|
Laser Damage Threshold
The laser damage threshold (LDT) or laser induced damage threshold (LIDT) is the limit at which an optic or material will be damaged by a laser given the fluence (energy per area), intensity (power per area), and wavelength. LDT values are relevant to both transmissive and reflective optical elements and in applications where the laser induced modification or destruction of a material is the intended outcome. Mechanisms Thermal For long pulses or continuous wave lasers the primary damage mechanism tends to be thermal. Since both transmitting and reflecting optics have non-zero absorption, the laser can deposit thermal energy into the optic. At a certain point, there can be sufficient localized heating to either affect the material properties or induce thermal shock. Dielectric breakdown Dielectric breakdown occurs in insulating materials whenever the electric field is sufficient to induce electrical conductivity. Although this concept is more common in the context of DC and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser
A laser is a device that emits light through a process of optical amplification based on the stimulated emission of electromagnetic radiation. The word ''laser'' originated as an acronym for light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation. The first laser was built in 1960 by Theodore Maiman at Hughes Research Laboratories, based on theoretical work by Charles H. Townes and Arthur Leonard Schawlow and the optical amplifier patented by Gordon Gould. A laser differs from other sources of light in that it emits light that is coherence (physics), ''coherent''. Spatial coherence allows a laser to be focused to a tight spot, enabling uses such as optical communication, laser cutting, and Photolithography#Light sources, lithography. It also allows a laser beam to stay narrow over great distances (collimated light, collimation), used in laser pointers, lidar, and free-space optical communication. Lasers can also have high temporal coherence, which permits them to emit light ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
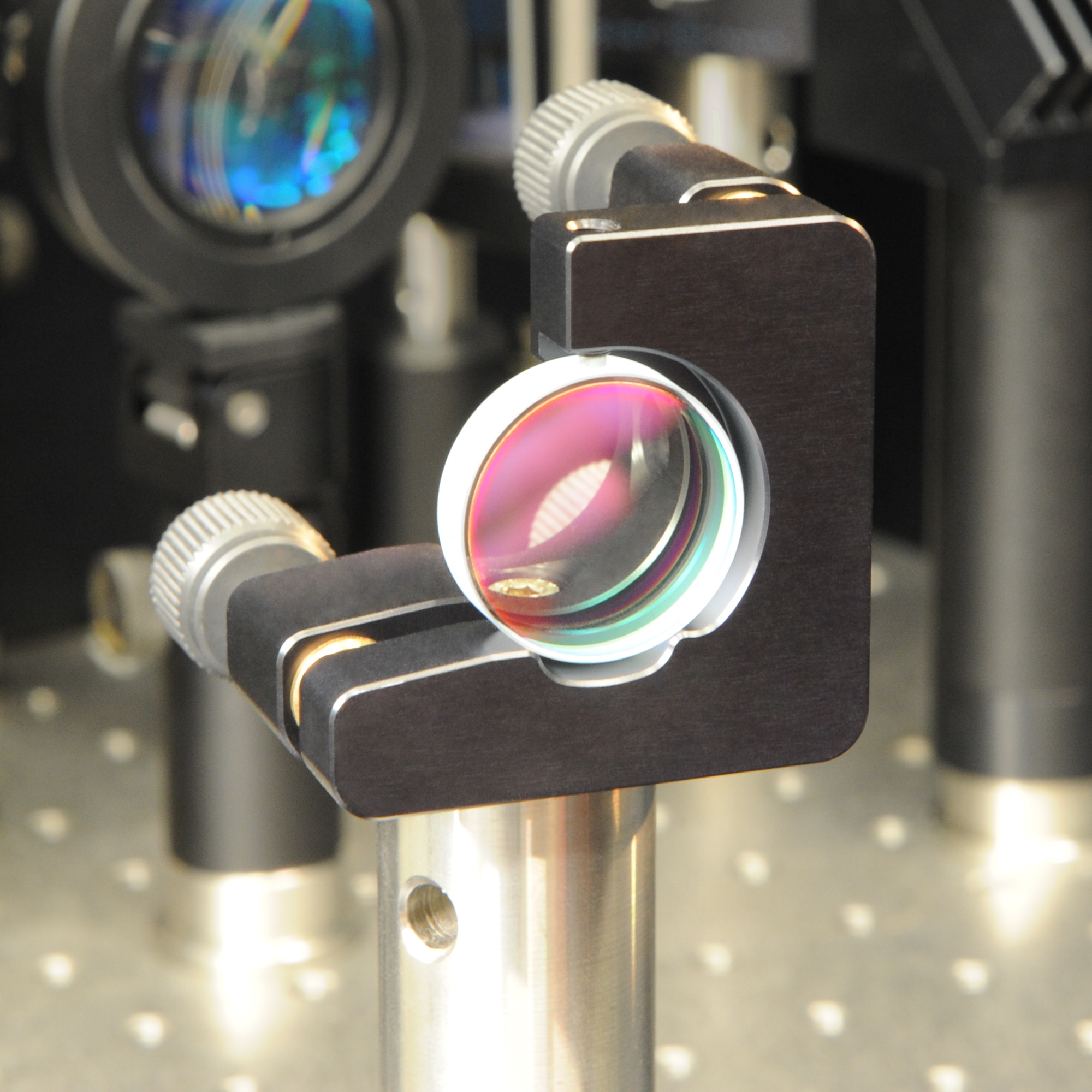
Dielectric Mirror
A dielectric mirror, also known as a Bragg mirror, is a type of mirror composed of multiple thin film, thin layers of dielectric material, typically deposited on a substrate of glass or some other optical material. By careful choice of the type and thickness of the dielectric layers, one can design an optical coating with specified reflectivity at different wavelengths of light. Dielectric mirrors are also used to produce ultra-high reflectivity mirrors: values of 99.999% or better over a narrow range of wavelengths can be produced using special techniques. Alternatively, they can be made to reflect a broad spectrum of light, such as the entire visible range or the spectrum of the Ti-sapphire laser. Dielectric mirrors are very common in optics experiments, due to improved techniques that allow inexpensive manufacture of high-quality mirrors. Examples of their applications include laser optical cavity, cavity end mirrors, Hot mirror, hot and cold mirrors, thin-film beam splitter ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma Acceleration
Plasma acceleration is a technique for accelerating charged particles, such as electrons or ions, using the electric field associated with an electron plasma wave or other high-gradient plasma structures. These structures are created using either ultra-short laser pulses or energetic particle beams that are matched to the plasma parameters. The technique offers a way to build affordable and compact particle accelerators. Fully developed, the technology could replace many of the traditional accelerators with applications ranging from high energy physics to medical and industrial applications. Medical applications include betatron and free-electron light sources for diagnostics or radiation therapy and proton sources for hadron therapy. History The basic concepts of plasma acceleration and its possibilities were conceived by Toshiki Tajima and John M. Dawson of UCLA in 1979. The initial experimental designs for a "wakefield" accelerator were developed at UCLA by Chandrash ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Medicine
Laser medicine is the use of lasers in medical diagnosis, treatments, or therapies, such as laser photodynamic therapy, photorejuvenation, and laser surgery. The word ''laser'' stands for "light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation". History The laser was invented in 1960 by Theodore Maiman, and its potential uses in medicine were subsequently explored. Lasers benefit from three interesting characteristics: directivity (multiple directional functions), impulse (possibility of operating in very short pulses), and monochromaticity. Several medical applications were found for this new instrument. In 1961, just one year after the laser's invention, Dr. Charles J. Campbell successfully used a ruby laser to destroy an angiomatous retinal tumor with a single pulse. In 1963, Dr. Leon Goldman used the ruby laser to treat pigmented skin cells and reported on his findings. The argon-ionized laser (wavelength: 488–514 nm) has since become the preferred laser for ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pulsed Laser Deposition
Pulsed laser deposition (PLD) is a physical vapor deposition (PVD) technique where a high-power pulsed laser beam is focused inside a vacuum chamber to strike a target of the material that is to be deposited. This material is vaporized from the target (in a plasma plume) which deposits it as a thin film on a substrate (such as a silicon wafer facing the target). This process can occur in ultra high vacuum or in the presence of a background gas, such as oxygen which is commonly used when depositing oxides to fully oxygenate the deposited films. While the basic setup is simple relative to many other deposition techniques, the physical phenomena of laser-target interaction and film growth are quite complex (see Process below). When the laser pulse is absorbed by the target, energy is first converted to electronic excitation and then into thermal, chemical and mechanical energy resulting in evaporation, ablation, plasma formation and even exfoliation.Pulsed Laser Deposition of Th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Laser Cutting
Laser cutting is a technology that uses a laser to vaporize materials, resulting in a cut edge. While typically used for industrial manufacturing applications, it is now used by schools, small businesses, architecture, and hobbyists. Laser cutting works by directing the output of a high-power laser most commonly through optics. The laser optics and CNC (computer numerical control) are used to direct the laser beam to the material. A commercial laser for cutting materials uses a motion control system to follow a CNC or G-code of the pattern to be cut onto the material. The focused laser beam is directed at the material, which then either melts, burns, vaporizes away, or is blown away by a jet of gas, leaving an edge with a high-quality surface finish. History In 1965, the first production laser cutting machine was used to drilling, drill holes in diamond Die (manufacturing), dies. This machine was made by the Western Electric Engineering Research Center. In 1967, the British pi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nobel Prize In Physics
The Nobel Prize in Physics () is an annual award given by the Royal Swedish Academy of Sciences for those who have made the most outstanding contributions to mankind in the field of physics. It is one of the five Nobel Prizes established by the will of Alfred Nobel in 1895 and awarded since 1901, the others being the Nobel Prize in Chemistry, Nobel Prize in Literature, Nobel Peace Prize, and Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine. Physics is traditionally the first award presented in the Nobel Prize ceremony. The prize consists of a medal along with a diploma and a certificate for the monetary award. The front side of the medal displays the same profile of Alfred Nobel depicted on the medals for Physics, Chemistry, and Literature. The first Nobel Prize in Physics was awarded to German physicist Wilhelm Röntgen in recognition of the extraordinary services he rendered by the discovery of X-rays. This award is administered by the Nobel Foundation and is widely regarded as the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirped Pulse Amplification
Chirped pulse amplification (CPA) is a technique for amplifying an ultrashort laser pulse up to the petawatt level, with the laser pulse being stretched out temporally and spectrally, then amplified, and then compressed again. The stretching and compression uses devices that ensure that the different color components of the pulse travel different distances. CPA for lasers was introduced by Donna Strickland and Gérard Mourou at the University of Rochester in the mid-1980s, work for which they received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2018. CPA is the technique used by most high-powered lasers in the world. Background Before the introduction of CPA in the mid-1980s, the peak power of laser pulses was limited because a laser pulse at intensities of gigawatts per square centimeter causes serious damage to the gain medium through nonlinear processes such as self-focusing. For example, some of the most powerful compressed CPA laser beams, even in an unfocused large aperture (afte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chirp
A chirp is a signal in which the frequency increases (''up-chirp'') or decreases (''down-chirp'') with time. In some sources, the term ''chirp'' is used interchangeably with sweep signal. It is commonly applied to sonar, radar, and laser systems, and to other applications, such as in spread-spectrum communications (see chirp spread spectrum). This signal type is biologically inspired and occurs as a phenomenon due to dispersion (a non-linear dependence between frequency and the propagation speed of the wave components). It is usually compensated for by using a matched filter, which can be part of the propagation channel. Depending on the specific performance measure, however, there are better techniques both for radar and communication. Since it was used in radar and space, it has been adopted also for communication standards. For automotive radar applications, it is usually called linear frequency modulated waveform (LFMW). In spread-spectrum usage, surface acoustic wave (S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Plasma (physics)
Plasma () is a state of matter characterized by the presence of a significant portion of charged particles in any combination of ions or electrons. It is the most abundant form of ordinary matter in the universe, mostly in stars (including the Sun), but also dominating the rarefied intracluster medium and Outer space#Intergalactic space, intergalactic medium. Plasma can be artificially generated, for example, by heating a neutral gas or subjecting it to a strong electromagnetic field. The presence of charged particles makes plasma electrically conductive, with the dynamics of individual particles and macroscopic plasma motion governed by collective electromagnetic fields and very sensitive to externally applied fields. The response of plasma to electromagnetic fields is used in many modern devices and technologies, such as plasma display, plasma televisions or plasma etching. Depending on temperature and density, a certain number of neutral particles may also be present, in wh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fluence
In radiometry, radiant exposure or fluence is the radiant energy ''received'' by a ''surface'' per unit area, or equivalently the irradiance of a ''surface,'' integrated over time of irradiation, and spectral exposure is the radiant exposure per unit frequency or wavelength, depending on whether the spectrum is taken as a function of frequency or of wavelength. The SI unit of radiant exposure is the joule per square metre (), while that of spectral exposure in frequency is the joule per square metre per hertz () and that of spectral exposure in wavelength is the joule per square metre per metre ()—commonly the joule per square metre per nanometre (). Mathematical definitions Radiant exposure Radiant exposure of a ''surface'', denoted ''H''e ("e" for "energetic", to avoid confusion with photometric quantities), is defined as H_\mathrm = \frac = \int_0^T E_\mathrm(t)\, \mathrmt, where *∂ is the partial derivative symbol; *''Q''e is the radiant energy; *''A'' is the area; *''T'' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Two-photon Absorption
In atomic physics, two-photon absorption (TPA or 2PA), also called two-photon excitation or non-linear absorption, is the (almost) simultaneous Absorption (electromagnetic radiation), absorption of two photons of identical or different frequencies in order to Electron excitation, excite an atom or a molecule from one state (usually the ground state), via a virtual energy level, to a higher energy, most commonly an excited electronic state. Absorption of two photons with the same frequency is called degenerate two-photon absorption, while absorption of two photons with different frequencies is called non-degenerate two-photon absorption. The energy difference between the involved lower and upper states is equal or smaller than the sum of the photon energy, photon energies of the two photons absorbed. Since TPA depends on the simultaneous absorption of two photons, the probability of two-photon absorption is proportional to the photon dose (), which is proportional to the square of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |