|
Lawrence School, Lovedale
The Lawrence School, Lovedale (formerly known as Lawrence Memorial Royal Military School), the namesake of its founder Brigadier-General Sir Henry Montgomery Lawrence KCB, is a co-educational boarding school located at Lovedale, which is a little town on the Nilgiri Mountains in the south Indian state of Tamil Nadu. Lawrence had mooted the idea of establishing a chain of British Raj military-style boarding schools at the hill stations of India to educate the children of the deceased and serving members of the British Indian Army. Although Lawrence was killed at The Residency, Lucknow during the Indian Rebellion of 1857 his dream took shape and four such schools, known as the Lawrence Military Asylums, were established: at Sanawar in 1847, and at Mount Abu in 1856, both during his lifetime; then at Lovedale, Ootacamund in 1858 and at Ghora Gali, Murree, in present-day Pakistan in 1860. Name, emblem and motto In 1913, the name of the school was changed from The Oot ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henry Montgomery Lawrence
Brigadier-General Sir Henry Montgomery Lawrence KCB (28 June 18064 July 1857) was a British military officer, surveyor, administrator and statesman in British India. He is best known for leading a group of administrators in the Punjab affectionately known as Henry Lawrence's "Young Men", as the founder of the Lawrence Military Asylums and for his death at the Siege of Lucknow during the Indian Rebellion. Background Lawrence was born in June 1806 into an Ulster-Scots family at Matara in Ceylon. Both his parents were from Ulster, the northern province of Ireland. His mother Letitia was the daughter of the Rev. George Knox from County Donegal, while his father, Lieutenant-Colonel Alexander William Lawrence, was born the son of a mill owner from Coleraine, County Londonderry, entered the service of the British Army and achieved distinction at the 1799 Siege of Seringapatnam. The Lawrences had seven sons, the first died in infancy and the fifth at the age of eighteen. The remainin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Indian Rebellion Of 1857
The Indian Rebellion of 1857 was a major uprising in India in 1857–58 against the rule of the British East India Company, which functioned as a sovereign power on behalf of the British Crown. The rebellion began on 10 May 1857 in the form of a mutiny of sepoys of the Company's army in the garrison town of Meerut, northeast of Delhi. It then erupted into other mutinies and civilian rebellions chiefly in the upper Gangetic plain and central India, though incidents of revolt also occurred farther north and east. The rebellion posed a considerable threat to British power in that region, and was contained only with the rebels' defeat in Gwalior on 20 June 1858., , and On 1 November 1858, the British granted amnesty to all rebels not involved in murder, though they did not declare the hostilities to have formally ended until 8 July 1859. Its name is contested, and it is variously described as the Sepoy Mutiny, the Indian Mutiny, the Great Rebellion, the Revolt of 1857, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
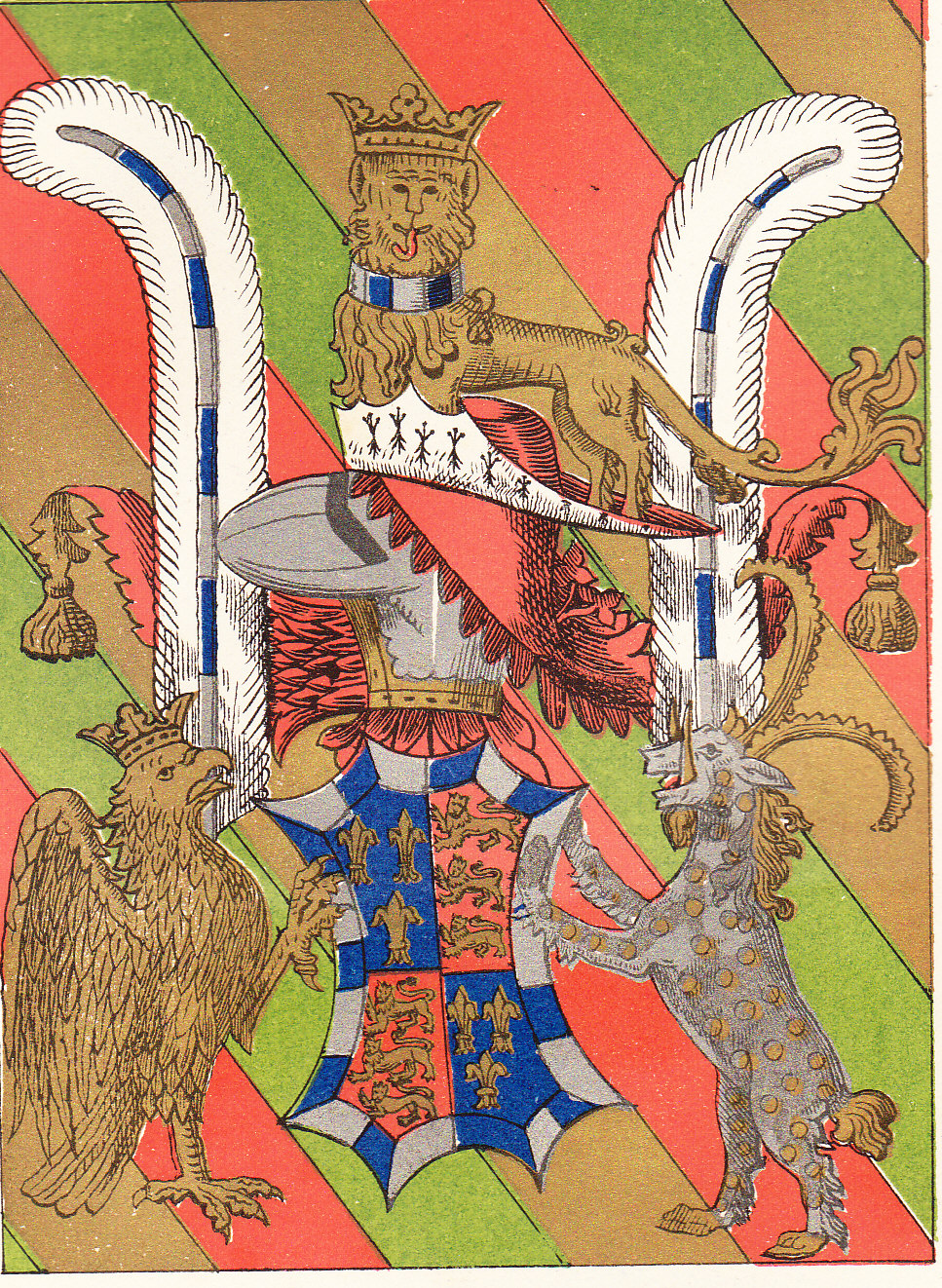
Blazon
In heraldry and heraldic vexillology, a blazon is a formal description of a coat of arms, flag or similar emblem, from which the reader can reconstruct the appropriate image. The verb ''to blazon'' means to create such a description. The visual depiction of a coat of arms or flag has traditionally had considerable latitude in design, but a verbal blazon specifies the essentially distinctive elements. A coat of arms or flag is therefore primarily defined not by a picture but rather by the wording of its blazon (though in modern usage flags are often additionally and more precisely defined using geometrical specifications). ''Blazon'' is also the specialized language in which a blazon is written, and, as a verb, the act of writing such a description. ''Blazonry'' is the art, craft or practice of creating a blazon. The language employed in ''blazonry'' has its own vocabulary, grammar and syntax, which becomes essential for comprehension when blazoning a complex coat of arms. Other ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Heraldry
Heraldry is a discipline relating to the design, display and study of armorial bearings (known as armory), as well as related disciplines, such as vexillology, together with the study of ceremony, rank and pedigree. Armory, the best-known branch of heraldry, concerns the design and transmission of the heraldic achievement. The achievement, or armorial bearings usually includes a coat of arms on a shield, helmet and crest, together with any accompanying devices, such as supporters, badges, heraldic banners and mottoes. Although the use of various devices to signify individuals and groups goes back to antiquity, both the form and use of such devices varied widely, as the concept of regular, hereditary designs, constituting the distinguishing feature of heraldry, did not develop until the High Middle Ages. It is often claimed that the use of helmets with face guards during this period made it difficult to recognize one's commanders in the field when large armies gathered toge ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Achievement (heraldry)
In heraldry, an achievement, armorial achievement or heraldic achievement (historical: hatchment) is a full display or depiction of all the heraldic components to which the bearer of a coat of arms is entitled. An achievement comprises not only the arms displayed on the escutcheon, the central element, but also the following elements surrounding it: * Crest placed atop a: * Torse (or Cap of Maintenance as a special honour) * Mantling * Helm of appropriate variety; if holder of higher rank than a baronet, issuing from a: * Coronet or Crown (not used by baronets), of appropriate variety. * Supporters (if the bearer is entitled to them, generally in modern usage not baronets), which may stand on a Compartment * Motto, if possessed * Order, if possessed * Badge, if possessed Coat of arms Sometimes the term " coat of arms" is used to refer to the full achievement, however this usage is incorrect in the strict sense of heraldic terminology, as a coat of arms refers to a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Government Of India
The Government of India ( ISO: ; often abbreviated as GoI), known as the Union Government or Central Government but often simply as the Centre, is the national government of the Republic of India, a federal democracy located in South Asia, consisting of 28 union states and eight union territories. Under the Constitution, there are three primary branches of government: the legislative, the executive and the judiciary, whose powers are vested in a bicameral Parliament, President, aided by the Council of Ministers, and the Supreme Court respectively. Through judicial evolution, the Parliament has lost its sovereignty as its amendments to the Constitution are subject to judicial intervention. Judicial appointments in India are unique in that the executive or legislature have negligible say. Etymology and history The Government of India Act 1833, passed by the British parliament, is the first such act of law with the epithet "Government of India". Basic structure The ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Partition Of India
The Partition of British India in 1947 was the Partition (politics), change of political borders and the division of other assets that accompanied the dissolution of the British Raj in South Asia and the creation of two independent dominions: Dominion of India, India and Dominion of Pakistan, Pakistan. The Dominion of India is today the India, Republic of India, and the Dominion of Pakistan—which at the time comprised two regions lying on either side of India—is now the Pakistan, Islamic Republic of Pakistan and the Bangladesh, People's Republic of Bangladesh. The partition was outlined in the Indian Independence Act 1947. The change of political borders notably included the division of two provinces of British India, Bengal Presidency, Bengal and Punjab Province (British India), Punjab. The majority Muslim districts in these provinces were awarded to Pakistan and the majority non-Muslim to India. The other assets that were divided included the British Indian Army, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 243 million people, and has the world's Islam by country#Countries, second-largest Muslim population just behind Indonesia. Pakistan is the List of countries and dependencies by area, 33rd-largest country in the world by area and 2nd largest in South Asia, spanning . It has a coastline along the Arabian Sea and Gulf of Oman in the south, and is bordered by India to India–Pakistan border, the east, Afghanistan to Durand Line, the west, Iran to Iran–Pakistan border, the southwest, and China to China–Pakistan border, the northeast. It is separated narrowly from Tajikistan by Afghanistan's Wakhan Corridor in the north, and also shares a maritime border with Oman. Islamabad is the nation's capital, while Karachi is its largest city and fina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murree Tehsil
Murree Tehsil ( ur, تحصیل مری) is one of the two Tehsils (i.e. sub-divisions) of Murree District in the Punjab province of Pakistan. Murree Tehsil is located in the northernmost part of Punjab province where it borders Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. The hill resort city of Murree is the capital city of this area. Administration Murree Tehsil is divided into 15 Union Councils. These are: Note: The UC prefix is used for administration purposes as Rawalpindi District has a total of 90 Union Councils. 2005 earthquake During the earthquake of 2005, 40% of houses in Murree tehsil were damaged or destroyed. Demographics According to population census of 2017 Murree Murree (Punjabi, Urdu: مری) is a mountain resort city, located in the Galyat region of the Pir Panjal Range, within the Muree District of Punjab, Pakistan. It forms the outskirts of the Islamabad-Rawalpindi metropolitan area, and is abou ... has a population of 233,017. References {{Murree-Union-Cou ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghora Gali
Ghora Gali is one of the tourist mountain resort towns of the Galyat area of northern Pakistan. It has an elevation of 1691m and is located in the northeastern tip of the Punjab province of Pakistan. Ghora Gali is also a Union council, an administrative subdivision, of Murree Tehsil in Murree District and is located at . According to the 1998 census of Pakistan it had a population of 14410. History British Era Ghora Gali served as a resort for British colonialists and troops during the British Raj. In 1860 the Lawrence College was established here originally as an asylum for orphans of British troops killed in the wars. Also in 1860 the Murree Brewery was established here and produced beer for British troops, however in 1947 following independence from Britain and the ensuing riots during the independence of Pakistan in 1947 the building was destroyed. Recreation Ghora Gali now features an 1,100 m long chairlift. It goes from Ghora Gali to Pindi Point. See also * Lawrence ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ooty
Ooty (), officially known as Udhagamandalam (also known as Ootacamund (); abbreviated as Udhagai), is a city and a municipality in the Nilgiris district of the South Indian States and territories of India, state of Tamil Nadu. It is located north west of Coimbatore and south of Mysore and is the headquarters of the Nilgiris district. It is a popular hill station located in the Nilgiri Hills. It is popularly called the Queen of Hill Stations. It was the summer capital of the Madras Presidency. Originally occupied by the Toda people, the area came under the rule of the East India Company at the end of the 18th century. The economy is based on tourism and agriculture, along with the manufacture of medicines and photographic film. The town is connected by the Nilgiri Ghat Roads, Nilgiri ghat roads and Nilgiri Mountain Railway. Its natural environment attracts tourists and it is a popular summer destination. In 2011, the town had a population of 88,430. Ootacamund was rated the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lovedale, India
Lovedale is a village situated in the Nilgiri Hills in the state of Tamil Nadu in India. It is one of the highest places above mean sea level in the Nilgiris. Today, it is notable for tourism. Nearest large population areas *Ooty (5 km away). The Queen of Hills is located just 5 km away from Lovedale. *Conoor (16 km) *Wellington *Nilambur Population The permanent population is about 1,000-1,500 people. The residents of The Lawrence School add another 1,000 people to this. Establishments The Lawrence School is a residential school. Lovedale has a police station that serves Lovedale and the nearby villages. It also has a small post office and a bank (branch of SBI), both of which primarily serve The Lawrence School. Educational institutions * Lawrence School, Lovedale * St. Antony's High School, Lovedale * Nilgiris Matriulation higher Secondary school, Lovedale Climate Lovedale features a subtropical highland climate (Cwb) under Köppen climate cla ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |