|
Larvicide
A larvicide (alternatively larvacide) is an insecticide that is specifically targeted against the larval life stage of an insect. Their most common use is against mosquitoes. Larvicides may be contact poisons, stomach poisons, growth regulators, or (increasingly) biological control agents. Biological agents The biological control agent ''Bacillus thuringiensis'', also known as ''Bt'', is a bacterial disease specific to Lepidopteran caterpillars. ''Bacillus thuringiensis israelensis'', also known as ''Bti'', and ''Bacillus sphaericus'', which affect larval mosquitoes and some midges, have come into increasing use in recent times. ''Bti'' and ''B. sphaericus'' are both naturally occurring soil bacterium registered as larvicides under the names Bactivec, Bacticide, Aquabac, Teknar, Vectobac, LarvX, and VectoLex CG. Typically in granular form, pellets are distributed on the surface of stagnant water locations. When the mosquito larvae ingest the bacteria, crystallized toxins are prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Pest Control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or plants by using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insects play an important part in limiting the densities of potential pests. Biological control agents such as these include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and com ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Neem Oil
Neem oil, also known as margosa oil, is a vegetable oil pressed from the fruits and seeds of the neem (''Azadirachta indica''), a tree which is indigenous to the Indian subcontinent and has been introduced to many other areas in the tropics. It is the most important of the commercially available products of neem, and is a potent pesticide used in organic farming. Composition Azadirachtin is the most well known and studied triterpenoid in neem oil. nimbin (chemical), Nimbin is another triterpenoid which has been credited with some of neem oil's properties as an antiseptic, antifungal, antipyretic and antihistamine. Uses Ayurveda Neem oil has a history of use in Ayurvedic traditional medicine, folk medicine. Pesticide Formulations that include neem oil have found wide usage as a biopesticide for horticulturists and for organic farming, as it repels a wide variety of insect pests including mealy bugs, beet armyworms, aphids, cabbage worms, thrips, whiteflies, mites, fungu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biological Control
Biological control or biocontrol is a method of controlling pests, whether pest animals such as insects and mites, weeds, or pathogens affecting animals or plants by using other organisms. It relies on predation, parasitism, herbivory, or other natural mechanisms, but typically also involves an active human management role. It can be an important component of integrated pest management (IPM) programs. There are three basic strategies for biological control: classical (importation), where a natural enemy of a pest is introduced in the hope of achieving control; inductive (augmentation), in which a large population of natural enemies are administered for quick pest control; and inoculative (conservation), in which measures are taken to maintain natural enemies through regular reestablishment. Natural enemies of insects play an important part in limiting the densities of potential pests. Biological control agents such as these include predators, parasitoids, pathogens, and co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Temephos
Temefos or temephos (trade name Abate) is an organophosphate larvicide used to treat water infested with disease-carrying insects (including mosquitoes, midges, and black fly larvae) and crustaceans (copepods). As with other organophosphates, temephos affects the central nervous system through inhibition of cholinesterase. In larvae, this results in death before reaching the adult stage. In the developing world where the vector-borne disease dengue fever is endemic, temephos is widely used and applied by both private and public pest control in areas of standing water where the ''Aedes aegypti'' mosquito breeds, in order to reduce the population of this disease-carrying insect. Temephos is also used in the Guinea Worm Eradication Program to kill the copepods that carry guinea worm larvae. Resistance to temephos by ''A. aegypti'' has been seen in Brazil. The Brazilian Aedes aegypti resistance monitoring program detected temephos resistance in ''A. aegypti'' populations from se ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bacillus Sphaericus
''Lysinibacillus sphaericus'' (previously known as ''Bacillus sphaericus'') is a Gram-positive, mesophilic, rod-shaped bacterium commonly found on soil. It can form resistant endospores that are tolerant to high temperatures, chemicals and ultraviolet light and can remain viable for long periods of time. It is of particular interest to the World Health Organization due to the larvicide effect of some strains against two mosquito genera (''Culex'' and ''Anopheles''), more effective than ''Bacillus thuringiensis'', frequently used as a biological pest control. ''L. sphaericus'' cells in a vegetative state are also effective against ''Aedes aegypti'' larvae, an important vector of yellow fever and dengue viruses. A bacterium similar to this species was found in a 25-million-year-old amber from the Dominican Republic. The endospore was successfully revived. Classification The reclassification from ''Bacillus sphaericus'' to ''Lysinibacillus sphaericus'' is based on the fact that ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Insecticide
Insecticides are pesticides used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. The major use of insecticides is in agriculture, but they are also used in home and garden settings, industrial buildings, for vector control, and control of insect parasites of animals and humans. Acaricides, which kill mites and ticks, are not strictly insecticides, but are usually classified together with insecticides. Some insecticides (including common bug sprays) are effective against other non-insect arthropods as well, such as scorpions, spiders, etc. Insecticides are distinct from insect repellents, which repel but do not kill. Sales In 2016 insecticides were estimated to account for 18% of worldwide pesticide sales. Worldwide sales of insecticides in 2018 were estimated as $ 18.4 billion, of which 25% were neonicotinoids, 17% were pyrethroids, 13% were diamides, and the rest were many other classes which sold for less th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
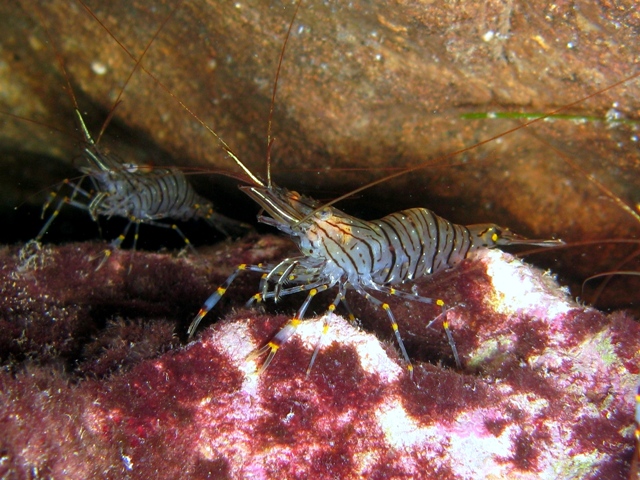
Shrimp
A shrimp (: shrimp (American English, US) or shrimps (British English, UK)) is a crustacean with an elongated body and a primarily Aquatic locomotion, swimming mode of locomotion – typically Decapods belonging to the Caridea or Dendrobranchiata, although some Shrimp#Non-decapods, crustaceans outside of this order are also referred to as "shrimp". Any small crustacean may also be referred to as "shrimp", regardless of resemblance. More narrow definitions may be restricted to Caridea, to smaller species of either of the aforementioned groups, or only the Marine life, marine species. Under a broader definition, ''shrimp'' may be synonymous with prawn, covering stalk-eyed swimming crustaceans with long, narrow muscular tails (Abdomen#Arthropoda, abdomens), long whiskers (Antenna (biology), antennae), and slender, Biramous, biramous legs. They swim forward by paddling the swimmerets on the underside of their abdomens, although their escape response is typically repeated flicks wit ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Index Of Pesticide Articles
This is an index of articles relating to pesticides. 0–9 A B C D E F G H I J K L M N P Q R S T U V W, X, Y, Z See also * List of fungicides * List of herbicides * List of insecticides {{Horticulture and Gardening Index Pesticides Pesticides are substances that are used to pest control, control pest (organism), pests. They include herbicides, insecticides, nematicides, fungicides, and many others (see table). The most common of these are herbicides, which account for a ... Pesticide articles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Azadirachta Indica
''Azadirachta indica'', commonly known as neem, margosa, nimtree or Indian lilac, is a tree in the mahogany family Meliaceae. It is one of the two species in the genus ''Azadirachta''. It is native to the Indian subcontinent and to parts of Southeast Asia, but is naturalized and grown around the world in tropical and subtropical areas. Its fruits and seeds are the source of neem oil. ''Nim'' is a Hindustani noun derived from Sanskrit ''nimba'' (). Description Margosa is a fast-growing tree that can reach a height of , and rarely . It is evergreen, shedding many of its leaves during the dry winter months. The branches are wide and spreading. The fairly dense crown is roundish and may reach a diameter of . The opposite, pinnate leaves are long, with 20 to 30 medium to dark green leaflets about long. The terminal leaflet often is missing. The petioles are short. White and fragrant flowers are arranged in more-or-less drooping axillary panicles which are up to long. The inflo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Genetic Modification
Genetic engineering, also called genetic modification or genetic manipulation, is the modification and manipulation of an organism's genes using technology. It is a set of technologies used to change the genetic makeup of cells, including the transfer of genes within and across species boundaries to produce improved or novel organisms. New DNA is obtained by either isolating and copying the genetic material of interest using recombinant DNA methods or by artificially synthesising the DNA. A construct is usually created and used to insert this DNA into the host organism. The first recombinant DNA molecule was made by Paul Berg in 1972 by combining DNA from the monkey virus SV40 with the lambda virus. As well as inserting genes, the process can be used to remove, or "knock out", genes. The new DNA can either be inserted randomly or targeted to a specific part of the genome. An organism that is generated through genetic engineering is considered to be genetically modif ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Copper
Copper is a chemical element; it has symbol Cu (from Latin ) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkish-orange color. Copper is used as a conductor of heat and electricity, as a building material, and as a constituent of various metal alloys, such as sterling silver used in jewelry, cupronickel used to make marine hardware and coins, and constantan used in strain gauges and thermocouples for temperature measurement. Copper is one of the few metals that can occur in nature in a directly usable, unalloyed metallic form. This means that copper is a native metal. This led to very early human use in several regions, from . Thousands of years later, it was the first metal to be smelted from sulfide ores, ; the first metal to be cast into a shape in a mold, ; and the first metal to be purposely alloyed with another metal, tin, to create bronze, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |