|
Landscape Design
Landscape design is an independent profession and a design and art tradition, practiced by landscape designers, combining nature and culture. In contemporary practice, landscape design bridges the space between landscape architecture and garden design. Design scope Landscape design focuses on both the integrated master landscape planning of a property and the specific garden design of landscape elements and plants within it. The practical, Design, aesthetic, Horticulture, horticultural, and environmental sustainability are also components of landscape design, which is often divided into hardscape design and softscape design. Landscape designers often collaborate with related disciplines such as architecture, civil engineering, surveying, Landscaping, landscape contracting, and artisan specialties. Design projects may involve two different professional roles: landscape design and landscape architecture. * Landscape design typically involves artistic composition and artisanship, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Southwest Corner Of Central Park, Looking East, NYC
The points of the compass are a set of horizontal, radially arrayed compass directions (or azimuths) used in navigation and cartography. A '' compass rose'' is primarily composed of four cardinal directions—north, east, south, and west—each separated by 90 degree (angle), degrees, and secondarily divided by four ordinal (intercardinal) directions—northeast, southeast, southwest, and northwest—each located halfway between two cardinal directions. Some disciplines such as meteorology and navigation further divide the compass with additional azimuths. Within European tradition, a fully defined compass has 32 "points" (and any finer subdivisions are described in fractions of points). Compass points or compass directions are valuable in that they allow a user to refer to a specific azimuth in a Colloquialism, colloquial fashion, without having to compute or remember degrees. Designations The names of the compass point directions follow these rules: 8-wind compass rose ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Native Plant
In biogeography, a native species is indigenous to a given region or ecosystem if its presence in that region is the result of only local natural evolution (though often popularised as "with no human intervention") during history. The term is equivalent to the concept of indigenous or autochthonous species. A wild organism (as opposed to a domesticated organism) is known as an introduced species within the regions where it was anthropogenically introduced. If an introduced species causes substantial ecological, environmental, and/or economic damage, it may be regarded more specifically as an invasive species. A native species in a location is not necessarily also endemic to that location. Endemic species are ''exclusively'' found in a particular place. A native species may occur in areas other than the one under consideration. The terms endemic and native also do not imply that an organism necessarily first originated or evolved where it is currently found. Notion The notion ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Natural Resource Management
Natural resource management (NRM) is the management of natural resources such as Land (economics), land, water, soil, plants and animals, with a particular focus on how management affects the quality of life for both present and future generations (stewardship). Natural resource management deals with managing the way in which people and natural landscapes interact. It brings together natural heritage management, land use planning, water management, Conservation biology, bio-diversity conservation, and the future sustainability of industries like agriculture, mining, tourism, fisheries and forestry. It recognizes that people and their livelihoods rely on the health and productivity of our landscapes, and their actions as stewards of the land play a critical role in maintaining this health and productivity. Natural resource management specifically focuses on a scientific and technical understanding of resources and ecology and the Life-supporting capacity of those resources. Env ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Horticulture
Horticulture (from ) is the art and science of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, trees, shrubs and ornamental plants. Horticulture is commonly associated with the more professional and technical aspects of plant cultivation on a smaller and more controlled scale than agronomy. There are various divisions of horticulture because plants are grown for a variety of purposes. These divisions include, but are not limited to: propagation, arboriculture, landscaping, floriculture and turf maintenance. For each of these, there are various professions, aspects, tools used and associated challenges -- each requiring highly specialized skills and knowledge on the part of the horticulturist. Typically, horticulture is characterized as the ornamental, small-scale and non-industrial cultivation of plants; horticulture is distinct from gardening by its emphasis on scientific methods, plant breeding, and technical cultivation practices, while gardening, even at a professional level, tends ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Environmental Design
Environmental design is the process of addressing surrounding environmental parameters when devising plans, programs, policies, buildings, or products. It seeks to create spaces that will enhance the natural, social, cultural and physical environment of particular areas. Classical prudent design may have always considered environmental factors; however, the environmental movement beginning in the 1940s has made the concept more explicit. Environmental design can also refer to the applied arts and sciences dealing with creating the human-designed environment. These fields include architecture, geography, urban planning, landscape architecture, and interior design. Environmental design can also encompass interdisciplinary areas such as historical preservation and lighting design. In terms of a larger scope, environmental design has implications for the industrial design of products: innovative automobiles, wind power generators, solar-powered equipment, and other kinds of equipment ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agricultural Education
Agricultural education is the systematic and organized teaching, instruction and training (theoretical as well as hands-on, real-world fieldwork-based) available to students, farmers or individuals interested in the science, business and technology of agriculture (animal and plant production) as well as the management of land, environment and natural resources. Agricultural education is part of the curriculum of primary and secondary schools along with tertiary institutions such as colleges, universities and vocational and technical schools. Agricultural education resources is provided by youth organizations, farm apprenticeships/internships, non-profit organizations, and government agencies/ministries. As well as agricultural workshops, trainings, shows, fairs, and research institutions. Online/distance learning programs are also available. In institutions, agricultural education serves as preparation for employment or careers in the farming and agricultural sector. Student ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beatrix Farrand
Beatrix Cadwalader Farrand (née Jones; June 19, 1872 – February 28, 1959) was an American landscape gardener and landscape architect. Her career included commissions to design about 110 gardens for private residences, estates and country homes, public parks, botanic gardens, college campuses, and the White House. Only a few of her major works survive: Dumbarton Oaks in Washington, D.C., the Abby Aldrich Rockefeller Garden on Mount Desert, Mount Desert, Maine, the restored Farm House Garden in Bar Harbor, Maine, Bar Harbor, the Peggy Rockefeller Rose Garden at the New York Botanical Garden (constructed after Farrand's death, using her original plans, and opened in 1988), and elements of the campuses of Princeton University, Princeton, Yale University, Yale, and Occidental College, Occidental.Parke, Margaret. "A portrait of Beatrix Farrand", ''American Horticulturist'', April 1985, pp. 10–13. Farrand was one of the founding eleven members, and the only woman, of the American ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Landscape Architect
A landscape architect is a person who is educated in the field of landscape architecture. The practice of landscape architecture includes: site analysis, site inventory, site planning, land planning, planting design, grading, storm water management, sustainable design, construction specification, and ensuring that all plans meet the current building codes and local and federal ordinances. The practice of landscape architecture dates to some of the earliest of human cultures and just as much as the practice of medicine has been inimical to the species and ubiquitous worldwide for several millennia. However, this article examines the modern profession and educational discipline of those practicing the design of landscape architecture. In the 1700s, Humphry Repton described his occupation as "landscape gardener" on business cards he had prepared to represent him in work that now would be described as that of a landscape architect. The title, "landscape architect", was first used ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
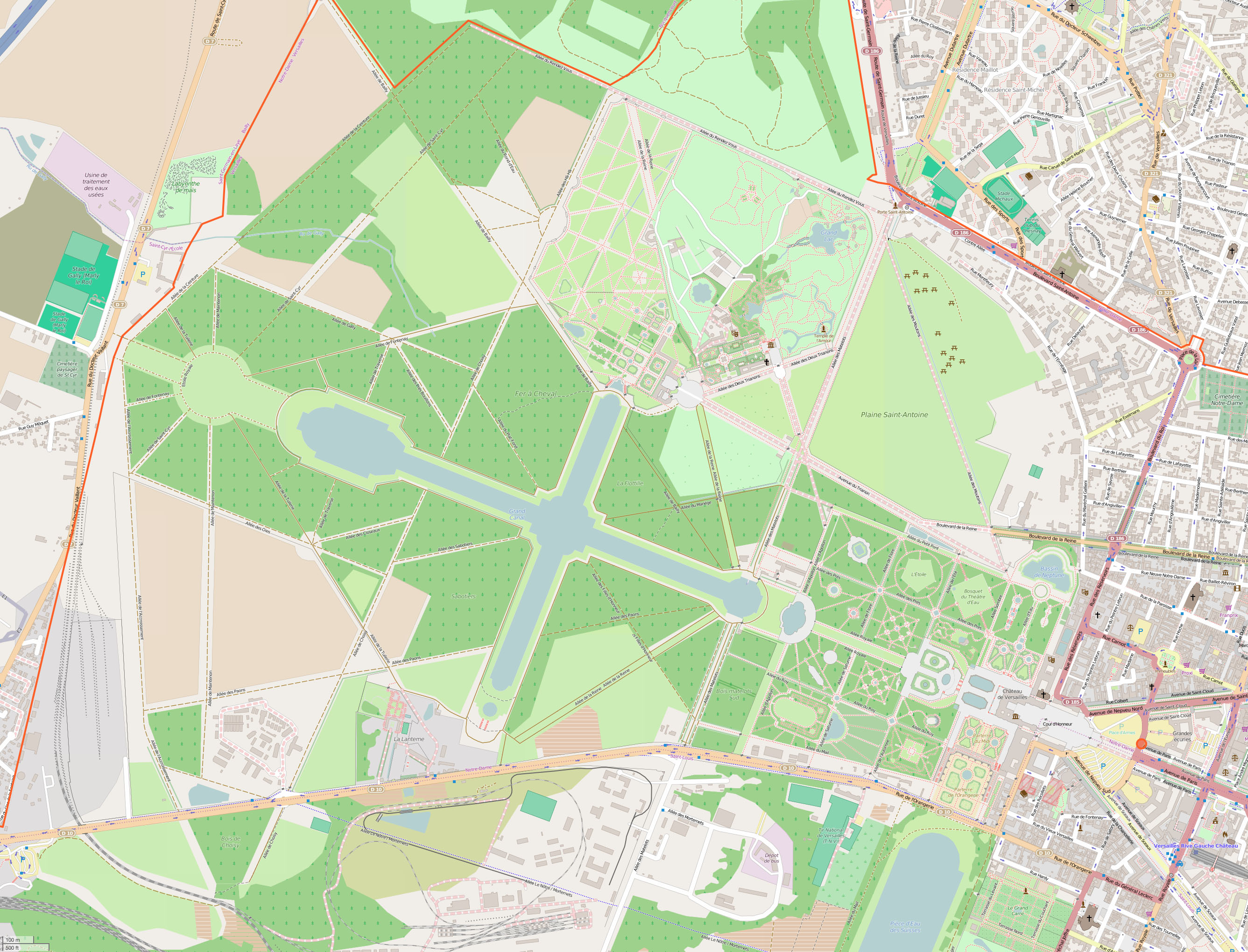
Gardens Of Versailles
The Gardens of Versailles ( ) occupy part of what was once the ''Domaine royal de Versailles'', the royal demesne of the Palace of Versailles, château of Versailles. Situated to the west of the Palace of Versailles, palace, the gardens cover some of land, much of which is landscaped in the classic French formal garden style perfected here by André Le Nôtre. Beyond the surrounding belt of woodland, the gardens are bordered by the urban areas of Versailles (city), Versailles to the east and Le Chesnay to the north-east, by the National Arboretum de Chèvreloup to the north, the Versailles plain (a protected wildlife preserve) to the west, and by the Satory Forest to the south. Administered by the Public Establishment of the Palace, Museum and National Estate of Versailles, an autonomous public entity operating under the aegis of the Ministry of Culture (France), French Ministry of Culture, the gardens are now one of the most visited public sites in France, receiving more than s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
André Le Nôtre
André Le Nôtre (; 12 March 1613 – 15 September 1700), originally rendered as André Le Nostre, was a French landscape architect and the principal gardener of King Louis XIV of France. He was the landscape architect who designed Gardens of Versailles, the gardens of the Palace of Versailles; his work represents the height of the French formal garden style, or ''French formal garden, jardin à la française''. Prior to working on Versailles, Le Nôtre collaborated with Louis Le Vau and Charles Le Brun on the park at Vaux-le-Vicomte. His other works include the design of gardens and parks at Bicton, Devon, Bicton Park Botanical Gardens, Château de Chantilly, Chantilly, Palace of Fontainebleau, Fontainebleau, Château de Saint-Cloud, Saint-Cloud and Château de Saint-Germain-en-Laye, Saint-Germain. His contribution to Urban planning, planning was also significant: at the Tuileries Palace, Tuileries in Paris he extended the westward vista, which later became the Champs-Élys ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Focal Point
{{disambiguation ...
Focal point may refer to: * Focus (optics) * Focus (geometry) * Conjugate points, also called focal points * Focal point (game theory) * Unicom Focal Point, a portfolio management software tool * Focal point review, a human resources process for employee evaluation * ''Focal Point'' (album), a 1976 studio album by McCoy Tyner * " Focal Point: Mark of the Leaf", a ''Naruto'' episode See also *Foca Point, Signy Island, South Orkney Islands *Focal (other) *Focus (other) Focus (: foci or focuses) may refer to: Arts * Focus or Focus Festival, former name of the Adelaide Fringe arts festival in East Australia Film * ''Focus'' (2001 film), a 2001 film based on the Arthur Miller novel * ''Focus'' (2015 film), a 201 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |