|
Labia (earwig)
''Labia'' is a genus of earwigs belonging to the family Spongiphoridae. The genus has almost cosmopolitan distribution. Species: *''Labia bhaktapurensis'' *''Labia fanta'' *''Labia harpya'' *''Labia minor'' *''Labia phanduwalensis'' *''Labia pluto The labia are part of the female genitalia; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (or the outer labia) are larger and thicker, while the '' labia minora'' are f ...'' References {{Taxonbar, from=Q17627415 Spongiphoridae Dermaptera families ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Earwig
Earwigs make up the insect order Dermaptera. With about 2,000 species in 12 families, they are one of the smaller insect orders. Earwigs have characteristic cerci, a pair of forcep-like pincers on their abdomen, and membranous wings folded underneath short, rarely used forewings, hence the scientific order name, "skin wings". Some groups are tiny parasites on mammals and lack the typical pincers. Earwigs are found on all continents except Antarctica. Earwigs are mostly nocturnal and often hide in small, moist crevices during the day, and are active at night, feeding on a wide variety of insects and plants. Damage to foliage, flowers, and various crops is commonly blamed on earwigs, especially the common earwig '' Forficula auricularia.'' Earwigs have five molts in the year before they become adults. Many earwig species display maternal care, which is uncommon among insects. Female earwigs may care for their eggs, and even after they have hatched as nymphs will conti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Spongiphoridae
Spongiphoridae is a family of little earwigs in the suborder Neodermaptera. There are more than 40 genera and 510 described species in Spongiphoridae. Genera These 43 genera belong to the family Spongiphoridae: * '' Auchenomus'' Karsch, 1886 * '' Barygerax'' Hebard, 1917 * '' Caecolabia'' Brindle, 1975 * '' Chaetolabia'' Brindle, 1972 * '' Chaetospania'' Karsch, 1886 * '' Circolabia'' Steinmann, 1987 * '' Cosmogerax'' Hebard, 1933 * '' Eugerax'' Hebard, 1917 * '' Filolabia'' Steinmann, 1989 * '' Formicilabia'' Rehn & Hebard, 1917 * '' Gerax'' Hebard, 1917 * '' Homotages'' Burr, 1909 * ''Irdex'' Burr, 1911 * '' Isolabella'' Verhoeff, 1902 * '' Isolaboides'' Hincks, 1958 * '' Isopyge'' Borelli, 1931 * ''Labia'' Leach, 1815 * '' Marava'' Burr, 1911 * '' Mecomera'' Audinet-Serville, 1838 * ''Nesogaster'' Verhoeff, 1902 * '' Nesolabia'' Hincks, 1957 * '' Paralabella'' Steinmann, 1990 * '' Paralaboides'' Steinmann, 1989 * '' Parapericomus'' Ramamurthi, 1967 * '' Paraspania'' Steinman ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cosmopolitan Distribution
In biogeography, cosmopolitan distribution is the term for the range of a taxon that extends across all or most of the world in appropriate habitats. Such a taxon, usually a species, is said to exhibit cosmopolitanism or cosmopolitism. The extreme opposite of a cosmopolitan species is an endemic one, being found only in a single geographical location. Qualification The caveat “in appropriate habitat” is used to qualify the term "cosmopolitan distribution", excluding in most instances polar regions, extreme altitudes, oceans, deserts, or small, isolated islands. For example, the housefly is highly cosmopolitan, yet is neither oceanic nor polar in its distribution. Related terms and concepts The term pandemism also is in use, but not all authors are consistent in the sense in which they use the term; some speak of pandemism mainly in referring to diseases and pandemics, and some as a term intermediate between endemism and cosmopolitanism, in effect regarding pandemism as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Bhaktapurensis
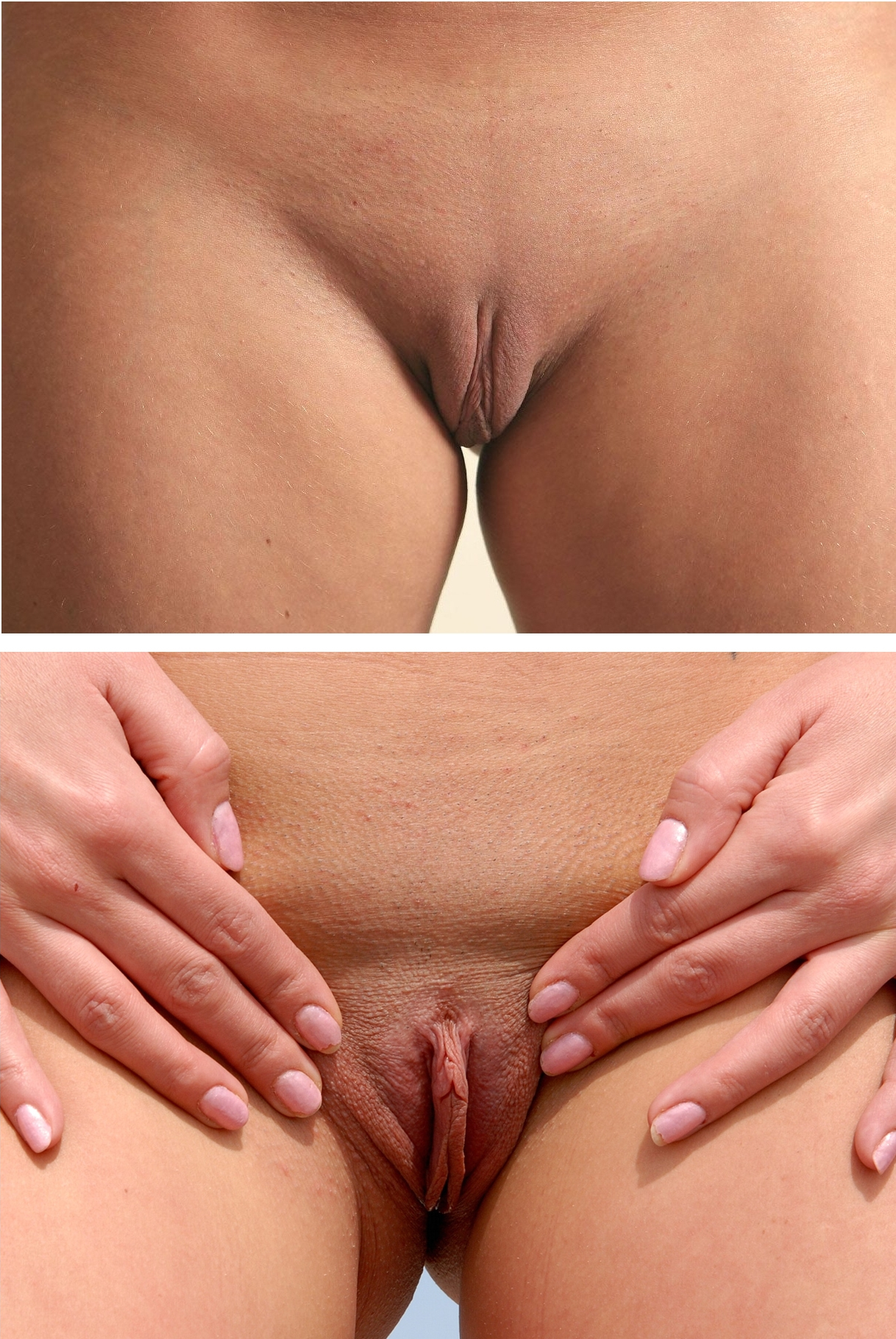
The labia are part of the female genitalia; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (or the outer labia) are larger and thicker, while the '' labia minora'' are folds of skin between the outer labia. The labia surround and protect the clitoris and the openings of the vagina and the urethra. Etymology ''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is a Latin-derived term meaning " lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labium'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva. Anatomy The labia majora, also commonly called outer labia or outer lips, are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose (fatty) tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva to form the pudendal cleft through the middle. The labia majora often have a plump appearance, and are thicker towards the anterior. The anterior junc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Minor
''Labia minor'', the lesser earwig or small earwig, is a species of earwig. It is widespread globally in temperate climates, preferring warm locations such as compost heaps in parts of its range. It is 4–7 mm long, including the pincer, and chocolate brown in color. Description ''Labia minor'' is about half the size of '' Forficula auricularia'', at long. It is chocolate brown, and less shiny than the chestnut brown ''F. auricularia''. The whole body is covered with fine yellow setae, and the antennae are a paler color. The ''forceps'' ( pincer) at the animal's tail are used to help unfurl the wings, in preparation for flight. Unlike ''F. auricularia'', ''Labia minor'' flies frequently. Ecology ''Labia minor'' feeds on decaying plant material and other detritus. In cooler climates, it is only found in warm places, such as actively decaying compost heaps, and are most often encountered when turning the compost. Unusually for an insect, there is extensive maternal c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Phanduwalensis
The labia are part of the female genitalia; they are the major externally visible portions of the vulva. In humans, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (or the outer labia) are larger and thicker, while the '' labia minora'' are folds of skin between the outer labia. The labia surround and protect the clitoris and the openings of the vagina and the urethra. Etymology ''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is a Latin-derived term meaning " lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labium'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva. Anatomy The labia majora, also commonly called outer labia or outer lips, are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose (fatty) tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva to form the pudendal cleft through the middle. The labia majora often have a plump appearance, and are thicker towards the anterior. The anterior junc ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |