|
LLZO
Lithium lanthanum zirconium oxide (LLZO, Li7La3Zr2O12) or lithium lanthanum zirconate is a lithium-stuffed garnet material that is under investigation for its use in solid-state electrolytes in lithium-based battery technologies. LLZO has a high ionic conductivity and thermal and chemical stability against reactions with prospective electrode materials, mainly lithium metal, giving it an advantage for use as an electrolyte in solid-state batteries. LLZO exhibits favorable characteristics, including the accessibility of starting materials, cost-effectiveness, and straightforward preparation and densification processes. These attributes position this zirconium-containing lithium garnet as a promising solid electrolyte for all-solid-state lithium-ion rechargeable batteries. Moreover, LLZO demonstrates a notable total conductivity, surpassing most other solid lithium-ion conductors and many lithium garnets. The fact that the total and bulk conductivities are of the same order of magni ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Solid-state Electrolyte
A solid-state electrolyte (SSE) is a solid ionic conductor and electron-insulating material and it is the characteristic component of the solid-state battery. It is useful for applications in electrical energy storage (EES) in substitution of the liquid electrolytes found in particular in lithium-ion battery. The main advantages are the absolute safety, no issues of leakages of toxic organic solvents, low flammability, non-volatility, mechanical and thermal stability, easy processability, low self-discharge, higher achievable power density and cyclability. This makes possible, for example, the use of a lithium metal anode in a practical device, without the intrinsic limitations of a liquid electrolyte thanks to the property of lithium dendrite suppression in the presence of a solid-state electrolyte membrane. The utilization of a high capacity anode and low reduction potential, like lithium with a specific capacity of 3860 mAh g−1 and a reduction potential of -3.04 V vs SHE, in ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
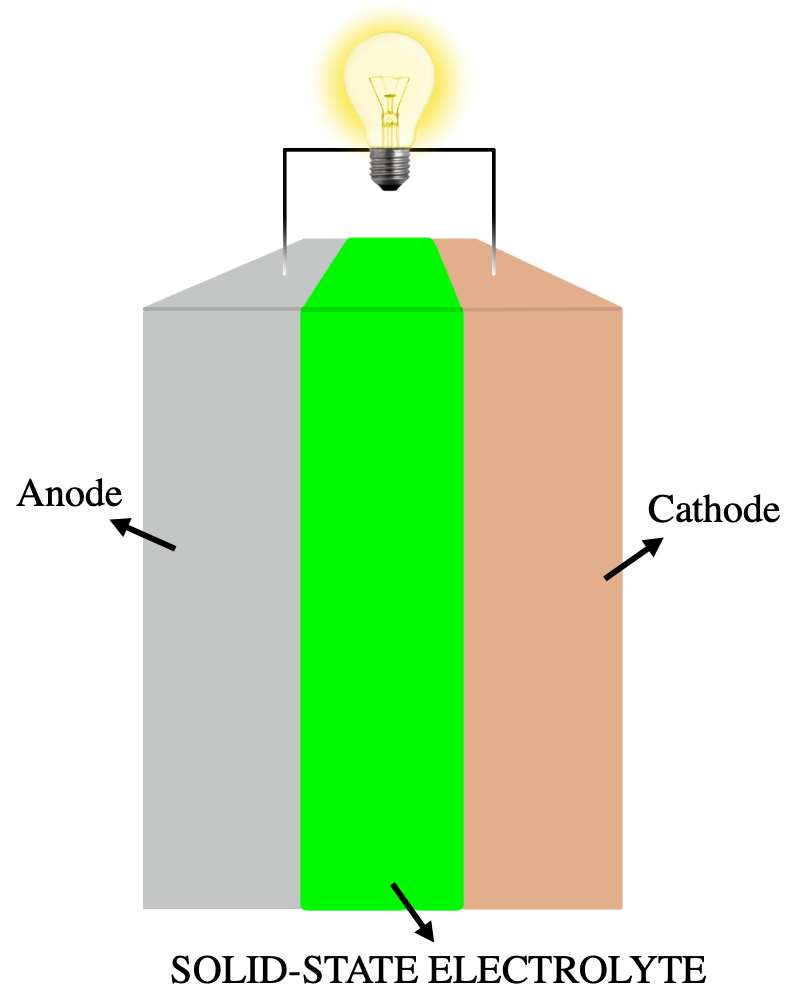
Solid-state Batteries
A solid-state battery is a battery technology that uses solid electrodes and a solid electrolyte, instead of the liquid or polymer gel electrolytes found in lithium-ion or lithium polymer batteries. While solid electrolytes were first discovered in the 19th century, several drawbacks have prevented widespread application. Developments in the late 20th and early 21st century have caused renewed interest in solid-state battery technologies, especially in the context of electric vehicles, starting in the 2010s. Solid-state batteries can provide potential solutions for many problems of liquid Li-ion batteries, such as flammability, limited voltage, unstable solid-electrolyte interphase formation, poor cycling performance and strength. Materials proposed for use as solid electrolytes in solid-state batteries include ceramics (e.g., oxides, sulfides, phosphates), and solid polymers. Solid-state batteries have found use in pacemakers, RFID and wearable devices. They are potential ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium
Lithium (from el, λίθος, lithos, lit=stone) is a chemical element with the symbol Li and atomic number 3. It is a soft, silvery-white alkali metal. Under standard conditions, it is the least dense metal and the least dense solid element. Like all alkali metals, lithium is highly reactive and flammable, and must be stored in vacuum, inert atmosphere, or inert liquid such as purified kerosene or mineral oil. When cut, it exhibits a metallic luster, but moist air corrodes it quickly to a dull silvery gray, then black tarnish. It never occurs freely in nature, but only in (usually ionic) compounds, such as pegmatitic minerals, which were once the main source of lithium. Due to its solubility as an ion, it is present in ocean water and is commonly obtained from brines. Lithium metal is isolated electrolytically from a mixture of lithium chloride and potassium chloride. The nucleus of the lithium atom verges on instability, since the two stable lithium isotopes ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Garnet
Garnets () are a group of silicate minerals that have been used since the Bronze Age as gemstones and abrasives. All species of garnets possess similar physical properties and crystal forms, but differ in chemical composition. The different species are pyrope, almandine, spessartine, grossular (varieties of which are hessonite or cinnamon-stone and tsavorite), uvarovite and andradite. The garnets make up two solid solution series: pyrope-almandine-spessartine (pyralspite), with the composition range ; and uvarovite-grossular-andradite (ugrandite), with the composition range . Etymology The word ''garnet'' comes from the 14th-century Middle English word ''gernet'', meaning 'dark red'. It is borrowed from Old French ''grenate'' from Latin ''granatus,'' from ''granum'' ('grain, seed'). This is possibly a reference to ''mela granatum'' or even ''pomum granatum'' (' pomegranate', ''Punica granatum''), a plant whose fruits contain abundant and vivid red seed covers ( arils), ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ionic Conductivity (solid State)
Ionic conductivity (denoted by ) is a measure of a substance's tendency towards ionic conduction. Ionic conduction is the movement of ions. The phenomenon is observed in solids and solutions. Ionic conduction is one mechanism of current. In crystalline solids In most solids, ions rigidly occupy fixed positions, strongly embraced by neighboring atoms or ions. In some solids, selected ions are highly mobile allowing ionic conduction. The mobility increases with temperature. Materials exhibiting this property are used in batteries. A well-known ion conductive solid is β''-alumina ("BASE"), a form of aluminium oxide that has channels through which sodium cations can hop. When this ceramic is complexed with a mobile ion, such as Na+, it behaves as so-called fast ion conductor. BASE is used as a membrane in several types of molten salt electrochemical cell. In glasses Ion conduction in disordered solids like glasses, polymers, nanocomposites, defective crystals and other d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tetragonal
In crystallography, the tetragonal crystal system is one of the 7 crystal systems. Tetragonal crystal lattices result from stretching a cubic lattice along one of its lattice vectors, so that the cube becomes a rectangular prism with a square base (''a'' by ''a'') and height (''c'', which is different from ''a''). Bravais lattices There are two tetragonal Bravais lattices: the primitive tetragonal and the body-centered tetragonal. The base-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the primitive tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell, while the face-centered tetragonal lattice is equivalent to the body-centered tetragonal lattice with a smaller unit cell. Crystal classes The point groups that fall under this crystal system are listed below, followed by their representations in international notation, Schoenflies notation, orbifold notation, Coxeter notation and mineral examples.Hurlbut, Cornelius S.; Klein, Cornelis, 1985, ''Manual of Mineralogy'', 20th ed. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cubic Crystal System
In crystallography, the cubic (or isometric) crystal system is a crystal system where the unit cell is in the shape of a cube. This is one of the most common and simplest shapes found in crystals and minerals. There are three main varieties of these crystals: *Primitive cubic (abbreviated ''cP'' and alternatively called simple cubic) *Body-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cI'' or bcc) *Face-centered cubic (abbreviated ''cF'' or fcc, and alternatively called ''cubic close-packed'' or ccp) Each is subdivided into other variants listed below. Although the ''unit cells'' in these crystals are conventionally taken to be cubes, the primitive unit cells often are not. Bravais lattices The three Bravais lattices in the cubic crystal system are: The primitive cubic lattice (cP) consists of one lattice point on each corner of the cube; this means each simple cubic unit cell has in total one lattice point. Each atom at a lattice point is then shared equally between eight adjacent c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Phase Transition
In chemistry, thermodynamics, and other related fields, a phase transition (or phase change) is the physical process of transition between one state of a medium and another. Commonly the term is used to refer to changes among the basic states of matter: solid, liquid, and gas, and in rare cases, plasma. A phase of a thermodynamic system and the states of matter have uniform physical properties. During a phase transition of a given medium, certain properties of the medium change as a result of the change of external conditions, such as temperature or pressure. This can be a discontinuous change; for example, a liquid may become gas upon heating to its boiling point, resulting in an abrupt change in volume. The identification of the external conditions at which a transformation occurs defines the phase transition point. Types of phase transition At the phase transition point for a substance, for instance the boiling point, the two phases involved - liquid and vapor, have ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
QuantumScape
QuantumScape is an American company that develops solid state lithium metal batteries for electric cars. The company is headquartered in San Jose, California and employs around 400 people. Investors include Bill Gates and Volkswagen. History QuantumScape was founded in 2010 by Jagdeep Singh, Tim Holme and Professor Fritz Prinz of Stanford University. In 2012, QuantumScape began working with German automaker Volkswagen. In 2018, Volkswagen invested $100 million in the company, becoming the largest shareholder. In the same year, Volkswagen and QuantumScape announced the establishment of a joint production project to prepare for mass production of solid state batteries. In June 2020, Volkswagen made an additional $200 million investment into the company. On September 3, 2020, QuantumScape announced a merger with the special-purpose acquisition company Kensington Capital Acquisition. As a result of the merger, QuantumScape will receive $1 billion in financing, including funding ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rechargeable Lithium Metal Battery
Rechargeable lithium metal batteries are secondary lithium metal batteries. They have metallic lithium as a negative electrode, sometimes referred to as the battery anode. The high specific capacity of lithium metal (3,860 mAh g−1), very low redox potential (−3.040 V versus standard hydrogen electrode) and low density (0.59 g cm−3) make it the ideal anode material for high energy density battery technologies. Rechargeable lithium metal batteries can have a long run time due to the high charge density of lithium. Several companies and many academic research groups are currently researching and developing rechargeable lithium metal batteries as they are considered a leading pathway for development beyond lithium-ion batteries. Some rechargeable lithium metal batteries employ a liquid electrolyte and some employ a solid-state electrolyte. History A rechargeable lithium metal battery was commercialized by Moli Energy (now known as E-One Moli Energy) in the 1980s, but after seve ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Niterra
is a public company established in 1936 and based in Nagoya, Japan. Formerly known as NGK Spark Plug Co. Ltd., the company’s automotive business (with its brands NGK Ignition Parts and NTK Vehicle Electronics) revolves around the manufacturing and the sale of spark plugs and related products for internal combustion engines, as well as vehicle electronics and ceramics for a wide range of applications in the automotive industry and beyond. Niterra is a coined word, which combines the Latin words ‘niteo’ meaning ‘shine’ and ‘terra/earth’. It expresses the Group’s desire to be a company that not only contributes to a sustainable society, but also one that makes the earth shine: a goal formulated in its 2040 Vision. As of April 2024, the company employs around 15,900 people and the company’s automotive and technical ceramics activities generate a total annual turnover of around 4.45 billion euros worldwide. It operates a network of 61 consolidated subsidiaries, 24 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lithium Ion Battery
A lithium-ion or Li-ion battery is a type of rechargeable battery which uses the reversible reduction of lithium ions to store energy. It is the predominant battery type used in portable consumer electronics and electric vehicles. It also sees significant use for grid-scale energy storage and military and aerospace applications. Compared to other rechargeable battery technologies, Li-ion batteries have high energy densities, low self-discharge, and no memory effect (although a small memory effect reported in LFP cells has been traced to poorly made cells). Chemistry, performance, cost and safety characteristics vary across types of lithium-ion batteries. Most commercial Li-ion cells use intercalation compounds as the active materials. The anode or negative electrode is usually graphite, although silicon-carbon is also being increasingly used. Cells can be manufactured to prioritize either energy or power density. Handheld electronics mostly use lithium polymer batterie ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |