|
Lagrangian Multipliers
Lagrangian may refer to: Mathematics * Lagrangian function, used to solve constrained minimization problems in optimization theory; see Lagrange multiplier ** Lagrangian relaxation, the method of approximating a difficult constrained problem with an easier problem having an enlarged feasible set ** Lagrangian dual problem, the problem of maximizing the value of the Lagrangian function, in terms of the Lagrange-multiplier variable; See Dual problem * Lagrangian, a functional whose extrema are to be determined in the calculus of variations * Lagrangian submanifold, a class of submanifolds in symplectic geometry * Lagrangian system, a pair consisting of a smooth fiber bundle and a Lagrangian density Physics * Lagrangian mechanics, a formulation of classical mechanics * Lagrangian (field theory), a formalism in classical field theory * Lagrangian point, a position in an orbital configuration of two large bodies * Lagrangian coordinates, a way of describing the motions of particles o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrange Multiplier
In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function (mathematics), function subject to constraint (mathematics), equation constraints (i.e., subject to the condition that one or more equations have to be satisfied exactly by the chosen values of the variable (mathematics), variables). It is named after the mathematician Joseph-Louis Lagrange. Summary and rationale The basic idea is to convert a constrained problem into a form such that the derivative test of an unconstrained problem can still be applied. The relationship between the gradient of the function and gradients of the constraints rather naturally leads to a reformulation of the original problem, known as the Lagrangian function or Lagrangian. In the general case, the Lagrangian is defined as \mathcal(x, \lambda) \equiv f(x) + \langle \lambda, g(x)\rangle for functions f, g; the notation \langle \cdot, \cdot \rangle denotes an inner prod ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Relaxation
In the field of mathematical optimization, Lagrangian relaxation is a relaxation method which approximates a difficult problem of constrained optimization by a simpler problem. A solution to the relaxed problem is an approximate solution to the original problem, and provides useful information. The method penalizes violations of inequality constraints using a Lagrange multiplier In mathematical optimization, the method of Lagrange multipliers is a strategy for finding the local maxima and minima of a function (mathematics), function subject to constraint (mathematics), equation constraints (i.e., subject to the conditio ..., which imposes a cost on violations. These added costs are used instead of the strict inequality constraints in the optimization. In practice, this relaxed problem can often be solved more easily than the original problem. The problem of maximizing the Lagrangian function of the dual variables (the Lagrangian multipliers) is the Lagrangian dual problem. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duality (optimization)
In mathematical optimization theory, duality or the duality principle is the principle that optimization problems may be viewed from either of two perspectives, the primal problem or the dual problem. If the primal is a minimization problem then the dual is a maximization problem (and vice versa). Any feasible solution to the primal (minimization) problem is at least as large as any feasible solution to the dual (maximization) problem. Therefore, the solution to the primal is an upper bound to the solution of the dual, and the solution of the dual is a lower bound to the solution of the primal. This fact is called weak duality. In general, the optimal values of the primal and dual problems need not be equal. Their difference is called the duality gap. For convex optimization problems, the duality gap is zero under a constraint qualification condition. This fact is called strong duality. Dual problem Usually the term "dual problem" refers to the ''Lagrangian dual problem'' but o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Calculus Of Variations
The calculus of variations (or variational calculus) is a field of mathematical analysis that uses variations, which are small changes in Function (mathematics), functions and functional (mathematics), functionals, to find maxima and minima of functionals: Map (mathematics), mappings from a set of Function (mathematics), functions to the real numbers. Functionals are often expressed as definite integrals involving functions and their derivatives. Functions that maximize or minimize functionals may be found using the Euler–Lagrange equation of the calculus of variations. A simple example of such a problem is to find the curve of shortest length connecting two points. If there are no constraints, the solution is a straight line between the points. However, if the curve is constrained to lie on a surface in space, then the solution is less obvious, and possibly many solutions may exist. Such solutions are known as ''geodesics''. A related problem is posed by Fermat's principle: li ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Submanifold
In differential geometry, a subject of mathematics, a symplectic manifold is a smooth manifold, M , equipped with a closed nondegenerate differential 2-form \omega , called the symplectic form. The study of symplectic manifolds is called symplectic geometry or symplectic topology. Symplectic manifolds arise naturally in abstract formulations of classical mechanics and analytical mechanics as the cotangent bundles of manifolds. For example, in the Hamiltonian formulation of classical mechanics, which provides one of the major motivations for the field, the set of all possible configurations of a system is modeled as a manifold, and this manifold's cotangent bundle describes the phase space of the system. Motivation Symplectic manifolds arise from classical mechanics; in particular, they are a generalization of the phase space of a closed system. In the same way the Hamilton equations allow one to derive the time evolution of a system from a set of differential equation ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian System
In mathematics, a Lagrangian system is a pair , consisting of a smooth fiber bundle and a Lagrangian density , which yields the Euler–Lagrange differential operator acting on sections of . In classical mechanics, many dynamical systems are Lagrangian systems. The configuration space of such a Lagrangian system is a fiber bundle Q \rarr \mathbb over the time axis \mathbb. In particular, Q = \mathbb \times M if a reference frame is fixed. In classical field theory, all field systems are the Lagrangian ones. Lagrangians and Euler–Lagrange operators A Lagrangian density (or, simply, a Lagrangian) of order is defined as an -form, , on the -order jet manifold of . A Lagrangian can be introduced as an element of the variational bicomplex of the differential graded algebra of exterior forms on jet manifolds of . The coboundary operator of this bicomplex contains the variational operator which, acting on , defines the associated Euler–Lagrange operator . In coor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Mechanics
In physics, Lagrangian mechanics is a formulation of classical mechanics founded on the d'Alembert principle of virtual work. It was introduced by the Italian-French mathematician and astronomer Joseph-Louis Lagrange in his presentation to the Turin Academy of Science in 1760 culminating in his 1788 grand opus, ''Mécanique analytique''. Lagrangian mechanics describes a mechanical system as a pair consisting of a configuration space (physics), configuration space ''M'' and a smooth function L within that space called a ''Lagrangian''. For many systems, , where ''T'' and ''V'' are the Kinetic energy, kinetic and Potential energy, potential energy of the system, respectively. The stationary action principle requires that the Action (physics)#Action (functional), action functional of the system derived from ''L'' must remain at a stationary point (specifically, a Maximum and minimum, maximum, Maximum and minimum, minimum, or Saddle point, saddle point) throughout the time evoluti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian (field Theory)
Lagrangian field theory is a formalism in classical field theory. It is the field-theoretic analogue of Lagrangian mechanics. Lagrangian mechanics is used to analyze the motion of a system of discrete particles each with a finite number of degrees of freedom. Lagrangian field theory applies to continua and fields, which have an infinite number of degrees of freedom. One motivation for the development of the Lagrangian formalism on fields, and more generally, for classical field theory, is to provide a clear mathematical foundation for quantum field theory, which is infamously beset by formal difficulties that make it unacceptable as a mathematical theory. The Lagrangians presented here are identical to their quantum equivalents, but, in treating the fields as classical fields, instead of being quantized, one can provide definitions and obtain solutions with properties compatible with the conventional formal approach to the mathematics of partial differential equations. This enabl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Point
In celestial mechanics, the Lagrange points (; also Lagrangian points or libration points) are points of equilibrium (mechanics), equilibrium for small-mass objects under the gravity, gravitational influence of two massive orbit, orbiting bodies. Mathematically, this involves the solution of the restricted three-body problem. Normally, the two massive bodies exert an unbalanced gravitational force at a point, altering the orbit of whatever is at that point. At the Lagrange points, the gravitational forces of the two large bodies and the centrifugal force balance each other. This can make Lagrange points an excellent location for satellites, as Orbital station-keeping, orbit corrections, and hence fuel requirements, needed to maintain the desired orbit are kept at a minimum. For any combination of two orbital bodies, there are five Lagrange points, L1 to L5, all in the orbital plane of the two large bodies. There are five Lagrange points for the Sun–Earth system, and five ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lagrangian Coordinates
Lagrangian may refer to: Mathematics * Lagrangian function, used to solve constrained minimization problems in optimization theory; see Lagrange multiplier ** Lagrangian relaxation, the method of approximating a difficult constrained problem with an easier problem having an enlarged feasible set ** Lagrangian dual problem, the problem of maximizing the value of the Lagrangian function, in terms of the Lagrange-multiplier variable; See Dual problem * Lagrangian, a functional whose extrema are to be determined in the calculus of variations * Lagrangian submanifold, a class of submanifolds in symplectic geometry * Lagrangian system, a pair consisting of a smooth fiber bundle and a Lagrangian density Physics * Lagrangian mechanics, a formulation of classical mechanics * Lagrangian (field theory), a formalism in classical field theory * Lagrangian point, a position in an orbital configuration of two large bodies * Lagrangian coordinates, a way of describing the motions of particles of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
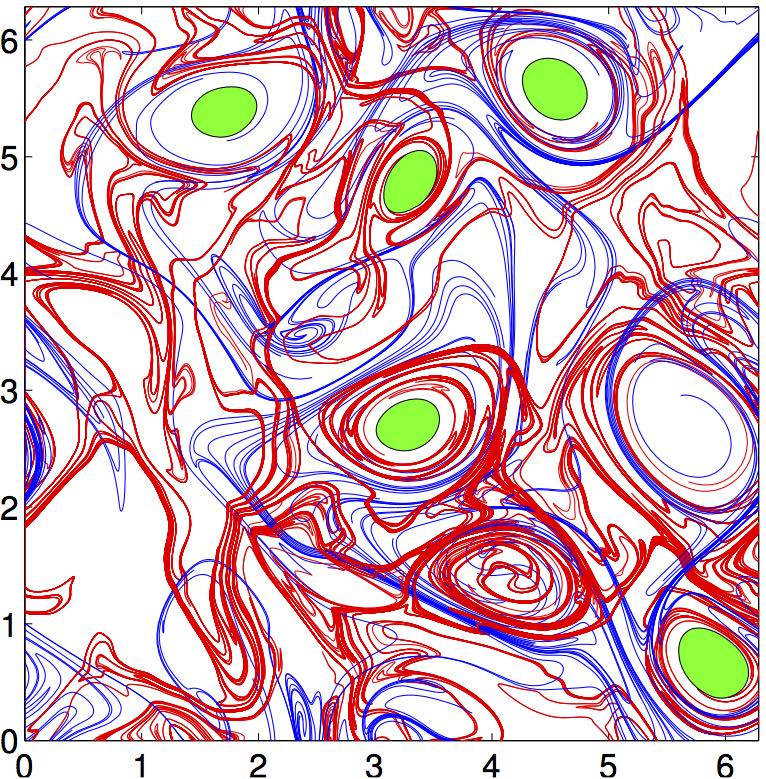
Lagrangian Coherent Structure
Lagrangian coherent structures (LCSs) are distinguished surfaces of trajectories in a dynamical system that exert a major influence on nearby trajectories over a time interval of interest. The type of this influence may vary, but it invariably creates a coherent trajectory pattern for which the underlying LCS serves as a theoretical centerpiece. In observations of tracer patterns in nature, one readily identifies coherent features, but it is often the underlying structure creating these features that is of interest. As illustrated on the right, individual tracer trajectories forming coherent patterns are generally sensitive with respect to changes in their initial conditions and the system parameters. In contrast, the LCSs creating these trajectory patterns turn out to be robust and provide a simplified skeleton of the overall dynamics of the system. The robustness of this skeleton makes LCSs ideal tools for model validation, model comparison and benchmarking. LCSs can also be use ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |