|
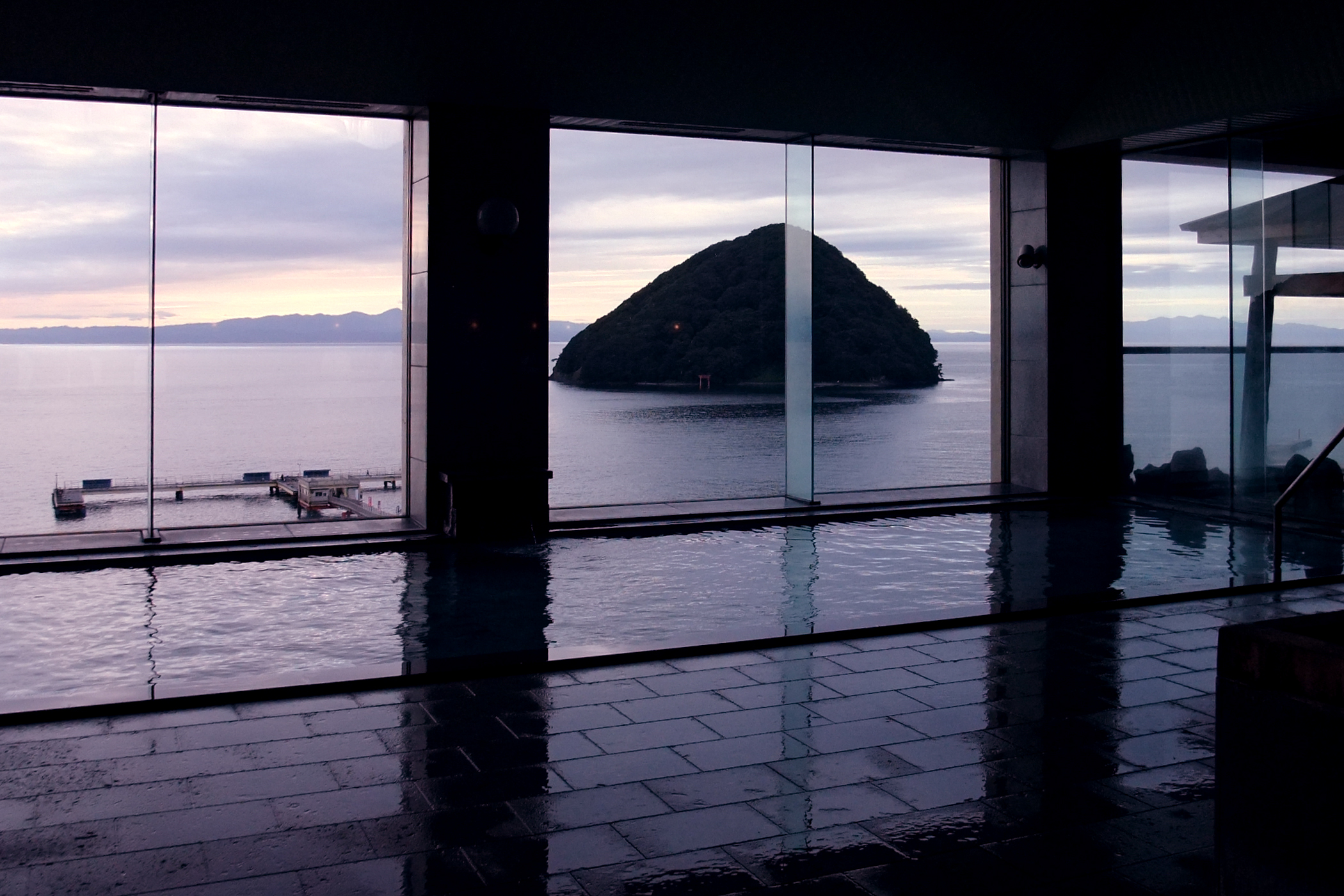
Lake Tōgō
is a brackish lake located in the town of Yurihama, Tottori Prefecture in the San'in Region of Japan. It has a circumference of 12 kilometers and is separated from the Sea of Japan by a narrow coastal strip. Lake Tōgō was a cove in ancient Japan that gradually became separated from the sea by sedimentation to become a lake. It is now connected to the Sea of Japan through Hashizu River, which is about 2 kilometers long. The lake has a number of hot springs on its bed and around its circumference. The area has been inhabited since prehistoric times, and the Hashizu Kofun Cluster located between the lake and the sea is believed to have belonged to the local ruling family that ruled the port during the Kofun period. Also in the area are a number of onsen In Japan, are hot springs and the bathing facilities and Ryokan (inn), traditional inns around them. There are approximately 25,000 hot spring sources throughout Japan, and approximately 3,000 ''onsen'' establishments ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yurihama, Tottori
is a List of towns in Japan, town located in Tōhaku District, Tottori, Tōhaku District, Tottori Prefecture, Japan. , the town had an estimated population of 16,515 in 6452 households and a population density of 210 persons per km². The total area of the town is . Geography Yurihama is located in central Tottori Prefecture, bordered by the Sea of Japan to the north. It is designated as a Snow country (Japan), heavy snowfall area. The Hawai Plain lies within Yurihama, near the coastline and is a flat section of land stretching from the eastern bank of the Tenjin River to the environs of Lake Tōgō, and forms part of the greater Kurayoshi Plain. Many of the town's rice farming plots are located on the Hawai Plain. Besides this section of land, much of the inland areas within the town are mountainous. Lake Tōgō Lake is a brackish lagoon, formed due to the sedimentation of the Tenjin River and the development of the Hōjō sand hills, cutting it off from the ocean. Natural hot s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tottori Prefecture
is a Prefectures of Japan, prefecture of Japan located in the Chūgoku region of Honshu. Tottori Prefecture is the List of Japanese prefectures by population, least populous prefecture of Japan at 538,525 (2023) and has a geographic area of . Tottori Prefecture borders Shimane Prefecture to the west, Hiroshima Prefecture to the southwest, Okayama Prefecture to the south, and Hyōgo Prefecture to the east. Tottori, Tottori, Tottori is the capital and largest city of Tottori Prefecture, with other major cities including Yonago, Kurayoshi, and Sakaiminato. Tottori Prefecture is home to the Tottori Sand Dunes, the largest sand dunes system in Japan, and Mount Daisen, the highest peak in the Chūgoku Mountains. Etymology The word "Tottori" in Japanese is formed from two ''kanji'' characters. The first, , means "bird" and the second, means "to get". Early residents in the area made their living catching the region's plentiful waterfowl. The name first appears in the in the 23rd y ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Brackish Water
Brackish water, sometimes termed brack water, is water occurring in a natural environment that has more salinity than freshwater, but not as much as seawater. It may result from mixing seawater (salt water) and fresh water together, as in estuary, estuaries, or it may occur in brackish Fossil water, fossil aquifers. The word comes from the Middle Dutch root '':wikt:brak#Dutch, brak''. Certain human activities can produce brackish water, in particular civil engineering projects such as dikes and the flooding of coastal marshland to produce brackish water pools for freshwater prawn farming. Brackish water is also the primary waste product of the Osmotic power, salinity gradient power process. Because brackish water is hostile to the growth of most terrestrial plant species, without appropriate management it can be damaging to the environment (see article on shrimp farming, shrimp farms). Technically, brackish water contains between 0.5 and 30 grams of salt per litre—more ofte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
San'in Region
The is an area in the southwest of Honshū, the main island of Japan. It consists of the northern part of the Chūgoku region, facing the Sea of Japan. Specifically, it is the two prefectures of Shimane Prefecture, Shimane and Tottori Prefecture, Tottori. Etymology The name San'in in the Japanese language is formed from two kanji characters. The first, , "mountain", and the second, represents the "yin" of yin and yang. The name means the northern, shady side of the mountains in contrast to the ''yang'' "southern, sunny" San'yō region to the south. History Early history The San'in region has numerous Japanese Paleolithic, Paleolithic and Jōmon period (14,000 – 300 BC) remains, but its Yayoi period (300 BC – 250 AD) remains are the largest in Japan. The Mukibanda Yayoi remains in the low foothills of Mount Daisen in the cities of Daisen, Tottori, Daisen and Yonago, Tottori, Yonago, Tottori Prefecture are the largest in Japan. The site is still only partially exc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sea Of Japan
The Sea of Japan is the marginal sea between the Japanese archipelago, Sakhalin, the Korean Peninsula, and the mainland of the Russian Far East. The Japanese archipelago separates the sea from the Pacific Ocean. Like the Mediterranean Sea, it has almost no tides due to its nearly complete enclosure from the Pacific Ocean. This isolation also affects faunal diversity and salinity, both of which are lower than in the open ocean. The sea has no large islands, bays or capes. Its water balance is mostly determined by the inflow and outflow through the straits connecting it to the neighboring seas and the Pacific Ocean. Few rivers discharge into the sea and their total contribution to the water exchange is within 1%. The seawater has an elevated concentration of Oxygen saturation, dissolved oxygen that results in high biological productivity. Therefore, fishing is the dominant economic activity in the region. The intensity of shipments across the sea has been moderate owing to politi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hot Spring
A hot spring, hydrothermal spring, or geothermal spring is a Spring (hydrology), spring produced by the emergence of Geothermal activity, geothermally heated groundwater onto the surface of the Earth. The groundwater is heated either by shallow bodies of magma (molten rock) or by circulation through fault (geology), faults to hot rock deep in the Earth's crust. Hot spring water often contains large amounts of dissolved minerals. The chemistry of hot springs ranges from acid sulfate springs with a pH as low as 0.8, to alkaline chloride springs saturated with silica, to bicarbonate springs saturated with carbon dioxide and carbonate minerals. Some springs also contain abundant dissolved iron. The minerals brought to the surface in hot springs often feed communities of extremophiles, microorganisms adapted to extreme conditions, and it is possible that life on Earth had its origin in hot springs. Humans have made use of hot springs for bathing, relaxation, or medical therapy for th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hashizu Kofun Cluster
The is a group of Kofun period burial mounds located in the Hashizu neighborhood of the town of Yurihama, Tottori Prefecture in the San'in region of Japan. The tumulus group was designated a National Historic Site of Japan in 1957. Overview The Hashizu Kofun Cluster is located on the Umanoyama Hill, between the Sea of Japan and Lake Tōgō at an elevation of 107 meters above sea level. The cluster consists of five , which are shaped like a keyhole, having one square end and one circular end, when viewed from above and 19 () tumuli dating from the early to late Kofun period. The site is therefore also called the . Of the 24 tumuli, 14 are covered in the National Historic Site designation. Of the keyhole-shaped burial mounds, Tumulus No. 4, which was built in the early Kofun period (around the middle of the 4th century) and which a total length of about 100 meters, is the largest, and includes a pit-style stone burial chamber and a cylindrical ''haniwa''-style coffin. The in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kofun Period
The is an era in the history of Japan from about 300 to 538 AD (the date of the introduction of Buddhism), following the Yayoi period. The Kofun and the subsequent Asuka periods are sometimes collectively called the Yamato period. This period is the earliest era of recorded history in Japan, but studies depend heavily on archaeology since the chronology of historical sources tends to be distorted. ''Kofun'' is Japanese for the type of tumulus, burial mound dating from this era. It was a period of cultural import. Continuing from the Yayoi period, the Kofun period is characterized by influence from China and the Korean Peninsula; archaeologists consider it a shared culture across the southern Korean Peninsula, Kyūshū and Honshū. On the other hand, the most prosperous keyhole-shaped burial mounds in Japan during this period were approximately 5,000 in Japan from the middle of the 3rd century in the Yayoi period to the 7th century in the Asuka period, and many of them had huge tom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Onsen
In Japan, are hot springs and the bathing facilities and Ryokan (inn), traditional inns around them. There are approximately 25,000 hot spring sources throughout Japan, and approximately 3,000 ''onsen'' establishments use naturally hot water from these Geothermal gradient, geothermally heated springs. ''Onsen'' may be either or . Traditionally, ''onsen'' were located outdoors, although many inns have now built indoor bathing facilities as well. Nowadays, as most households have their baths, the number of traditional public baths has decreased, but the number and popularity of have increased since the end of World War II, Second World War. Baths may be either publicly run by a municipality or privately, often connecting to a lodging establishment such as a hotel, ''Ryokan (inn), ryokan'', or ''Ryokan (inn)#Minshuku, minshuku''. The presence of an ''onsen'' is often indicated on signs and maps by the symbol ♨, the kanji (''yu'', meaning "hot water"), or the simpler phonet ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lakes Of Tottori Prefecture
A lake is often a naturally occurring, relatively large and fixed body of water on or near the Earth's surface. It is localized in a depression (geology), basin or interconnected basins surrounded by dry land. Lakes lie completely on land and are separate from the ocean, although they may be connected with the ocean by rivers. Lakes, as with other bodies of water, are part of the water cycle, the processes by which water moves around the Earth. Most lakes are fresh water and account for almost all the world's surface freshwater, but some are salt lakes with salinities even higher than that of seawater. Lakes vary significantly in surface area and volume of water. Lakes are typically larger and deeper than ponds, which are also water-filled basins on land, although there are no official definitions or scientific criteria distinguishing the two. Lakes are also distinct from lagoons, which are generally shallow tidal pools dammed by sandbars or other material at coastal regions ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |