|
Lealt, Skye
Lealt () is a crofting township, on the western coastline of the Sound of Raasay on the Trotternish peninsula of Skye, in the Highlands of Scotland and the council area of Highland. The Lealt River which gives its name to Lealt, passes through on the way to the Sound of Raasay. The name "Lealt" means "Stream with one high bank". References See also * Lealt Valley Diatomite Railway The Lealt Valley Diatomite Railway was a Narrow gauge railway, narrow gauge Tramway (industrial), tramway on the Isle of Skye, Scotland, which ran parallel with the River Lealt. Work was underway to lay the tramway in March 1889. At the openi .... * Populated places in the Isle of Skye {{SkyeLochalsh-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland (council Area)
Highland (, ; ) is a council areas of Scotland, council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in both Scotland and the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census. It has land borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. The wider upland area of the Scottish Highlands after which the council area is named extends beyond the Highland council area into all the neighbouring council areas plus Angus, Scotland, Angus and Stirling (council area), Stirling. The Highland Council is based in Inverness, the area's largest settlement. The area is generally sparsely populated, with much of the inland area being mountainous with numerous lochs. The area includes Ben Nevis, the highest mountain in the British Isles. Most of the area's towns lie close to the eastern coasts. Off the west coast of the mainland the council area includes some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Township
A township is a form of human settlement or administrative subdivision. Its exact definition varies among countries. Although the term is occasionally associated with an urban area, this tends to be an exception to the rule. In Australia, Canada, Scotland, and parts of the United States, the term refers to settlements too small or scattered to be considered urban. Australia '' The Australian National Dictionary'' defines a township as "a site reserved for and laid out as a town; such a site at an early stage of its occupation and development; a small town". The term refers purely to the settlement; it does not refer to a unit of government. Townships are governed as part of a larger council (such as that of a shire, district or city) or authority. Canada In Canada, two kinds of township occur in common use: *In Eastern Canada, a township is one form of the subdivision of a county. In Canadian French, this is a . Townships are referred to as "lots" in Prince Edward Island ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
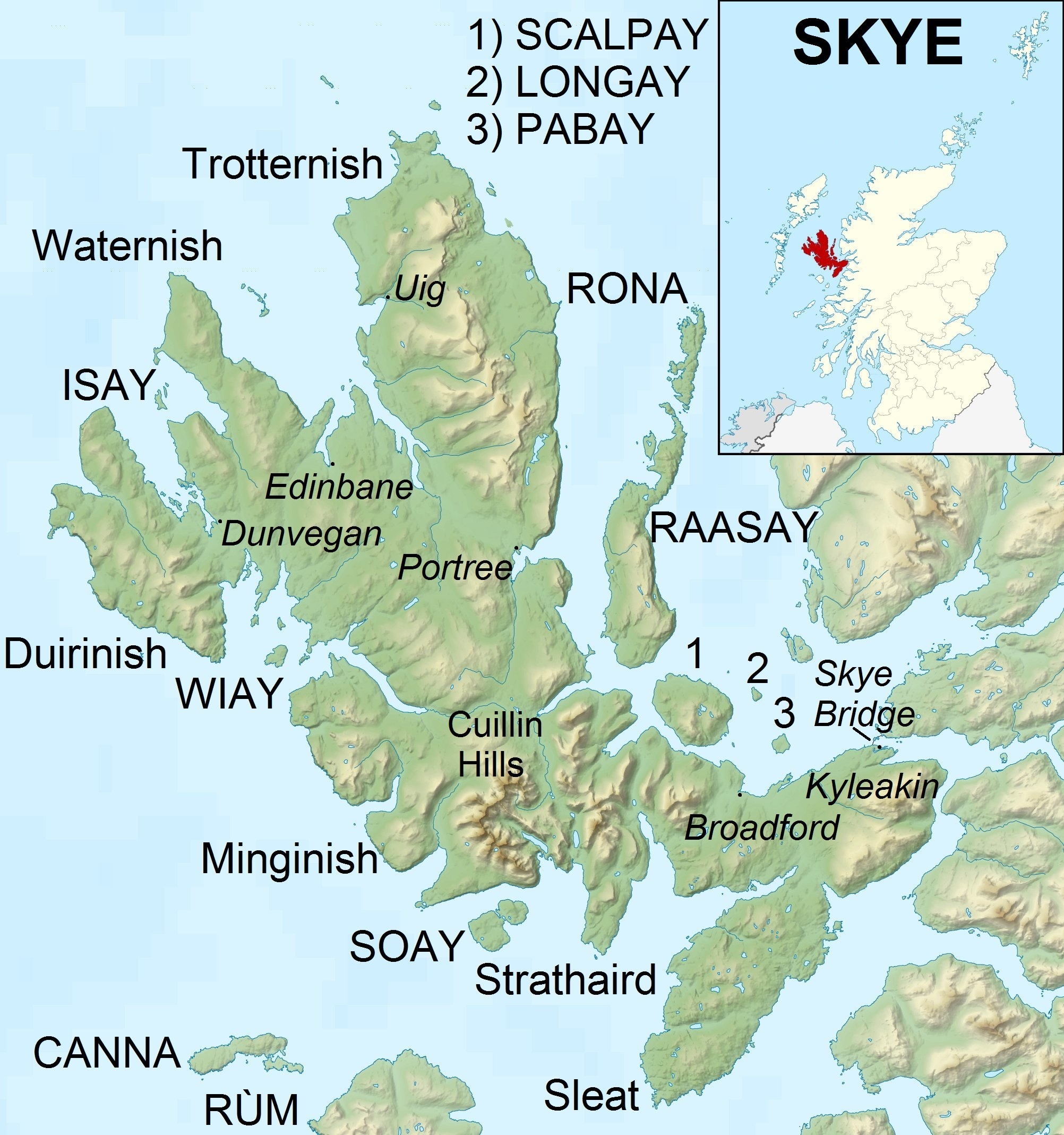
Sound Of Raasay
The Sound of Raasay () is the sound between the islands of Raasay and Skye. See also * Inner Sound, Scotland * Isle of Skye * Loch Kishorn * Mealt Waterfall * Quiraing References External links and references One link, mentions Raasay's depth Landforms of the Inner Hebrides Raasay Raasay (; ), sometimes the Isle of Raasay, is an island between the Isle of Skye and the mainland of Scotland. It is separated from Skye by the Sound of Raasay and from Applecross by the Inner Sound, Scotland, Inner Sound. It is famous fo ... Landforms of Highland (council area) {{Highland-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Trotternish
Trotternish () is the northernmost peninsula of the Isle of Skye in Scotland, spanning in length from Portree to Rubha Hunish. The Trotternish escarpment runs almost the full length of the peninsula, some ,Ordnance Survey ''Landranger'' 1:50000 Map. Sheet 23. North Skye, Dunvegan & Portree. and contains landmarks such as the Old Man of Storr and the Quiraing. The summit of The Storr, overlooking the Old Man, is the highest point of the peninsula at 719 m above sea level. The north-eastern part of the peninsula around Quiraing is designated as a National Scenic Area and the entire escarpment is a Special Area of Conservation. Dinosaur footprints have been found at ''An Corran'', which is also a Mesolithic hunter-gatherer site dating to the 7th millennium BC. The ruins of the 14th–15th-century Duntulm Castle stand at the northern end of the peninsula. The three major settlements on Trotternish are Portree, generally regarded as the capital of Skye, Uig, a ferry terminus, an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skye
The Isle of Skye, or simply Skye, is the largest and northernmost of the major islands in the Inner Hebrides of Scotland. The island's peninsulas radiate from a mountainous hub dominated by the Cuillin, the rocky slopes of which provide some of the most dramatic mountain scenery in the country. Slesser (1981) p. 19. Although has been suggested to describe a winged shape, no definitive agreement exists as to the name's origin."Gaelic Culture" . VisitScotland. Retrieved 5 January 2013. The island has been occupied since the period, and over its history has been occupied at various times by Celtic tribes includ ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scottish Highlands
The Highlands (; , ) is a historical region of Scotland. Culturally, the Highlands and the Scottish Lowlands, Lowlands diverged from the Late Middle Ages into the modern period, when Scots language, Lowland Scots language replaced Scottish Gaelic throughout most of the Lowlands. The term is also used for the area north and west of the Highland Boundary Fault, although the exact boundaries are not clearly defined, particularly to the east. The Great Glen divides the Grampian Mountains to the southeast from the Northwest Highlands. The Scottish Gaelic name of ' literally means "the place of the Gaels" and traditionally, from a Gaelic-speaking point of view, includes both the Western Isles and the Highlands. The area is very sparsely populated, with many mountain ranges dominating the region, and includes the highest mountain in the British Isles, Ben Nevis. During the 18th and early 19th centuries the population of the Highlands rose to around 300,000, but from c. 1841 and for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Highland Council Area
Highland (, ; ) is a council areas of Scotland, council area in the Scottish Highlands and is the largest local government area in both Scotland and the United Kingdom. It was the 7th most populous council area in Scotland at the United Kingdom Census 2011, 2011 census. It has land borders with the council areas of Aberdeenshire, Argyll and Bute, Moray and Perth and Kinross. The wider upland area of the Scottish Highlands after which the council area is named extends beyond the Highland council area into all the neighbouring council areas plus Angus, Scotland, Angus and Stirling (council area), Stirling. The Highland Council is based in Inverness, the area's largest settlement. The area is generally sparsely populated, with much of the inland area being mountainous with numerous lochs. The area includes Ben Nevis, the highest mountain in the British Isles. Most of the area's towns lie close to the eastern coasts. Off the west coast of the mainland the council area includes some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lealt Valley Diatomite Railway
The Lealt Valley Diatomite Railway was a Narrow gauge railway, narrow gauge Tramway (industrial), tramway on the Isle of Skye, Scotland, which ran parallel with the River Lealt. Work was underway to lay the tramway in March 1889. At the opening, the line was worked by gravity – the line being on a falling gradient – and manpower. Later, the line began the use of a steam locomotive. The western end of the line was at Loch Cuithir, where diatomite - known locally as ''Cailc'' (Scottish Gaelic for chalk) - was taken out from the lochbed and dried on wire nets. The seaward terminus had warehouses on the cliff-top at Invertote. At the base of the cliff was a factory where the diatomite was kiln dried, ground and calcination, calcined. The line was extended from the factory onto a pier into the Sound of Raasay. Diatomite was also gotten from Loch Valerain and transported by aerial ropeway to Staffin Bay Formation, Staffin Bay. During its existence, the Skye Diatomite Company ext ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |