|
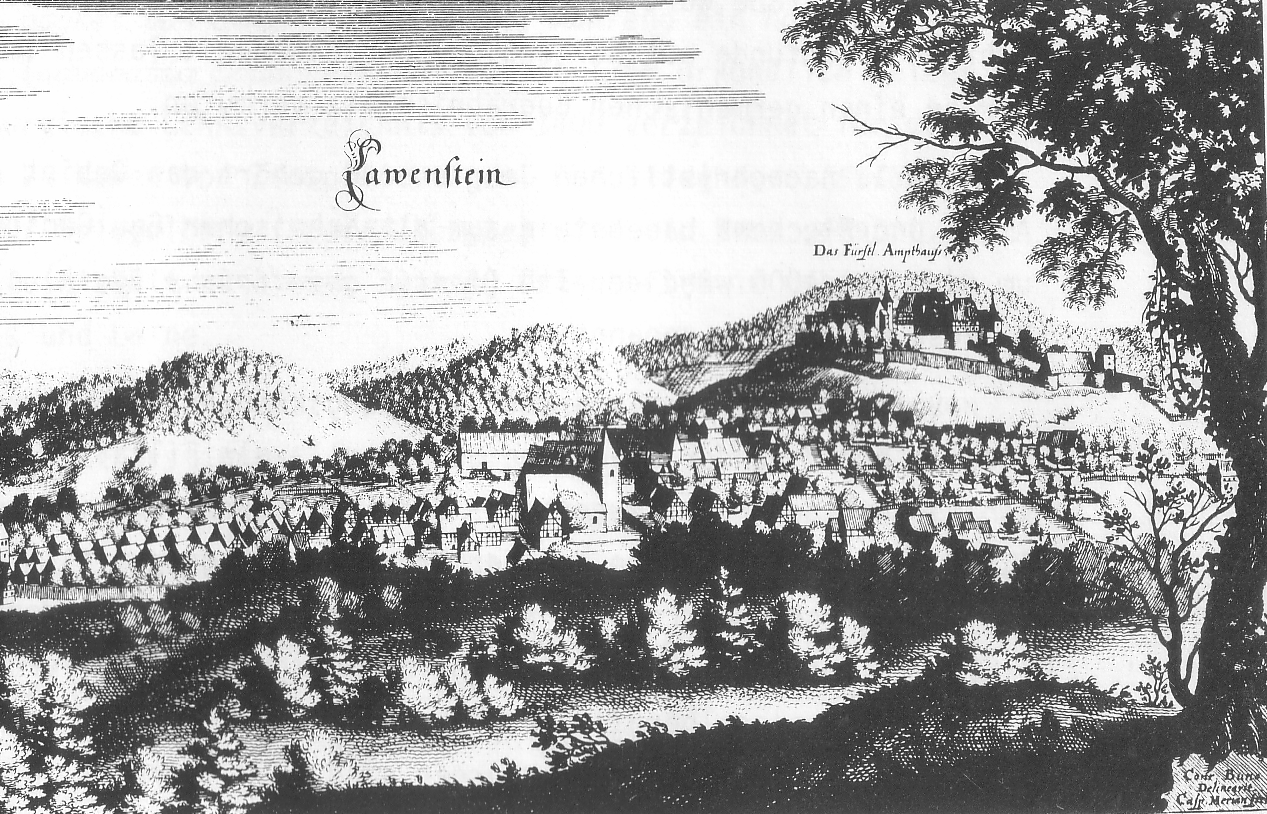
Lauenstein (Salzhemmendorf)
Lauenstein is a village in the municipality of Salzhemmendorf in the Lower Saxon district of Hameln-Pyrmont in north Germany. It has about 2,100 inhabitants. Geography Lauenstein lies in the Weser Uplands, not far from the only low saddle in the crest of the Ith, in a valley that descends eastwards at right angles to the Ith ridge. Part of its more recent built-up area extends out of the valley to the eastern slopes of the Ith and into the Saale valley. History Feudal tenure The feudal lords in the district (''Amt'') area were the barons of Homburg, who exercised power from 1152 to 1409. Their seat was the castle of Homburg near Eschershausen. The counts of Spiegelberg were also feudal lords here from 1152 to 1557. They resided at Spiegelberg Castle and later at Coppenbrügge Castle. Another important feudal lord was ''Bock von Nordholz'', who was resident at Nordholz Castle in Nordholz on the Osterwald. Middle Ages Around 1215 Count Bernard of Poppenburg bu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salzhemmendorf
Salzhemmendorf is a village and a municipality in the Hamelin-Pyrmont district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximately 20 km east of Hamelin and 31 km west of Hildesheim Hildesheim (; nds, Hilmessen, Hilmssen; la, Hildesia) is a city in Lower Saxony, Germany with 101,693 inhabitants. It is in the district of Hildesheim, about southeast of Hanover on the banks of the Innerste River, a small tributary of the ... and is located on the route 1. It is a nationally recognized health resort with a therapeutic brine thermal bath "Ith-Sole-Therme". Salzhemmendorf consists of Salzhemmendorf proper, as well as Ahrenfeld, Benstorf, Hemmendorf, Lauenstein, Levedagsen, Ockensen, Oldendorf, Osterwald, Thüste and Wallensen. Main sights *Weserbergland *The "Water tree" in Ockensen, a worldwide attraction *The nearby located holiday park Rastiland References External links a web page of Salzhemmendorf for touriststermal bath "Ith-Sole-Therme" {{Author ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vogt
During the Middle Ages, an (sometimes given as modern English: advocate; German: ; French: ) was an office-holder who was legally delegated to perform some of the secular responsibilities of a major feudal lord, or for an institution such as an abbey. Many such positions developed, especially in the Holy Roman Empire. Typically, these evolved to include responsibility for aspects of the daily management of agricultural lands, villages and cities. In some regions, advocates were governors of large provinces, sometimes distinguished by terms such as (in German). While the term was eventually used to refer to many types of governorship and advocacy, one of the earliest and most important types of was the church advocate (). These were originally lay lords, who not only helped defend religious institutions in the secular world, but were also responsible for exercising lordly responsibilities within the church's lands, such as the handling of legal cases which might require the u ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lauenstein (Oswald Reißert)
Lauenstein is the name of the following: Places: * Lauenstein (Altenberg), a suburb of the town of Altenberg in the district of Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge in Saxony, Germany * Lauenstein (Ludwigsstadt) a suburb of the town of Ludwigsstadt in the district of Kronach in Bavaria, Germany * Lauenstein (Salzhemmendorf), a village in the municipality of Salzhemmendorf in the district of Hameln-Pyrmont in Lower Saxony, Germany Castles: * Lauenstein (Altenberg), castle ruins and manor house in Lauenstein in the district of Sächsische Schweiz-Osterzgebirge in Saxony, Germany * Lauenstein Castle (Franconian Forest) in Ludwigsstadt in the district of Kronach in Bavaria, Germany * Lauenstein Castle (Ith) in Salzhemmendorf in the district of Hameln-Pyrmont in Lower Saxony, Germany People: * Christoph Lauenstein (b 1962), German film maker * Diether Lauenstein (1914–1990), German indologist, priest and journalist * Wolfgang Lauenstein (b 1962), German film maker Radiographic po ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Afterlehen
An ''Afterlehen'' or ''Afterlehn'' ''(plural: Afterlehne, Afterlehen)'' is a fief that the liege lord has himself been given as a fief and has then, in turn, enfeoffed it wholly or partially to a lesser vassal or vassals. The term is German. It is variously referred to in English as a mesne-fiefFahrenkrüger (1801), 2nd Part, p. 26. Retrieved 11 May 201(in German-English)/ref> or mesne-tenure, an arriere-fief or subfief, under-tenure or mesnalty. Within the Holy Roman Empire these mesne fiefs even became inheritable over time and could have up to five "stations" between the actual holder of the fief and the overarching liege lord. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Saldern
Saldern (up to the 17th century, Salder) or von Saldern, is the name of an old German aristocratic family from the areas of Hildesheim and Brunswick Land. The family seat of the same name is an eponymous castle on the River Fuhse in Salzgitter- Salder. Originally the family, whose branches are still alive today, only owned estates in the Lower Saxony area, but from the middle of the 16th century they also owned extensive property in the March of Brandenburg. Family history According to legend the founder of the line (), Sieghard de Rosis, came to Germany from Rome in 718 with St. Boniface. In 1102, the family is mentioned for the first time in the chronicle , in Hildesheim. According to this document, the knightly family of von Saldern was enfeoffed that year with tithe rights () by St. Michael's Abbey near Nettlingen ( Söhlde). According to historical records the first member of the family to be classed amongst the ('lay nobility') was ''Thidericius de Saldere'' in 1161. Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cramm
{{More citations needed, date=September 2022 CRAMM (CCTA Risk Analysis and Management Method) is a risk management methodology, currently on its fifth version, CRAMM Version 5.0. History CRAMM was created in 1987 by the Central Computer and Telecommunications Agency (CCTA), now renamed into Cabinet Office, of the United Kingdom government. Methodology CRAMM comprises three stages, each supported by objective questionnaires and guidelines. The first two stages identify and analyze the risks to the system. The third stage recommends how these risks should be managed. The three stages of CRAMM are as follows: Stage 1 The establishment of the objectives for security by: * Defining the boundary for the study for Risk Assessment * Identifying and valuing the physical assets that form part of the system; * Determining the 'value' of the data held by interviewing users about the potential business impacts that could arise from unavailability, destruction, disclosure or modification; * ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
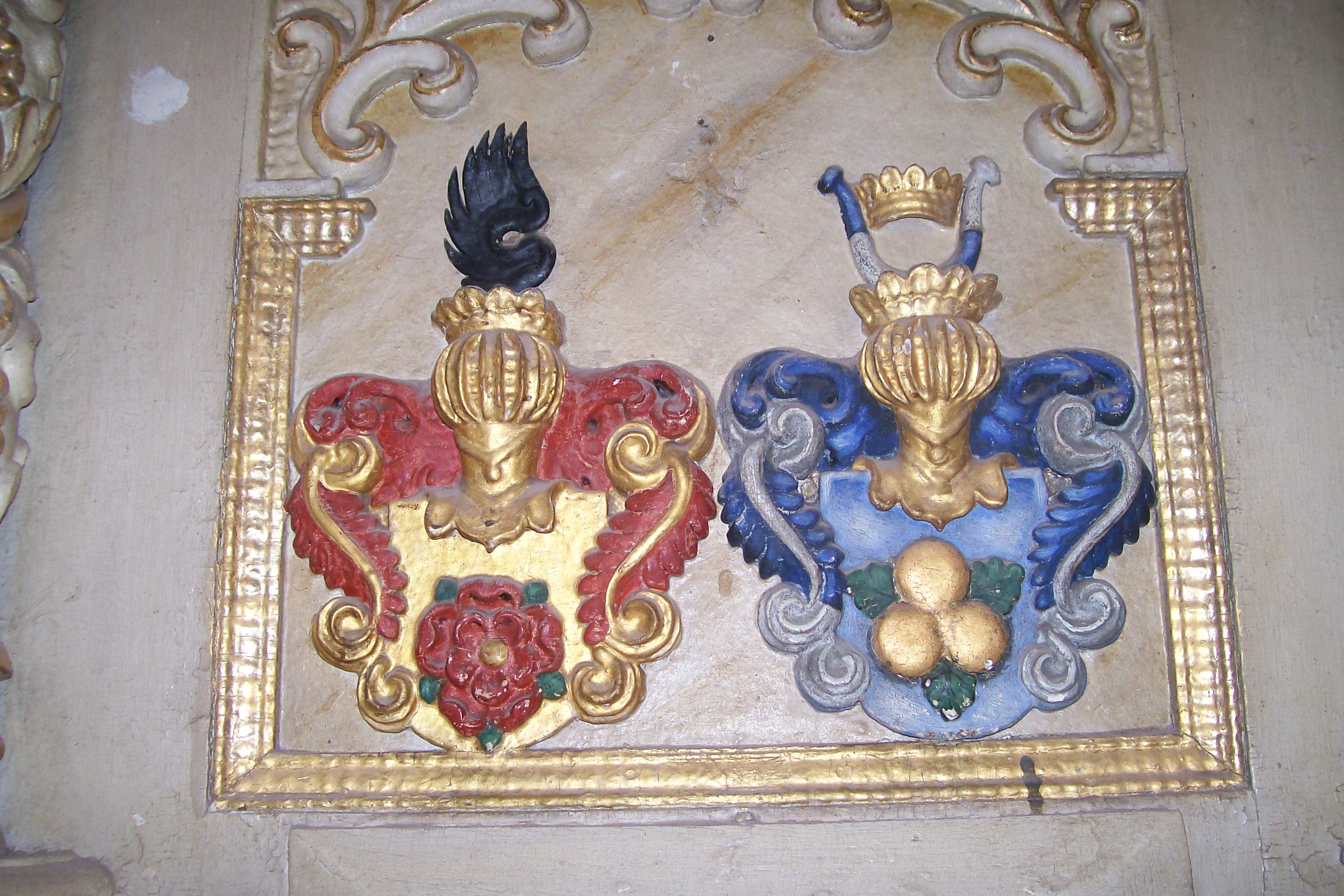
Burg Lauenstein (Ith)
Lauenstein Castle (german: Burg Lauenstein) is a former hill castle that is now in ruins. It lies above the Salzhemmendorf village of Lauenstein in the German state of Lower Saxony. The castle was built in the 13th century by the barons of Homburg. From the 16th century it became militarily insignificant and was demolished in the 19th century due to its increasing state of dilapidation. Location The ruins of Lauenstein castle are located on the edge of Ith ridge on a hill summit above the village of Lauenstein. The castle terrain is covered by thick forest that was planted in the 19th century when the hill was reutilised. Site The roughly 50 x 50 metre castle plateau lies on an eminence that is surrounded by steep hillsides. It is protected on all sides by a wide moat. The direct access to the castle was built in the form of a ''zwinger'' in front of the gateway whose walls are still 4 metres high today. Parts of the enceinte of the castle still exists. There is an informa ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Coppenbrügge
Coppenbrügge is a municipality in the Hamelin-Pyrmont district, in Lower Saxony, Germany. It is situated approximatively 15 km (10 miles) east of Hamelin. The Municipality covers the following villages: * Bäntorf * Behrensen * Bessingen * Bisperode Brünnighausen* Coppenbrügge * Diedersen * Dörpe * Harderode * Herkensen * Hohnsen * Marienau History Coppenbrügge was first documented around 1000 in a borderline description of the Bishopric of Hildesheim as '' Cobbanbrug '' mentioned. On March 9, 1062, Emperor Henry IV granted Bishop Hezilo of Hildesheim the forest ban at Coppenbrügge. Built around 1200 Count Bernhard of Poppenburg, who sat on the castle Poppenburg, the mirror castle at Lauenstein. After that he called himself Bernhard von Poppenburg and Spiegelberg. The Spiegelburg was built in the valley between Ith and Osterwald on the old army and trade route near a swamp area. The road was Hellweg, which led from Aachen to Königsberg. After that it was the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leine (Aller)
The Leine (; Old Saxon ''Lagina'') is a river in Thuringia and Lower Saxony, Germany. It is a left tributary of the Aller and the Weser and is long. The river's source is located close to the town of Leinefelde in Thuringia. About downriver, the river enters Lower Saxony and runs northwards. Important towns along its course, from upstream to downstream, are Göttingen, Einbeck, Freden, Alfeld, and Gronau, before the river enters Hanover, the largest city on its banks. Downstream some north of Hanover, near Schwarmstedt, the river joins the Aller and reaches the North Sea via the Weser. Its northern (lower) reaches are only navigable today by the smallest commercial carriers, though in the past, it served as an important pre-railway barge transport artery as far upriver as Göttingen. The river is somewhat polluted by industry, so the water is not used for drinking, but the pollution has never been severe enough to prevent fish from living in it. Like many western rivers sin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |