|
Learning-by-doing (economics)
Learning-by-doing is a concept in economic theory by which productivity is achieved through practice, self-perfection and minor innovations. An example is a factory that increases output by learning how to use equipment better without adding workers or investing significant amounts of capital. With roots all the way by to Adam Smith's analysis of pin manufacturing, the quantification of the idea was realised from the manufacturing of B17 Flying Fortress bombers during world war II. For B17's the costs reduced proportionally with the cumulative manufacturing, rather than with ongoing volume. This explains the non-linearity of learning-by-doing cost reduction, as seen for example in semiconductor manufacturing or with solar PV production. The concept of learning-by-doing has been used by Kenneth Arrow in his design of endogenous growth theory to explain effects of innovation and technical change. Robert Lucas, Jr. adopted the concept to explain increasing returns to embodi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Concept
A concept is an abstract idea that serves as a foundation for more concrete principles, thoughts, and beliefs. Concepts play an important role in all aspects of cognition. As such, concepts are studied within such disciplines as linguistics, psychology, and philosophy, and these disciplines are interested in the logical and psychological structure of concepts, and how they are put together to form thoughts and sentences. The study of concepts has served as an important flagship of an emerging interdisciplinary approach, cognitive science. In contemporary philosophy, three understandings of a concept prevail: * mental representations, such that a concept is an entity that exists in the mind (a mental object) * abilities peculiar to cognitive agents (mental states) * Fregean senses, abstract objects rather than a mental object or a mental state Concepts are classified into a hierarchy, higher levels of which are termed "superordinate" and lower levels termed "subordinate". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Economic Theory
Economics () is a behavioral science that studies the production, distribution, and consumption of goods and services. Economics focuses on the behaviour and interactions of economic agents and how economies work. Microeconomics analyses what is viewed as basic elements within economies, including individual agents and markets, their interactions, and the outcomes of interactions. Individual agents may include, for example, households, firms, buyers, and sellers. Macroeconomics analyses economies as systems where production, distribution, consumption, savings, and investment expenditure interact; and the factors of production affecting them, such as: labour, capital, land, and enterprise, inflation, economic growth, and public policies that impact these elements. It also seeks to analyse and describe the global economy. Other broad distinctions within economics include those between positive economics, describing "what is", and normative economics, advo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Productivity
Productivity is the efficiency of production of goods or services expressed by some measure. Measurements of productivity are often expressed as a ratio of an aggregate output to a single input or an aggregate input used in a production process, i.e. output per unit of input, typically over a specific period of time. The most common example is the (aggregate) labour productivity measure, one example of which is GDP per worker. There are many different definitions of productivity (including those that are not defined as ratios of output to input) and the choice among them depends on the purpose of the productivity measurement and data availability. The key source of difference between various productivity measures is also usually related (directly or indirectly) to how the outputs and the inputs are aggregated to obtain such a ratio-type measure of productivity. Productivity is a crucial factor in the production performance of firms and nations. Increasing national productivi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Innovation
Innovation is the practical implementation of ideas that result in the introduction of new goods or service (economics), services or improvement in offering goods or services. ISO TC 279 in the standard ISO 56000:2020 defines innovation as "a new or changed entity, realizing or redistributing value (economics), value". Others have different definitions; a common element in the definitions is a focus on newness, improvement, and spread of ideas or technologies. Innovation often takes place through the development of more-effective product (business), products, processes, Service (economics), services, technologies, art works or business models that innovators make available to Market (economics), markets, governments and society. Innovation is related to, but not the same as, ''invention'': innovation is more apt to involve the practical implementation of an invention (i.e. new / improved ability) to make a meaningful impact in a market or society, and not all innovations requir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kenneth Arrow
Kenneth Joseph Arrow (August 23, 1921 – February 21, 2017) was an American economist, mathematician and political theorist. He received the John Bates Clark Medal in 1957, and the Nobel Memorial Prize in Economic Sciences in 1972, along with John Hicks. In economics, Arrow was a major figure in postwar neoclassical economic theory. Four of his students (Roger Myerson, Eric Maskin, John Harsanyi, and Michael Spence) went on to become Nobel laureates themselves. His contributions to social choice theory, notably his " impossibility theorem", and his work on general equilibrium analysis are significant. His work in many other areas of economics, including endogenous growth theory and the economics of information, was also foundational. Education and early career Arrow was born on August 23, 1921, in New York City. Arrow's mother, Lilian (Greenberg), was from Iași, Romania, and his father, Harry Arrow, was from nearby Podu Iloaiei. The family was of Romanian-Jewish desc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Endogenous Growth Theory
Endogenous growth theory holds that economic growth is primarily the result of endogenous and not external forces. Endogenous growth theory holds that investment in human capital, innovation, and knowledge are significant contributors to economic growth. The theory also focuses on positive externalities and spillover effects of a knowledge-based economy which will lead to economic development. The endogenous growth theory primarily holds that the long run growth rate of an economy depends on policy measures. For example, subsidies for research and development or education increase the growth rate in some endogenous growth models by increasing the incentive for innovation. Models In the mid-1980s, a group of growth theorists became increasingly dissatisfied with common accounts of exogenous factors determining long-run growth, such as the Solow–Swan model. They favored a model that replaced the exogenous growth variable (unexplained technical progress) with a model in whic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Robert Lucas, Jr
The name Robert is an ancient Germanic given name, from Proto-Germanic "fame" and "bright" (''Hrōþiberhtaz''). Compare Old Dutch ''Robrecht'' and Old High German ''Hrodebert'' (a compound of '' Hruod'' () "fame, glory, honour, praise, renown, godlike" and ''berht'' "bright, light, shining"). It is the second most frequently used given name of ancient Germanic origin.Reaney & Wilson, 1997. ''Dictionary of English Surnames''. Oxford University Press. It is also in use as a surname. Another commonly used form of the name is Rupert. After becoming widely used in Continental Europe, the name entered England in its Old French form ''Robert'', where an Old English cognate form (''Hrēodbēorht'', ''Hrodberht'', ''Hrēodbēorð'', ''Hrœdbœrð'', ''Hrœdberð'', ''Hrōðberχtŕ'') had existed before the Norman Conquest. The feminine version is Roberta. The Italian, Portuguese, and Spanish form is Roberto. Robert is also a common name in many Germanic languages, including En ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
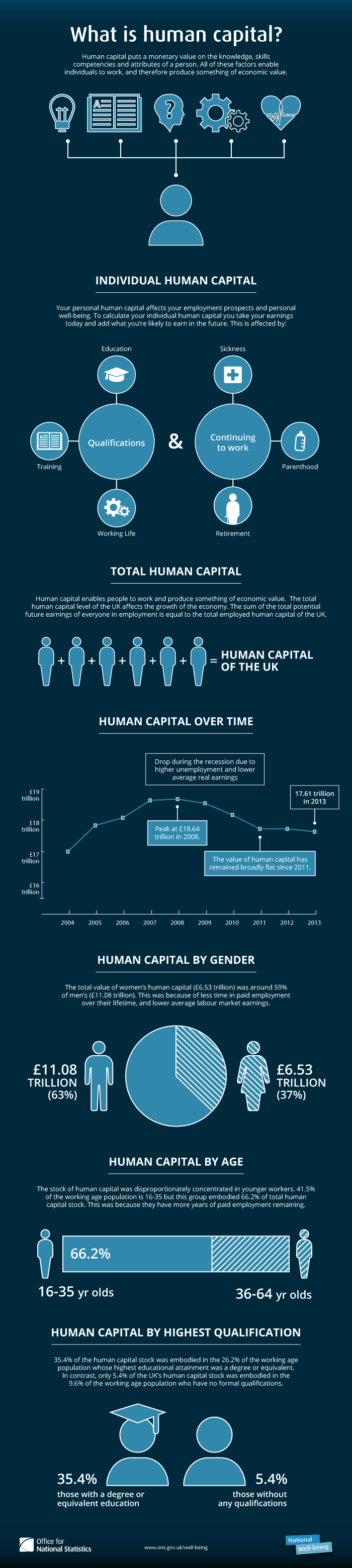
Human Capital
Human capital or human assets is a concept used by economists to designate personal attributes considered useful in the production process. It encompasses employee knowledge, skills, know-how, good health, and education. Human capital has a substantial impact on individual earnings. Research indicates that human capital investments have high economic returns throughout childhood and young adulthood. Companies can invest in human capital; for example, through education and training, improving levels of quality and production. History Adam Smith included in his definition of Capital (economics), capital "the acquired and useful abilities of all the inhabitants or members of the society". The first use of the term "human capital" may be by Irving Fisher. An early discussion with the phrase "human capital" was from Arthur Cecil Pigou: But the term only found widespread use in economics after its popularization by economists of the Chicago School of economics, Chicago School, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Xiaokai Yang
Xiaokai Yang (born as Yang Xiguang; Simplified Chinese: 杨小凯; 6 October 1948 – 7 July 2004) was a Chinese-Australian economist. He was one of the world's pre-eminent theorists in economic analysis, and an influential campaigner for democracy in China. Biography Early life Yang was born in China, the son of Chinese Communist Party officials. His parents' status meant that he initially had a privileged life, receiving an excellent education by Chinese standards at the time. Life under the Maoist government His life changed dramatically in the early days of the Cultural Revolution. Yang was a Red Guard in Hunan who was part of the Rebel faction Shengwulian. On behalf of the group, Yang wrote and published an influential political treatise titled "Whither China?", a scathing critique of Mao Zedong's communist regime from a farther left perspective. Yang contended that the essential conflict in China was between the new " red capitalist class", consisting of CCP cadres ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jeff Borland
Jeff Borland is an Australian academic and labour economist. He is currently the Truby Williams Professor of Economics at the University of Melbourne. He received the 2020 Distinguished Fellow Award from the Economic Society of Australia. He regularly appears in the Australian media on the topic of economics and public policy, and has published research papers on the Australian labour market, among others. Education Borland completed a Bachelor of Arts and Master of Arts at the University of Melbourne, and a PhD in economics from Yale University. He was previously a visiting professor at Harvard University Harvard University is a Private university, private Ivy League research university in Cambridge, Massachusetts, United States. Founded in 1636 and named for its first benefactor, the History of the Puritans in North America, Puritan clergyma ... as well as Head of the Department of Economics and Deputy Dean of the business faculty at University of Melbourne. Publi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Evolutionary Economics
Evolutionary economics is a school of economic thought that is inspired by evolutionary biology. Although not defined by a strict set of principles and uniting various approaches, it treats economic development as a process rather than an equilibrium and emphasizes change (qualitative, organisational, and structural), innovation, complex interdependencies, self-evolving systems, and limited rationality as the drivers of economic evolution. Hodgson, G. M. (2012). ''Evolutionary Economics'', in Fundamental Economics, edited by Mukul Majumdar, Ian Wills, Pasquale Michael Sgro, John M. Gowdy, in Encyclopedia of Life Support Systems (EOLSS), Developed under the Auspices of the UNESCO, EOLSS Publishers, Paris, France fro [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Resource-based View
The resource-based view (RBV), often referred to as the "resource-based view of the firm", is a managerial framework used to determine the strategic resources a firm can exploit to achieve sustainable competitive advantage. Jay Barney's 1991 article "Firm Resources and Sustained Competitive Advantage" is widely cited as a pivotal work in the emergence of the resource-based view, although some scholars (see below) argue that there was evidence for a fragmentary resource-based theory from the 1930s. RBV proposes that firms are heterogeneous because they possess heterogeneous resources, meaning that firms can adopt differing strategies because they have different resource mixes. The RBV focuses managerial attention on the firm's internal resources in an effort to identify those assets, capabilities and competencies with the potential to deliver superior competitive advantages. Origins and background During the 1990s, the ''resource-based view'' (also known as the ''resource-advantage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |