|
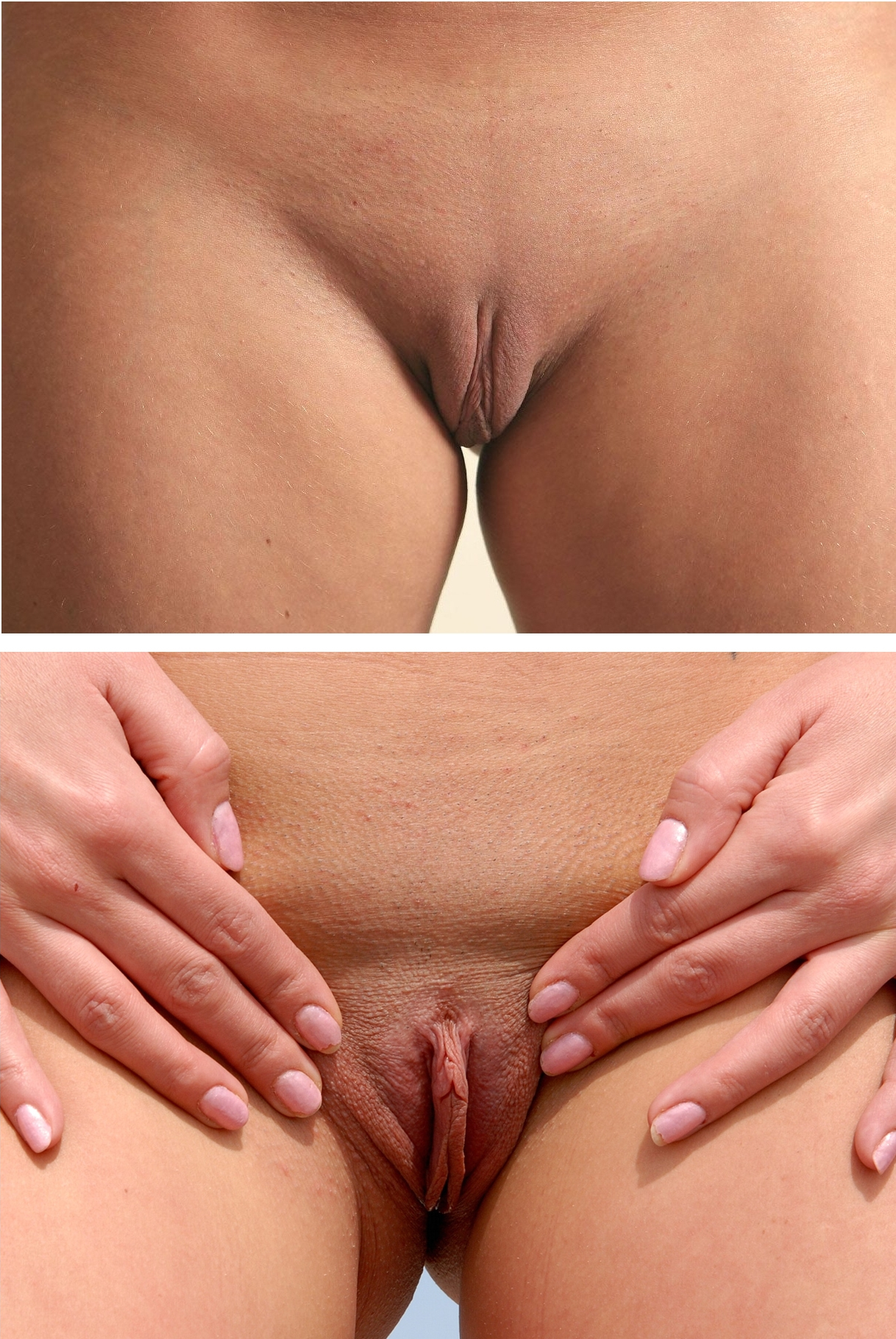
Labia
The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (outer lips) are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the ''labia minora'' (inner lips) are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urinary meatus, urethral and Vagina#Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoridis. In other mammals, the labia majora are not present and the labia minora are instead referred to as the ''labia vulvae''. Etymology ''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is a Latin-derived term meaning "lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labia'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva. Structure The labia majora are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose tissue, adipose (fatty) tissue, which extend on ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vulva
In mammals, the vulva (: vulvas or vulvae) comprises mostly external, visible structures of the female sex organ, genitalia leading into the interior of the female reproductive tract. For humans, it includes the mons pubis, labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vulval vestibule, vestibule, urinary meatus, vaginal introitus, hymen, and openings of the vestibular glands (Bartholin's gland, Bartholin's and Skene's gland, Skene's). The folds of the outer and inner labia provide a double layer of protection for the vagina (which leads to the uterus). Pelvic floor muscles support the structures of the vulva. Other muscles of the urogenital triangle also give support. Blood supply to the vulva comes from the three pudendal arteries. The internal pudendal veins give drainage. Lymphatic vessel#Afferent vessels, Afferent lymph vessels carry lymph away from the vulva to the inguinal lymph nodes. The nerves that supply the vulva are the pudendal nerve, perineal nerve, ilioinguinal nerve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Minora Variation
The labia are the major externally visible structures of the vulva. In humans and other primates, there are two pairs of labia: the ''labia majora'' (outer lips) are large and thick folds of skin that cover the vulva's other parts, while the ''labia minora'' (inner lips) are the folds of skin between the outer labia that surround and protect the urethral and vaginal openings, as well as the glans clitoridis. In other mammals, the labia majora are not present and the labia minora are instead referred to as the '' labia vulvae''. Etymology ''Labium'' (plural ''labia'') is a Latin-derived term meaning "lip". ''Labium'' and its derivatives (including labial, labrum) are used to describe any lip-like structure, but in the English language, ''labia'' often specifically refers to parts of the vulva. Structure The labia majora are lip-like structures consisting mostly of skin and adipose (fatty) tissue, which extend on either side of the vulva to form the pudendal cleft through t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Vulvae
The labia minora (Latin for 'smaller lips', : labium minus), also known as the inner labia, inner lips, or nymphae, are two flaps of skin that are part of the primate vulva, extending outwards from the inner vaginal and urethral openings to encompass the vestibule. At the glans clitoridis, each labium splits, above forming the clitoral hood, and below the frenulum of the clitoris. At the bottom, the labia meet at the ''labial commissure''. The labia minora vary widely in size, color and shape from individual to individual. The labia minora are situated between the labia majora and together form the labia. The labia minora are homologous to the penile raphe and ventral penile skin in males. Structure and functioning The labia minora extend from the clitoris obliquely downward, laterally, and backward on either side of the vulval vestibule, ending between the bottom of the vulval vestibule and the labia majora. The posterior ends (bottom) of the labia minora are usually joined a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labia Majora
In primates, and specifically in humans, the labia majora (: labium majus), also known as the outer lips or outer labia, are two prominent Anatomical terms of location, longitudinal skin folds that extend downward and backward from the mons pubis to the perineum. Together with the labia minora, they form the labia of the vulva. The labia majora are Homology (biology), homologous to the male scrotum. Etymology ''Labia majora'' is the Latin plural for big ("major") lips. The Latin term ''labium/labia'' is used in anatomy for a number of usually paired parallel structures, but in English, it is mostly applied to two pairs of parts of the vulva—labia majora and labia minora. Traditionally, to avoid confusion with other lip-like structures of the body, the vulvar labia were termed by anatomists in Latin as ''labia majora (''or ''minora) pudendi.'' Embryology Embryologically, they develop from labioscrotal folds. The labia majora after puberty may become of a darker color than the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Clitoris
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous zone, erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female Human sexuality, sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 Nerve, nerve endings. * * Peters, B; Uloko, M; Isabey, PHow many Nerve Fibers Innervate the Human Clitoris? A Histomorphometric Evaluation of the Dorsal Nerve of the Clitoris 2 p.m. ET 27 October 2022, 23rd annual joint scientific meeting of Sexual Medicine Society of North America and International Society for Sexual Medicine Sexology, Sexological, medical, and psychological debate has focused on the clitoris, and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies. Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, g ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Glans Clitoridis
In amniotes, the clitoris ( or ; : clitorises or clitorides) is a female sex organ. In humans, it is the vulva's most erogenous area and generally the primary anatomical source of female sexual pleasure. The clitoris is a complex structure, and its size and sensitivity can vary. The visible portion, the glans, of the clitoris is typically roughly the size and shape of a pea and is estimated to have at least 8,000 nerve endings. * * Peters, B; Uloko, M; Isabey, PHow many Nerve Fibers Innervate the Human Clitoris? A Histomorphometric Evaluation of the Dorsal Nerve of the Clitoris 2 p.m. ET 27 October 2022, 23rd annual joint scientific meeting of Sexual Medicine Society of North America and International Society for Sexual Medicine Sexological, medical, and psychological debate has focused on the clitoris, and it has been subject to social constructionist analyses and studies. Such discussions range from anatomical accuracy, gender inequality, female genital mutilation, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Labial Adhesion
Labial fusion is a medical condition of the vulva where the labia minora become fused together. It is generally a pediatric condition. Presentation Labial fusion is rarely present at birth, but rather acquired later in infancy, since it is caused by insufficient estrogen exposure and newborns have been exposed to maternal estrogen ''in utero''. It typically presents in infants at least 3 months old. Most presentations are asymptomatic and are discovered by a parent or during routine medical examination. In other cases, patients may present with associated symptoms of dysuria, urinary frequency, refusal to urinate, or post-void dribbling. Some patients present with vaginal discharge due to pooling of urine in the vulval vestibule or vagina. Complications Labial fusion can lead to urinary tract infection, vulvar vestibulitis and inflammation caused by chronic urine exposure. In severe cases, labial adhesions can cause complete obstruction of the urethra, leading to anuria and urinary ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vagina
In mammals and other animals, the vagina (: vaginas or vaginae) is the elastic, muscular sex organ, reproductive organ of the female genital tract. In humans, it extends from the vulval vestibule to the cervix (neck of the uterus). The #Vaginal opening and hymen, vaginal introitus is normally partly covered by a thin layer of mucous membrane, mucosal tissue called the hymen. The vagina allows for Copulation (zoology), copulation and birth. It also channels Menstruation (mammal), menstrual flow, which occurs in humans and closely related primates as part of the menstrual cycle. To accommodate smoother penetration of the vagina during sexual intercourse or other sexual activity, vaginal moisture increases during sexual arousal in human females and other female mammals. This increase in moisture provides vaginal lubrication, which reduces friction. The texture of the vaginal walls creates friction for the penis during sexual intercourse and stimulates it toward ejaculation, en ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Urogenital Folds
The development of the reproductive system is the part of embryonic growth that results in the sex organs and contributes to sexual differentiation. Due to its large overlap with development of the urinary system, the two systems are typically described together as the genitourinary system. The reproductive organs develop from the intermediate mesoderm and are preceded by more primitive structures that are superseded before birth. These embryonic structures are the mesonephric ducts (also known as ''Wolffian ducts'') and the paramesonephric ducts, (also known as ''Müllerian ducts''). The mesonephric duct gives rise to the male seminal vesicles, epididymides and vasa deferentia. The paramesonephric duct gives rise to the female fallopian tubes, uterus, cervix, and upper part of the vagina. Mesonephric ducts The mesonephric duct originates from a part of the pronephric duct. Origin In the outer part of the intermediate mesoderm, immediately under the ectoderm, in the re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |