|
Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania
Lackawanna County (; ) is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. It had a population of 215,615 in 2022. Its county seat and most populous city is Scranton, Pennsylvania, Scranton. The county is part of the Northeastern Pennsylvania, Northeast region of the commonwealth. The county was created on August 13, 1878, following decades of trying to gain its independence from Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, Luzerne County.Henry C. BradsbyHistory of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania Volume 1, 1893, Pages 232-233 Lackawanna was Pennsylvania's last county to be created, and the only county to be created after the American Civil War. It is named for the Lackawanna River. Lackawanna County is the second largest county in the Scranton–Wilkes-Barre, Pennsylvania, Wilkes-Barre–Hazleton, Pennsylvania, Hazleton, PA Metropolitan statistical area. It lies northwest of the Pocono Mountains approximately from the New Jersey border in Montague ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Scranton, Pennsylvania
Scranton is a city in and the county seat of Lackawanna County, Pennsylvania, United States. With a population of 76,328 as of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, Scranton is the most populous city in Northeastern Pennsylvania and the Wyoming Valley metropolitan area, which has a population of 562,037 as of 2020. It is the List of municipalities in Pennsylvania, sixth-most populous city in Pennsylvania. The contiguous network of five City, cities and more than 40 boroughs all built in a straight line in Northeastern Pennsylvania's urban core act culturally and logistically as one continuous city, so while Scranton is a mid-sized city, the larger Scranton/Wilkes-Barre metropolitan area contains half a million residents in roughly 300 square miles (780 km2). Scranton is the cultural and economic center of Northeastern Pennsylvania, a region of the state with over 1.3 million residents. Scranton hosts a United States federal courts, federal court building for the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kirkwood, New York
Kirkwood is a town in Broome County, New York, United States. The population was 5,495 as of the 2020 census. The town is named after James P. Kirkwood, the civil engineer responsible for constructing the local railroad. The town is located within the Binghamton Metropolitan Area, and lies approximately 10 miles southeast of the city proper. The town itself is also in close proximity to the border with the U.S. State of Pennsylvania, and both Interstate 81 and New York Route 7 run through it. History , Jonathan Fitch built a water-powered gristmill at what is present-day Fivemile Point, becoming the first settler to live in the area. Many others arrived in the years following and settled on the Susquehanna River, enabling the area (which was then a part of the larger town of Conklin) to develop into a location more suitable for an agrarian lifestyle. Evidence of pre-colonial history can be found in the form of Native American artifacts along the river, many of which can s ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monroe County, Pennsylvania
Monroe County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 census, the population was 168,327. Its county seat is Stroudsburg. The county is part of the Northeast Pennsylvania region of the state. The county was formed from sections of Northampton and Pike counties on April 1, 1836. It was named in honor of James Monroe, the fifth president of the United States. The county borders Northampton County and the Lehigh Valley to its south, Pike and Wayne counties to its north, Carbon and Luzerne counties to its west, and the Delaware River and Warren County, New Jersey to its east. It is part of the New York metropolitan area, but also receives media from the Scranton/Wilkes-Barre and Philadelphia radio and television markets. In the late 20th and early 21st centuries, Monroe County was one of the fastest-growing counties in Pennsylvania, largely due to Pocono Mountain-related tourism and partly due to an influx of residents from New York City and its m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wayne County, Pennsylvania
Wayne County is a county in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. The county's population was 51,155 at the 2020 census. The county seat is the Borough of Honesdale. The county was formed from part of Northampton County on March 21, 1798, and was named for the Revolutionary War General Anthony Wayne. The county is part of the Northeast Pennsylvania and Pocono Mountains region of the state. The Lehigh River, a tributary of the Delaware River, begins in southern Wayne County. Geography According to the U.S. Census Bureau, Wayne County has a total area of , of which is land and (3.3%) is water. The terrain of the county is varied. In the wider northern half, the land is rugged along its border with New York State, while the southern portion tends to be swampier. Higher hills and mountains are predominantly found along the county's western edge, while lower ones are more common in the east, near the Delaware River. The middle section of Wayne County is a wide plain. The high ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Susquehanna County, Pennsylvania
Susquehanna County is a County (United States), county in the Commonwealth (U.S. state), Commonwealth of Pennsylvania. As of the 2020 United States census, 2020 census, the population was 38,434 Its county seat is Montrose, Pennsylvania, Montrose. The county was created on February 21, 1810, from part of Luzerne County, Pennsylvania, Luzerne County and later organized in 1812. It is named for the Susquehanna River. The county is part of the Northeastern Pennsylvania, Northeast Pennsylvania region of the state. History Settlement and conflict The first non-Indigenous people, Indigenous settlers began to move into the area from Philadelphia and Connecticut in the mid-1700s. At the time, the area was part of Luzerne County. As more and more people from Connecticut moved in, there began to be some conflict. Connecticut's original land grant gave it control of land within the northern and southern boundaries from present-day Connecticut to the Pacific Ocean. Their land grant overlapp ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
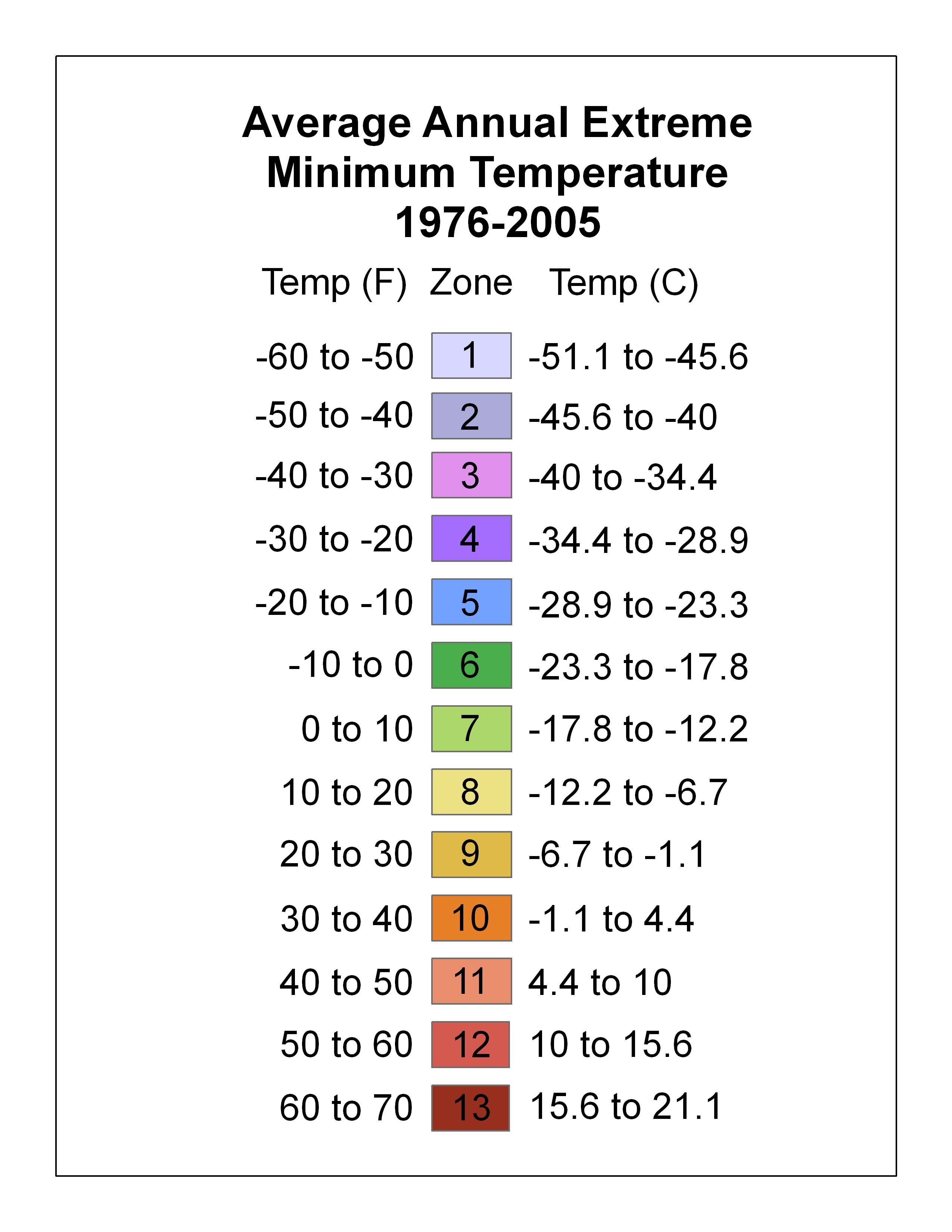
Hardiness Zone
A hardiness zone is a geographic area defined as having a certain average annual minimum temperature, a factor relevant to the survival of many plants. In some systems other statistics are included in the calculations. The original and most widely used system, developed by the United States Department of Agriculture (USDA) as a rough guide for landscaping and gardening, defines 13 zones by long-term average annual extreme minimum temperatures. It has been adapted by and to other countries (such as Canada) in various forms. A plant may be described as "hardy to zone 10": this means that the plant can withstand a minimum temperature of . Unless otherwise specified, in American contexts "hardiness zone" or simply "zone" usually refers to the USDA scale. However, some confusion can exist in discussing buildings and HVAC, where "climate zone" can refer to the International Energy Conservation Code zones, where Zone 1 is warm and Zone 8 is cold. Other hardiness rating schemes have been ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Humid Continental Climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers, and cold (sometimes severely cold in the northern areas) and snowy winters. Precipitation is usually distributed throughout the year, but often these regions do have dry seasons. The definition of this climate in terms of temperature is as follows: the mean temperature of the coldest month must be below or depending on the isotherm, and there must be at least four months whose mean temperatures are at or above . In addition, the location in question must not be semi-arid or arid. The cooler ''Dfb'', ''Dwb'', and ''Dsb'' subtypes are also known as hemiboreal climates. Although amount of snowfall is not a factor used in defining the humid continental climate, snow during the winter in this type of climate is almost a guarantee, either intermitte ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
United States Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau, officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the Federal statistical system, U.S. federal statistical system, responsible for producing data about the American people and American economy, economy. The U.S. Census Bureau is part of the United States Department of Commerce, U.S. Department of Commerce and its Director of the United States Census Bureau, director is appointed by the president of the United States. Currently, Ron S. Jarmin is the acting director of the U.S. Census Bureau. The Census Bureau's primary mission is conducting the United States census, U.S. census every ten years, which allocates the seats of the United States House of Representatives, U.S. House of Representatives to the U.S. state, states based on their population. The bureau's various censuses and surveys help allocate over $675 billion in federal funds every year and it assists states, local communities, and businesses in making informed decisions. T ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
William Walker Scranton
William Walker Scranton (April 4, 1844 – December 3, 1916) was an American businessman based in Scranton, Pennsylvania. He became president and manager of the Lackawanna Iron and Coal Company after his father's death in 1872. The company had been founded by his father's cousin George W. Scranton. Among his innovations, Scranton adopted the Bessemer process for his operations in 1876, greatly increasing production of steel ties with a new mill. Scranton founded the Scranton Steel Company, in 1891 consolidated as Lackawanna Iron and Steel Company. The steel company became the second largest in the nation. He later also managed the Scranton Gas and Water Company, developing a secure water supply outside the city by creating Lake Scranton. William W. Scranton managed the Lackawanna works during and after the Scranton General Strike of 1877. In 1902 Lackawanna Steel Company moved to a location south of Buffalo, New York on Lake Erie for access to new production of iron o ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Anthracite
Anthracite, also known as hard coal and black coal, is a hard, compact variety of coal that has a lustre (mineralogy)#Submetallic lustre, submetallic lustre. It has the highest carbon content, the fewest impurities, and the highest energy density of all types of coal and is the highest Coal analysis#Coal classification by rank, ranking of coals. The Coal Region of Northeastern Pennsylvania in the United States has the largest known deposits of anthracite coal in the world with an estimated reserve of seven billion short ton, short tons. Coal in China, China accounts for the majority of global production; other producers include Coal in Russia, Russia, Coal in Ukraine, Ukraine, Coal in North Korea, North Korea, Coal in South Africa, South Africa, Coal in Vietnam, Vietnam, Coal in Australia, Australia, Coal in Canada, Canada, and the Coal mining in the United States, United States. Total production in 2020 was 615 million tons. Anthracite is the most metamorphism, metamorphosed ty ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
George Washington Statue In Scranton, PA IMG 1536
George may refer to: Names * George (given name) * George (surname) People * George (singer), American-Canadian singer George Nozuka, known by the mononym George * George Papagheorghe, also known as Jorge / GEØRGE * George, stage name of Giorgio Moroder * George, son of Andrew I of Hungary Places South Africa * George, South Africa, a city ** George Airport United States * George, Iowa, a city * George, Missouri, a ghost town * George, Washington, a city * George County, Mississippi * George Air Force Base, a former U.S. Air Force base located in California Computing * George (algebraic compiler) also known as 'Laning and Zierler system', an algebraic compiler by Laning and Zierler in 1952 * GEORGE (computer), early computer built by Argonne National Laboratory in 1957 * GEORGE (operating system), a range of operating systems (George 1–4) for the ICT 1900 range of computers in the 1960s * GEORGE (programming language), an autocode system invented by Charles Leonard H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |