|
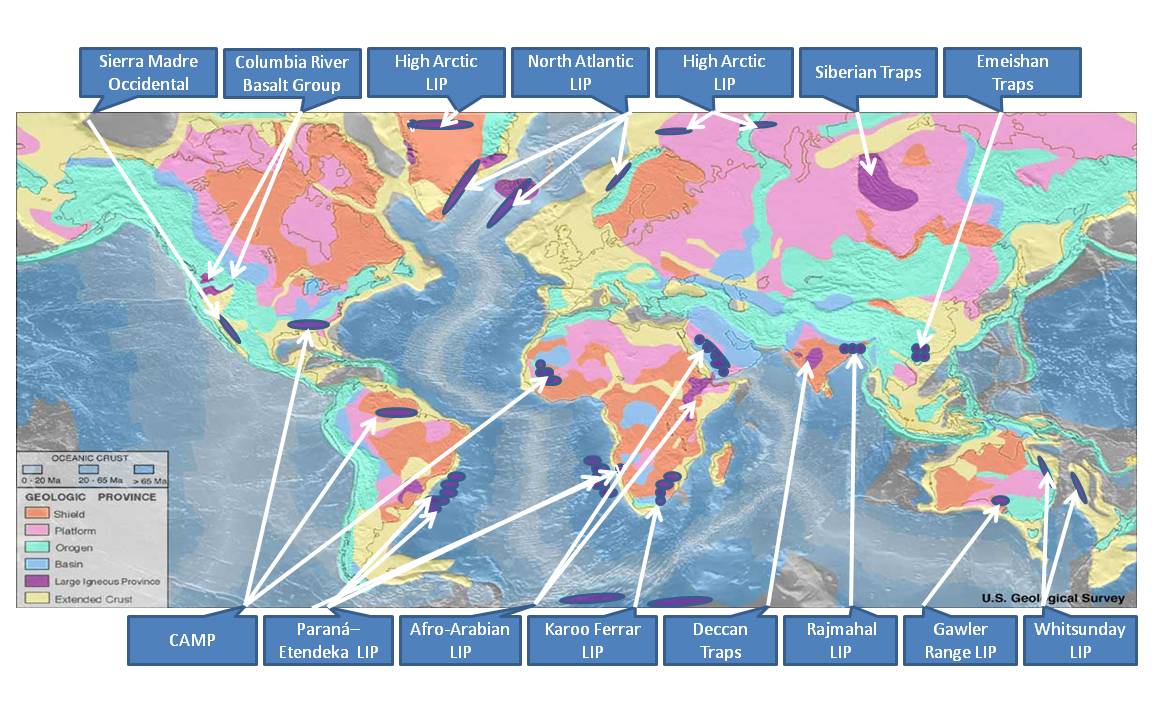
Large Igneous Provinces
A large igneous province (LIP) is an extremely large accumulation of igneous rocks, including intrusive ( sills, dikes) and extrusive (lava flows, tephra deposits), arising when magma travels through the crust towards the surface. The formation of LIPs is variously attributed to mantle plumes or to processes associated with divergent plate tectonics. The formation of some of the LIPs in the past 500 million years coincide in time with mass extinctions and rapid climatic changes, which has led to numerous hypotheses about causal relationships. LIPs are fundamentally different from any other currently active volcanoes or volcanic systems. Overview Definition In 1992, Coffin and Eldholm initially defined the term "large igneous province" as representing a variety of mafic igneous provinces with areal extent greater than 100,000 km2 that represented "massive crustal emplacements of predominantly mafic (magnesium- and iron-rich) extrusive and intrusive rock, and origina ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Flood Basalt Map
A flood is an overflow of water (list of non-water floods, or rarely other fluids) that submerges land that is usually dry. In the sense of "flowing water", the word may also be applied to the inflow of the tide. Floods are of significant concern in agriculture, civil engineering and public health. Environmental issues, Human changes to the environment often increase the intensity and frequency of flooding. Examples for human changes are land use changes such as deforestation and Wetland conservation, removal of wetlands, changes in waterway course or flood controls such as with levees. Global environmental issues also influence causes of floods, namely climate change which causes an Effects of climate change on the water cycle, intensification of the water cycle and sea level rise. For example, climate change makes Extreme weather, extreme weather events more frequent and stronger. This leads to more intense floods and increased flood risk. Natural types of floods include riv ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Plateau
An oceanic or submarine plateau is a large, relatively flat elevation that is higher than the surrounding relief with one or more relatively steep sides. There are 184 oceanic plateaus in the world, covering an area of or about 5.11% of the oceans. The South Pacific region around Australia and New Zealand contains the greatest number of oceanic plateaus (see map). Oceanic plateaus produced by large igneous provinces are often associated with hotspot (geology), hotspots, mantle plumes, and volcanic islands — such as Iceland, Hawaii, Cape Verde, and Kerguelen. The three largest plateaus, the Caribbean large igneous province, Caribbean, Ontong Java Plateau, Ontong Java, and Mid-Pacific Mountains, are located on swell (geology), thermal swells. Other oceanic plateaus, however, are made of rifted continental crust, for example the Falkland Plateau, Lord Howe Rise, and parts of Kerguelen Plateau, Kerguelen, Mascarene Plateau, Seychelles, and Arctic ridges. Plateaus formed by larg ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Volcanology
Volcanology (also spelled vulcanology) is the study of volcanoes, lava, magma and related geology, geological, geophysical and geochemistry, geochemical phenomena (volcanism). The term ''volcanology'' is derived from the Latin language, Latin word ''Vulcan (mythology), vulcan''. Vulcan was the ancient Roman mythology, Roman god of fire. A volcanologist is a geologist who studies the eruptive activity and formation of volcanoes and their current and historic eruptions. Volcanologists frequently visit volcanoes, especially active ones, to observe volcanic eruptions, collect eruptive products including tephra (such as Volcanic ash, ash or pumice), Rock (geology), rock and lava samples. One major focus of enquiry is the prediction of eruptions; there is currently no accurate way to do this, but predicting or forecasting eruptions, like predicting earthquakes, could save many lives. Modern volcanology image:Icelandic tephra.JPG, Volcanologist examining tephra horizons in south- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Biostratigraphy
Biostratigraphy is the branch of stratigraphy which focuses on correlating and assigning relative ages of rock strata by using the fossil assemblages contained within them.Hine, Robert. "Biostratigraphy." ''Oxford Reference: Dictionary of Biology'', 8th ed., Oxford University Press, 2019. The primary objective of biostratigraphy is ''correlation'', demonstrating that a particular horizon in one geological section represents the same period of time as another horizon at a different section. Fossils within these strata are useful because sediments of the same age can look completely different, due to local variations in the sedimentary environment. For example, one section might have been made up of clays and marls, while another has more chalky limestones. However, if the fossil species recorded are similar, the two sediments are likely to have been laid down around the same time. Ideally these fossils are used to help identify biozones, as they make up the basic biostratigraphy ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Richard Stothers
Richard Stothers was an astronomer and planetary scientist with the Goddard Institute for Space Studies, which he joined in June 1961 as a graduate student. Within two years, he had received his Ph.D. from Harvard and became a permanent staff member of the institute, where he spent the remainder of his career. He contributed to the modern understanding of the origin and evolution of stars and, later in life, to climate science. He was able to read original papers in several languages, which allowed him to extract information on historical climate change from ancient writings. Stothers also examined ancient reports of unidentified flying objects An unidentified flying object (UFO) is an object or phenomenon seen in the sky but not yet identified or explained. The term was coined when United States Air Force (USAF) investigations into flying saucers found too broad a range of shape ... and examined the factual basis for myths of "giant serpents". Stothers was raised in N ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Michael Rampino
Michael R. Rampino is a Geologist and Professor of Biology and Environmental Studies at New York University, known for his scientific contributions on causes of mass extinctions of life. Along with colleagues, he's developed theories about periodic mass extinctions being strongly related to the earth's position in relation to the galaxy. "The solar system and its planets experience cataclysms every time they pass "up" or "down" through the plane of the disk-shaped galaxy." These ~30 million year cyclical breaks are an important factor in evolutionary theory, along with other longer 60-million- and 140-million-year cycles potentially caused by mantle plumes within the planet, opining "The Earth seems to have a pulse," He is also a research consultant at NASA's Goddard Institute for Space Studies (GISS) in New York City. Rampino's research has been concentrated in several areas including: studies of climate change on various timescales; the products and dynamics of volcanic eruption ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Extinction Event
An extinction event (also known as a mass extinction or biotic crisis) is a widespread and rapid decrease in the biodiversity on Earth. Such an event is identified by a sharp fall in the diversity and abundance of multicellular organisms. It occurs when the rate of extinction increases with respect to the background extinction rate and the rate of speciation. Estimates of the number of major mass extinctions in the last 540 million years range from as few as five to more than twenty. These differences stem from disagreement as to what constitutes a "major" extinction event, and the data chosen to measure past diversity. The "Big Five" mass extinctions In a landmark paper published in 1982, Jack Sepkoski and David M. Raup identified five particular geological intervals with excessive diversity loss. They were originally identified as outliers on a general trend of decreasing extinction rates during the Phanerozoic, but as more stringent statistical tests have been applied t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Andes
The Andes ( ), Andes Mountains or Andean Mountain Range (; ) are the List of longest mountain chains on Earth, longest continental mountain range in the world, forming a continuous highland along the western edge of South America. The range is long and wide (widest between 18th parallel south, 18°S and 20th parallel south, 20°S latitude) and has an average height of about . The Andes extend from south to north through seven South American countries: Argentina, Chile, Bolivia, Peru, Ecuador, Colombia, and Venezuela. Along their length, the Andes are split into several ranges, separated by intermediate depression (geology), depressions. The Andes are the location of several high plateaus—some of which host major cities such as Quito, Bogotá, Cali, Arequipa, Medellín, Bucaramanga, Sucre, Mérida, Mérida, Mérida, El Alto, and La Paz. The Altiplano, Altiplano Plateau is the world's second highest after the Tibetan Plateau. These ranges are in turn grouped into three majo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Central Atlantic Magmatic Province
The Central Atlantic magmatic province (CAMP) is the Earth's largest continental large igneous province, covering an area of roughly 11 million km2. It is composed mainly of basalt that formed before Pangaea broke up in the Mesozoic Era, near the end of the Triassic and the beginning of the Jurassic periods. The subsequent breakup of Pangaea created the Atlantic Ocean, but the massive igneous upwelling provided a legacy of basaltic dikes, sills, and lavas now spread over a vast area around the present central North Atlantic Ocean, including large deposits in northwest Africa, southwest Europe, as well as northeast South America and southeast North America (found as continental tholeiitic basalts in subaerial flows and intrusive bodies). The name and CAMP acronym were proposed by Andrea Marzoli (Marzoli et al. 1999) and adopted at a symposium held at the 1999 Spring Meeting of the American Geophysical Union. The CAMP volcanic eruptions occurred about 201 million years ago and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
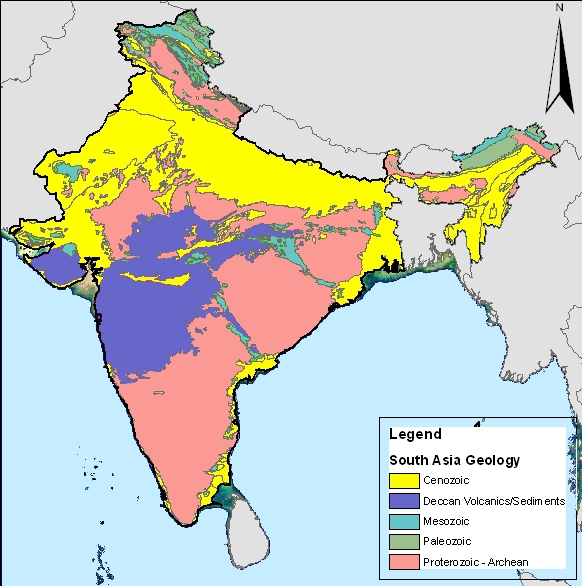
Deccan Traps
The Deccan Traps are a large igneous province of west-central India (17–24°N, 73–74°E). They are one of the largest volcanic features on Earth, taking the form of a large shield volcano. They consist of many layers of solidified flood basalt that together are more than about thick, cover an area of about , and have a volume of about . Originally, the Deccan Traps may have covered about ,"What really killed the dinosaurs?" Jennifer Chu, MIT News Office, 11 December 2014 with a correspondingly larger original volume. This volume overlies the age Indian Shield, which is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Island Arc
Island arcs are long archipelago, chains of active volcanoes with intense earthquake, seismic activity found along convergent boundary, convergent plate tectonics, tectonic plate boundaries. Most island arcs originate on oceanic crust and have resulted from the descent of the lithosphere into the Earth's mantle, mantle along the subduction zone. They are the principal way by which continental growth is achieved. Island arcs can either be active or inactive based on their seismicity and presence of volcanoes. Active arcs are ridges of recent volcanoes with an associated deep seismic zone. They also possess a distinct curved form, a chain of active or recently extinct volcanoes, a oceanic trench, deep-sea trench, and a large negative Bouguer anomaly on the convex side of the volcanic arc. The small positive gravity anomaly associated with volcanic arcs has been interpreted by many authors as due to the presence of dense volcanic rocks beneath the arc. Inactive arcs are a chain of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Columbia River Basalt Group
The Columbia River Basalt Group (CRBG) is the youngest, smallest and one of the best-preserved continental flood basalt provinces on Earth, covering over mainly eastern Oregon and Washington, western Idaho, and part of northern Nevada. The basalt group includes the Steens and Picture Gorge basalt formations. Introduction During the middle to late Miocene epoch, the Columbia River flood basalts engulfed about of the Pacific Northwest, forming a large igneous province with an estimated volume of . Eruptions were most vigorous 17–14 million years ago, when over 99 percent of the basalt was released. Less extensive eruptions continued 14–6 million years ago. Erosion resulting from the Missoula Floods has extensively exposed these lava flows, laying bare many layers of the basalt flows at Wallula Gap, the lower Palouse River, the Columbia River Gorge and throughout the Channeled Scablands. The Columbia River Basalt Group is thought to be a potential link ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |