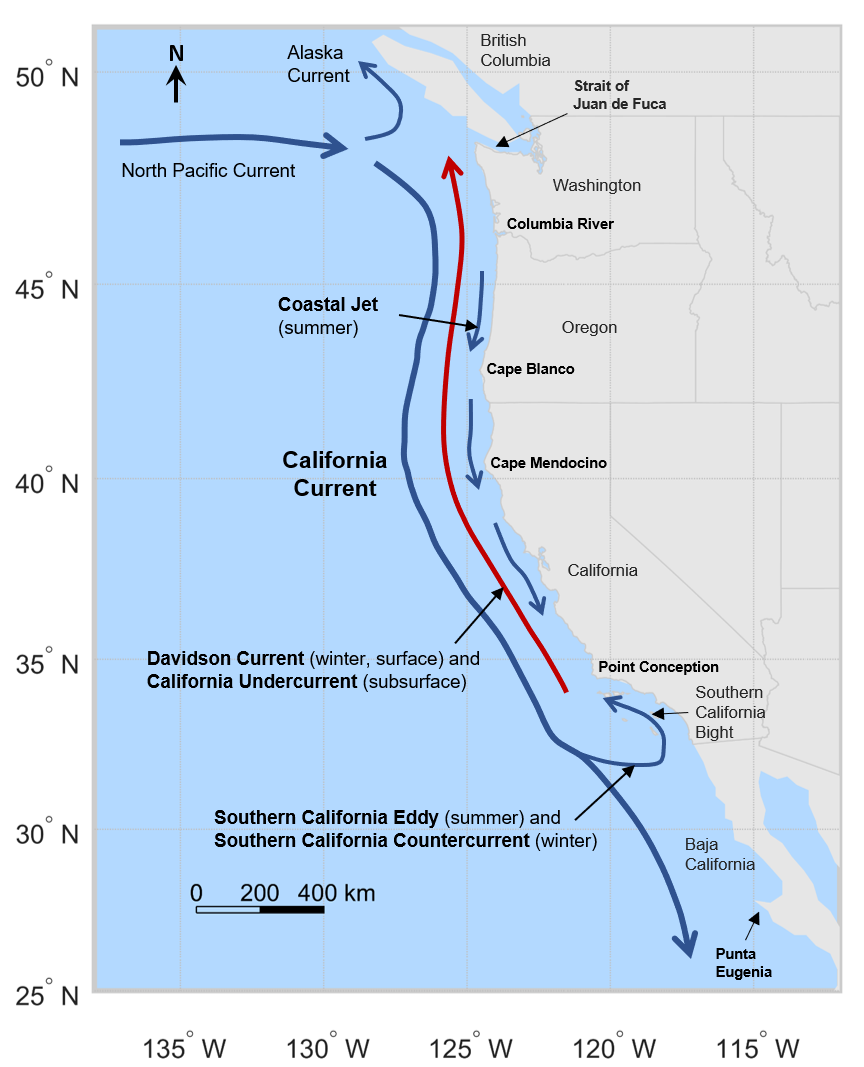
California Current
The California Current () is a cold water Pacific Ocean ocean current, current that moves southward along the western coast of North America, beginning off southern British Columbia and ending off southern Baja California Sur. It is considered an Eastern boundary current due to the influence of the North American coastline on its course. It is also one of six major coastal currents affiliated with strong upwelling zones, the others being the Humboldt Current, the Canary Current, the Benguela Current, the Oyashio Current, and the Somali Current. The California Current is part of the North Pacific Gyre, a large swirling current that occupies the northern basin of the Pacific. The related California Current Conservation Complex is a grouping of federally-designated marine protected areas that have been on the UNESCO list of tentative World Heritage Site, World Heritage Sites since 2017, which includes the following areas found throughout the current: the Point Reyes National Seashore ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Humboldt Current
The Humboldt Current, also called the Peru Current, is a cold, low-salinity ocean current that flows north along the western coast of South America.Montecino, Vivian, and Carina B. Lange. "The Humboldt Current System: Ecosystem components and processes, fisheries, and sediment studies." ''Progress in Oceanography'' 83.1 (2009): 65-79. doi:10.1016/j.pocean.2009.07.041 It is an eastern boundary current flowing in the direction of the equator, and extends offshore. The Humboldt Current is named after the German naturalist Alexander von Humboldt even though it was discovered by José de Acosta 250 years before Humboldt. In 1846, von Humboldt reported measurements of the cold-water current in his book ''Cosmos''. The current extends from southern Chile (~ 45th parallel south) to northern Peru (~ 4th parallel south) where cold, upwelled, waters intersect warm tropical waters to form the Equatorial Front. Sea surface temperatures off the coast of Peru, around 5th parallel south, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Benguela Current
The Benguela Current is the broad, northward flowing ocean current that forms the eastern portion of the South Atlantic Ocean gyre. The current extends from roughly Cape Point in the south, to the position of the Angola-Benguela Front in the north, at around 16°S. The current is driven by the prevailing south easterly trade winds. Inshore of the Benguela Current proper, the south easterly winds drive coastal upwelling, forming the Benguela Upwelling System. The cold, nutrient rich waters that upwell from around depth in turn fuel high rates of phytoplankton growth, and sustain the productive Benguela ecosystem. Boundaries Source waters for the Benguela include cold upwelled waters from the depths of the Atlantic Ocean close inshore, joined further off-shore by nutrient poor water that has crossed the Southern Atlantic from South America as part of South Atlantic Gyre. Eddies from the warm South Indian Ocean Agulhas current along South Africa's east coast come round the Ca ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
El Niño
EL, El or el may refer to: Arts and entertainment Fictional entities * El, a character from the manga series ''Shugo Chara!'' by Peach-Pit * Eleven (''Stranger Things'') (El), a fictional character in the TV series ''Stranger Things'' * El, family name of Kal-El (Superman) and his father Jor-El in the Superman dynasty * E.L. Faldt, character in the road comedy film '' Road Trip'' Music * Él Records, an independent record label from the UK founded by Mike Alway * ''Él ''(Lucerito album), a 1982 album by Lucerito * "Él", Spanish song by Rubén Blades from the album '' Caminando'' * "Él" (Lucía song), the Spanish entry performed by Lucía in the Eurovision Song Contest 1982 Other media * ''Él'', 1926 autobiographical novel by Mercedes Pinto * ''Él'' (film), a 1953 film by Luis Buñuel based on the 1926 novel * ''Él'' (visual novel), a 1991 Japanese adult visual novel * EL TV, an Azerbaijani regional television channel Companies and organizations * Estée Lauder Co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Continental Shelf
A continental shelf is a portion of a continent that is submerged under an area of relatively shallow water, known as a shelf sea. Much of these shelves were exposed by drops in sea level during glacial periods. The shelf surrounding an island is known as an "''insular shelf''." The continental margin, between the continental shelf and the abyssal plain, comprises a steep continental slope, surrounded by the flatter continental rise, in which sediment from the continent above cascades down the slope and accumulates as a pile of sediment at the base of the slope. Extending as far as 500 km (310 mi) from the slope, it consists of thick sediments deposited by turbidity currents from the shelf and slope. The continental rise's gradient is intermediate between the gradients of the slope and the shelf. Under the United Nations Convention on the Law of the Sea, the name continental shelf was given a legal definition as the stretch of the seabed adjacent to the shores ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |