|
Lakshmana
Lakshmana (, ), also known as Laxmana, Lakhan, Saumitra, and Ramanuja, is the younger brother of Rama in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is considered as an incarnation of Shesha, the lord of serpents. Lakshmana was married to Urmila, and is known for his loyalty and dedication towards Rama. Lakshmana was born to King Dasharatha of Ayodhya and Queen Sumitra. Shatrughna, is his twin brother. He was married to Urmila, after his brother Rama married Sita in her swayamvara. Lakshmana devoted himself to Rama since childhood and accompanied him during his fourteen-year exile, serving him and Sita endlessly. He also played a pivotal role in the war and killed Meghanada. Lakshmana is worshipped in Hinduism, at various places in India, alongside Rama and Sita. Etymology The name Lakshmana is of Sanskrit origin, which means 'the one endowed with auspicious signs'. He bears the epithets of Saumitra (, ) and Ramanuja (, ). Legend Birth and early life King Dasharatha of A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chandraketu
Lakshmana (, ), also known as Laxmana, Lakhan, Saumitra, and Ramanuja, is the younger brother of Rama in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is considered as an incarnation of Shesha, the lord of serpents. Lakshmana was married to Urmila, and is known for his loyalty and dedication towards Rama. Lakshmana was born to King Dasharatha of Ayodhya and Queen Sumitra. Shatrughna, is his twin brother. He was married to Urmila, after his brother Rama married Sita in her swayamvara. Lakshmana devoted himself to Rama since childhood and accompanied him during his fourteen-year exile, serving him and Sita endlessly. He also played a pivotal role in the war and killed Meghanada. Lakshmana is worshipped in Hinduism, at various places in India, alongside Rama and Sita. Etymology The name Lakshmana is of Sanskrit origin, which means 'the one endowed with auspicious signs'. He bears the epithets of Saumitra (, ) and Ramanuja (, ). Legend Birth and early life King Dasharatha of Ayodhya ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Exile Of Rama
The exile of Rama is an event featured in the ''Ramayana'',Exile of Rama begins in the ''Ayōdhyākānda,'' or the Book of Ayodhya''.'' the second chapter of the Ramayana, while ends in the ''Uttarakānda'' or the Book of Later Events. the last chapter of the epic. and is an important period in the life of Rama. In the epic, Rama is exiled by his father, Dasharatha, under the urging of his stepmother Kaikeyi, accompanied by his wife Sita and half-brother Lakshmana for 14 years. Rama's exile is a prelude to subsequent events of the epic, such as abduction of his wife Sita,According to some sources, such as Ramcharitmanas by Tulsidas (1511–1623) states that a ''Maya Sita, Māyā Sita'' (The Illusional Sita) or ''Chāyā Sita'' (The shadow of Sita) was abducted by Ravana, while real actual Sita kept safe with Agni, the List of fire deities, god of fire, and was retained during ''Agnipariksha.'' his meeting with Hanuman and Sugriva, his battle with Ravana, and ultimately, the killi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
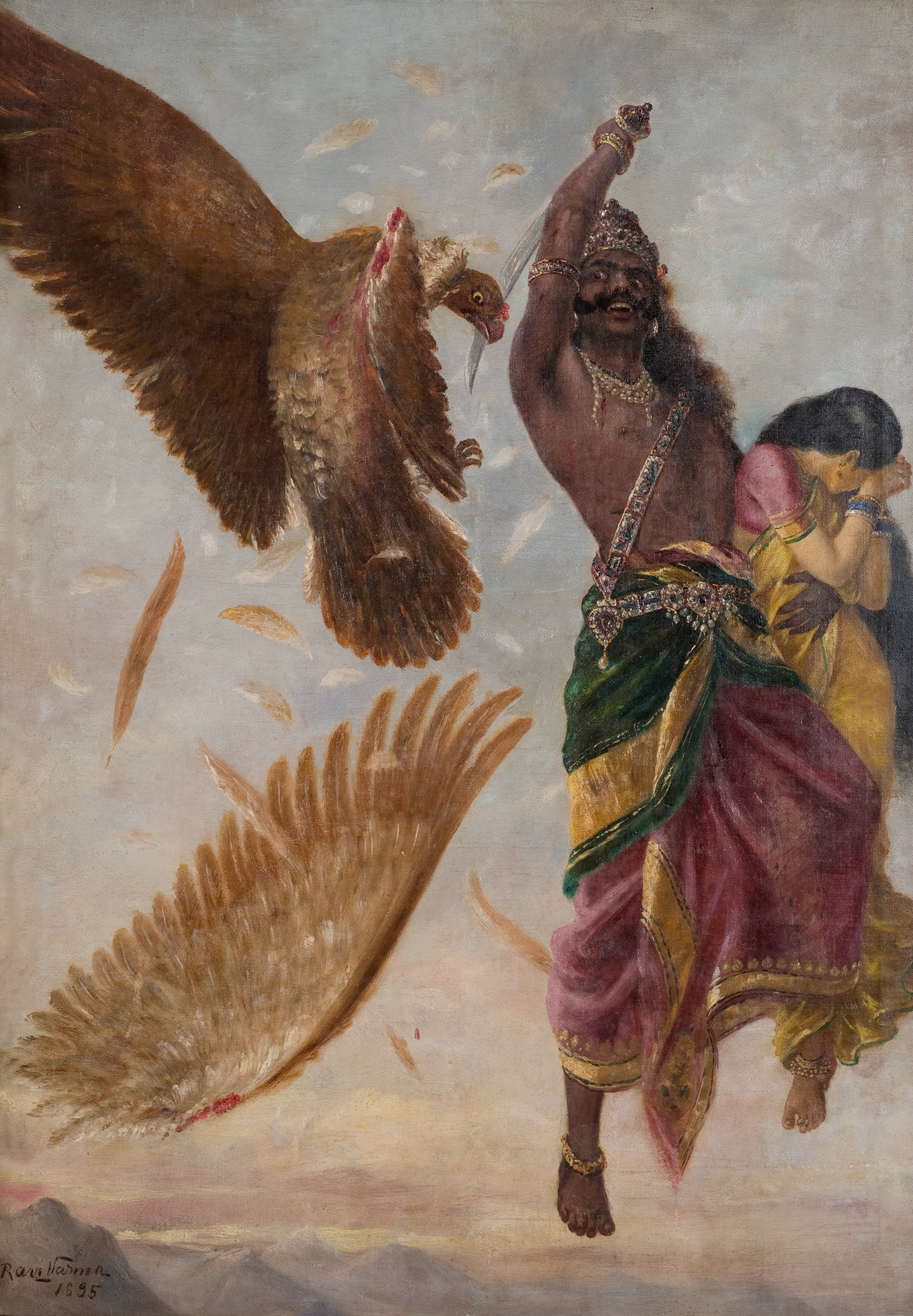
Indrajit
Meghanada (, ), also referred to by his epithet Indrajit (), according to Hindu texts, was the eldest son of Ravana and the crown prince of Lanka, who conquered Indraloka (Heaven). He is regarded as one of the greatest warriors in Hindu texts. He is a major character mentioned in the Indian epic ''Ramayana.'' Meghanada is the central character in Bengali epic poem '' Meghnad Badh Kavya''. He played an active role in the great war between Rama and Ravana. He acquired many kinds of celestial weapons from his Guru Shukra. His most prominent feat is having defeated the devas in heaven. Using the Brahmastra, Indrajit killed 670 million vanaras in a single day; nearly exterminating the entirety of the vanara race. No warrior had ever achieved this statistical feat before in the Ramayana. He is the only warrior in the entire Ramayana to defeat both Rama and Lakshmana twice while they were both armed by making them unconscious in a battle with the help of astras and sorcery (once ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urmila
Urmila (), is a Hindu goddess and the princess of Videha in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. She is considered to be an avatāra of Nagalakshmi, the serpent goddess. Urmila was married to Lakshmana and is known for her dedication towards her husband, for her sacrifice. Urmila was born as the daughter of King Janaka of Mithila and Queen Sunayana. Sita, the female protagonist of the epic, is her elder sister. She was married to Lakshmana, after her sister's '' svayamvara''. According to a legend, Urmila slept continuously for fourteen years, so that her husband could protect Rama and Sita during the exile. She is notable for this unparalleled sacrifice, which is called ''Urmila Nidra''. Urmila is worshipped in Hinduism, at various places in India, alongside her husband. Etymology The name Urmila is of Sanskrit origin, and could be divided into ''Ur'' meaning waves, and ''mila'', meaning to join''.'' Thus'','' her name means 'waves of passion that unite a couple'. Her name al ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rama
Rama (; , , ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the seventh and one of the most popular avatars of Vishnu. In Rama-centric Hindu traditions, he is considered the Supreme Being. Also considered as the ideal man (''maryāda'' ''puruṣottama''), Rama is the male protagonist of the Hindu epic '' Ramayana''. His birth is celebrated every year on Rama Navami, which falls on the ninth day of the bright half ( Shukla Paksha) of the lunar cycle of Chaitra (March–April), the first month in the Hindu calendar. According to the ''Ramayana'', Rama was born to Dasaratha and his first wife Kausalya in Ayodhya, the capital of the Kingdom of Kosala. His siblings included Lakshmana, Bharata, and Shatrughna. He married Sita. Born in a royal family, Rama's life is described in the Hindu texts as one challenged by unexpected changes, such as an exile into impoverished and difficult circumstances, and challenges of ethical questions and moral dilemmas. The most not ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sita
Sita (; ), also known as Siya, Jānaki and Maithili, is a Hindu goddess and the female protagonist of the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sita is the consort of Rama, the avatar of god Vishnu, and is regarded as an avatar of goddess Lakshmi. She is the chief goddess of the Ramanandi Sampradaya and is the goddess of beauty and devotion. Sita's birthday is celebrated every year on the occasion of Sita Navami. Described as the daughter of Bhūmi (the earth), Sita is brought up as the adopted daughter of King Janaka of Videha. Sita, in her youth, chooses Rama, the prince of Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya as her husband in a swayamvara. After the Sita Swayamvara, swayamvara, she accompanies her husband to his kingdom but later chooses to accompany him along with her brother-in-law Lakshmana, in his exile. While in exile, the trio settles in the Dandaka forest from where she is abducted by Ravana, the Rakshasa king of Lanka. She is imprisoned in the garden of Ashoka Vatika, in Lanka, until she ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ramayana
The ''Ramayana'' (; ), also known as ''Valmiki Ramayana'', as traditionally attributed to Valmiki, is a smriti text (also described as a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic) from ancient India, one of the two important epics of Hinduism known as the ''Itihasas'', the other being the ''Mahabharata''. The epic narrates the life of Rama, the seventh ''avatar'' of the Hindu deity Vishnu, who is a prince of Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya in the kingdom of Kosala. The epic follows Exile of Lord Rama, his fourteen-year exile to the forest urged by his father King Dasharatha, on the request of Rama's stepmother Kaikeyi; his travels across the forests in the Indian subcontinent with his wife Sita and brother Lakshmana; the kidnapping of Sita by Ravana, the king of Lanka, that resulted in bloodbath; and Rama's eventual return to Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya along with Sita to be crowned as a king amidst jubilation and celebration. Scholarly estimates for the earliest stage ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sumitra
Sumitra (, IAST: Sumitrā) is a princess of Kashi and the queen of Kosala in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. Sumitra is the second queen consort of Dasharatha, the king of Kosala, who ruled from Ayodhya. Regarded to be a wise and dedicated woman, she is the mother of the twins Lakshmana and Shatrughna. Etymology The name Sumitra is of Sanskrit origin, and could be divided into ''Su'' meaning good, and ''Mitra,'' meaning friend''.'' Thus'','' her name means 'a good friend' or 'one with a friendly nature'. She is known in other languages as Tamil: சுமித்திரை (), Burmese: Thumitra, Malay: Samutra, Khmer '' and '' ''Samutthra Thewi''). Legend Birth While Valmiki is silent on her parentage, later texts variously described her as a princess of Kashi or of Magadha, and belonging to the Haiheya clan. She is called the daughter of Magadha, as per Kalidasa’s '' Raghuvamsham''. Kalidasa wrote, Marriage and children Sumitra was married to king Da ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bharata (Ramayana)
Bharata ( ) is the younger brother of Rama in Hindu epic ''Ramayana'', and the regent of Ayodhya during Rama's exile. Bharata is considered as an incarnation of the Panchajanya of god Vishnu, and was married to Mandavi. Bharata is regarded for his devotion towards his elder brother Rama. He went against his mother and refused the throne of Ayodhya while elder brother, Rama, was exiled. Bharata also lived a life in exile, in Nandigram, Ayodhya, till Rama, Sita and Lakshmana returned to Ayodhya. He is mostly worshipped in Kerala. Etymology The name Bharata is of Sanskrit origin. His name means "one to be r beingmaintained". Legend Birth and early life King Dasharatha of Ayodhya had three wives: Kausalya, Kaikeyi, and Sumitra. Bharata was born to Kaikeyi, while Rama was born to Kausalya, and Lakshmana and Shatrughna were born to Sumitra. In the ''Ramayana'', he is described as an incarnation of Panchajanya. While Lakshmana was a loyalist of Rama, his twin, Shatrughn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shatrughna
''Shatrughna'' (, ), also known as Ripudaman, is the younger brother of Rama, and King of Mathura, Madhupura and Vidisha, in the Hindu epic ''Ramayana''. He is considered as an incarnation of the Sudarshana Chakra of god Vishnu, and was married to Shrutakirti. Shatrughna is the twin of Lakshmana. He is a loyalist of Bharata (Ramayana), Bharata, just like Lakshmana is to Rama. Shatrughna appears as the 412th name of Vishnu in the ''Vishnu Sahasranama'' of the ''Mahabharata''. Etymology The name Shatrughna is of Sanskrit origin. ''Shatru'' means 'enemy' and ''Ghna'' means 'kill'. His name means 'killer of enemies'. Legend Birth and early life King Dasharatha of Ayodhya (Ramayana), Ayodhya had three wives: Kausalya, Kaikeyi, and Sumitra. Shatrughan and his elder brother Lakshmana were born to Sumitra, while Rama and Bharata (Ramayana), Bharata were born to Kausalya and Kaikeyi. In the ''Ramayana'', he is described as an incarnation of Sudarshana Chakra. Marriage to Shrutakir ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shesha
Shesha (), also known by his epithets Sheshanaga () and Adishesha (), is a serpentine demigod ( naga) and king of the serpents ( Nagaraja), as well as a primordial being of creation in Hinduism. In the Puranas, Shesha is said to hold all the planets of the universe on his hoods and to constantly sing the glories of Vishnu from all his mouths. He is sometimes referred to as Ananta Shesha. The Narayana form of Vishnu is often depicted as resting on Shesha, accompanied by his consort Lakshmi. Shesha is considered as one of the two mounts of Vishnu alongside Garuda. He is said to have descended upon Earth in the following human forms or incarnations: Lakshmana, brother of Vishnu's incarnation Rama during the Treta Yuga, and according to some traditions, as Balarama, brother of Vishnu's incarnation Krishna during the Dvapara Yuga. According to the Mahabharata (Adi Parva), his father was Kashyapa and his mother Kadru, though in other accounts, he is usually a primordial being cre ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Raghuvaṃśa
(Devanagari: , lit. 'lineage of Raghu') is a Sanskrit epic poem ('' mahakavya'') by the celebrated Sanskrit poet Kalidasa. Though an exact date of composition is unknown, the poet is presumed to have flourished in the 5th century CE. It narrates, in 19 ''sarga''s (cantos), the stories related to the Raghu dynasty, namely the family of Dilipa and his descendants up to Agnivarna, who include Raghu, Dasharatha and Rama. The earliest surviving commentary written on the work is that of the 10th-century Kashmiri scholar Vallabhadeva. The most popular and widely available commentary, however, is the ''Sanjivani'', written by Mallinatha (ca.1350–1450). Contents The ''Raghuvaṃśa'' is a mahākāvya (roughly, epic poem) containing 1564 stanzas. It describes the line of kings of the Raghu dynasty (also known as the ''sūryavaṃśa'' or the solar dynasty) that includes Raghu. It is written in 19 ''sarga''s (cantos), that can be regarded as being divided into three parts:Ryde ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |