|
LDPR
) , abbreviation = LDPR (English)ЛДПР (Russian) , native_name = , newspaper = ''For the Russian People'' , youth_wing = , seats1_title = Seats in the Federation Council , seats1 = , seats2_title = Seats in the State Duma , seats2 = , seats3_title = Governors , seats3 = , seats4_title = Seats in the Regional Parliaments , seats4 = , seats5_title = Ministers , seats5 = , colours = Gold and blue (official) Light blue (customary) , flag = , website = , country = Russia LDPR — Liberal Democratic Party of Russia (russian: ЛДПР — Либерально-демократическая партия России, LDPR — Liberal'no-demokraticheskaya partiya Rossii) is a right-wing populist and ultranationalist political party in Russia. It succeeded the Liberal Democratic Party of the Soviet Union (LDPSU) in Russia after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vladimir Zhirinovsky
Vladimir Volfovich Zhirinovsky, ''né'' Eidelshtein (russian: link=false, Эйдельштейн) (25 April 1946 – 6 April 2022) was a Russian right-wing populist politician and the leader of the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia (LDPR) from its creation in 1992 until his death. He had been a member of the State Duma since 1993 and leader of the LDPR group in the State Duma from 1993 to 2000, and from 2011 to 2022. He served as a deputy chairman of the State Duma from 2000 until 2011. He also worked as a delegate in the Parliamentary Assembly of the Council of Europe from 1996 to 2008. During his lifetime, Zhirinovsky ran in every single Russian presidential election apart from in 2004. He was known for many controversies, as well as staunch advocacy for Russian military action against NATO. Early life and background Zhirinovsky was born in Almaty, the capital of the Kazakh Soviet Socialist Republic, modern-day Kazakhstan. His father, Volf Isaakovich Eidelshtein, was a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
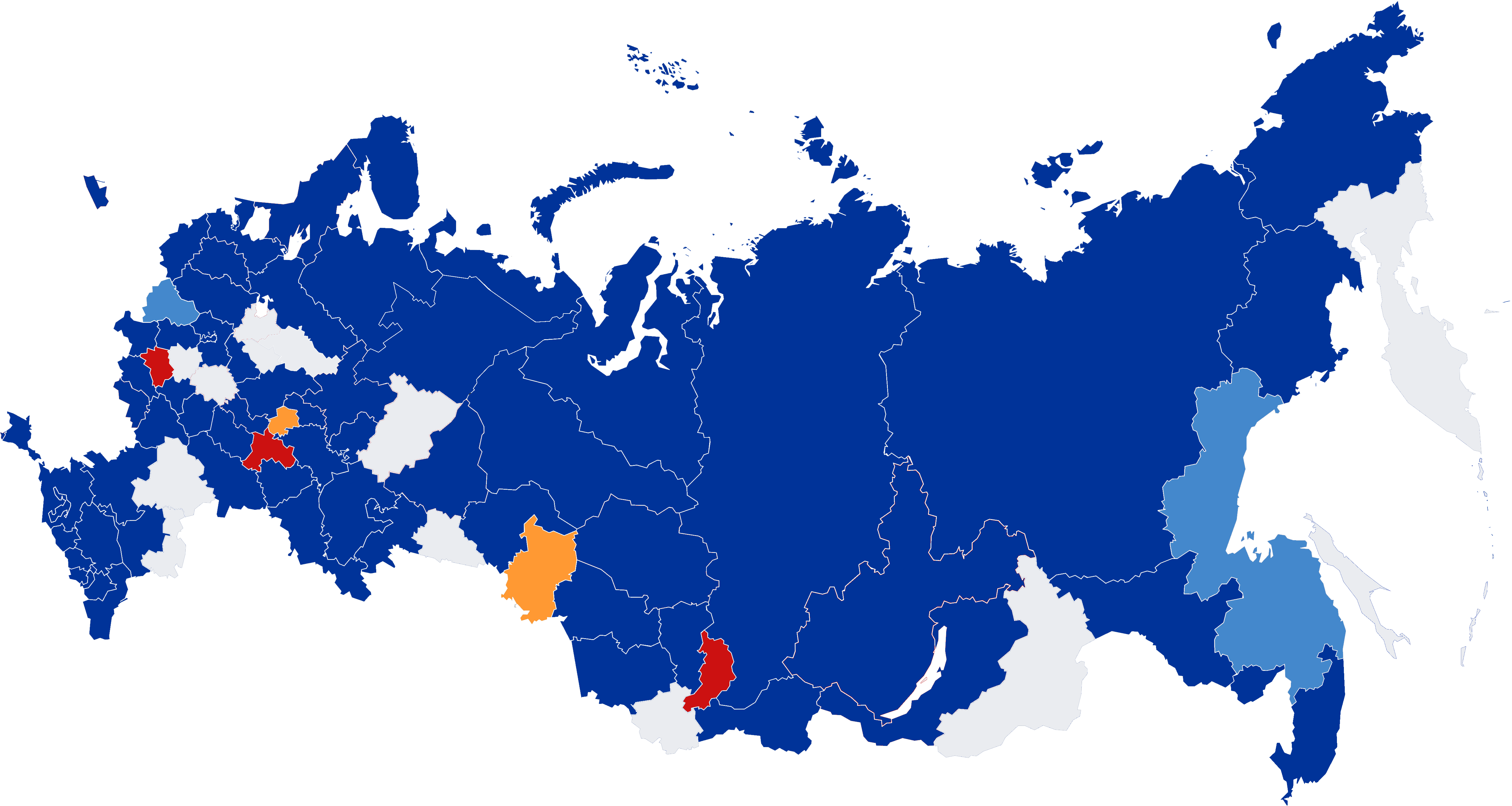
2021 Russian Legislative Election
Legislative elections were held in Russia from 17 to 19 September 2021. At stake were 450 seats in the 8th convocation of the State Duma, the lower house of the Federal Assembly. Going into the elections, United Russia was the ruling party after winning the 2016 elections with 343 of the 450 seats, and retaining a supermajority. In March 2020, it was proposed to hold a snap election in September 2020 due to proposed constitutional reforms, but this idea was abandoned. On 18 June 2021 Vladimir Putin signed a decree calling the election for 19 September the same year. Owing to the COVID-19 pandemic in Russia, voting in the election lasted for three days, from 17 to 19 September. Final turnout was reported to be 51.72%. Fifteen political parties applied for participation, 14 of which were guaranteed automatic access to the ballots, and one unsuccessfully attempted to be included in the ballot by collecting voters' signatures. Half, or 225 seats, of the State Duma were elected th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Political Party In Russia
This article discusses political parties in Russia. The Russia, Russian Federation has a ''de jure'' multi-party system, however it operates as a near ''de facto'' one-party system. six parties have members in the federal parliament, the State Duma, with one Dominant-party system, dominant party (United Russia). History image:Свидетельство о рег. партии Минюстом РФ.jpeg, 200px, Certificate of state registration of political parties in Russia, issued by the Ministry of Justice (Russia), Ministry of Justice of Russia After the Perestroika reforms in the 1980s Russia had over 100 registered political party, parties, but the people elected to the State Duma represented only a small number of parties. After 2000, during Vladimir Putin's first presidency (2000–2008), the number of parties quickly decreased. From 2008 to 2012 there were only seven parties in Russia, and every new attempt to register new, independent parties was blocked. The last-regis ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Liberal Democratic Party Of The Soviet Union
The Liberal Democratic Party of the Soviet Union (LDPSU; russian: Либерально-демократическая партия Советского Союза (ЛДПСС), Liberal'no-demokraticheskaya partiya Sovetskogo Soyuza (LDPSS)) was a political party in the Soviet Union which preceded the modern-day Liberal Democratic Party of Russia (LDPR). History An effectively multi-party system emerged in Soviet Union in the late 1980s in wake of the Gorbachev reforms. In March 1990, Article 6 of the Soviet Constitution, which ensured the Communist Party of the Soviet Union (CPSU) a monopoly on power, was amended to allow other political parties to hold public office. This gave room to the rise of other political parties, specifically the LDPSU. In April 1991, the LDPSU became the second officially registered party in the country. Former KGB General Philipp Bobkov has stated that "in line with Zubatov's ideas," the Central Committee of the Communist Party of the Soviet Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
State Duma
The State Duma (russian: Госуда́рственная ду́ма, r=Gosudárstvennaja dúma), commonly abbreviated in Russian as Gosduma ( rus, Госду́ма), is the lower house of the Federal Assembly of Russia, while the upper house is the Federation Council. The Duma headquarters are located in central Moscow, a few steps from Manege Square. Its members are referred to as deputies. The State Duma replaced the Supreme Soviet as a result of the new constitution introduced by Boris Yeltsin in the aftermath of the Russian constitutional crisis of 1993, and approved in a nationwide referendum. In the 2007 and 2011 Russian legislative elections a full party-list proportional representation with 7% electoral threshold system was used, but this was subsequently repealed. The legislature's term length was initially 2 years in the 1993–1995 elections period, and 4 years in 1999–2007 elections period; since the 2011 elections the term length is 5 years. History Early ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Alexei Didenko
Alexei Nikolayevich Didenko (russian: Алексей Николаевич Диденко; born March 30, 1983) is a Russian politician. From 2007 to 2010, he was deputy of the Tomsk Oblast Duma. Since 2011, he has been a deputy in the State Duma of the Russian Federation. He is a member of the Duma Committee on Constitutional Legislation and State Building. He is a leading member of the ultranationalist Liberal Democratic Party of Russia. Early life Alexei Didenko was born March 30, 1983 to Nikolai in the village of Pochapintsy in Cherkasy region of Ukraine. Alexei later moved with his family to Tomsk where he attended high school from 1990 to 1993. He graduated from “Russian classical school No. 2” in 2000. Education In 2005, Didenko graduated from the Law Institute of Tomsk State University. In the same year, he became of the coordinator of Tomsk regional branch of the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia Member of parliament In 2016 election, Didenko won the Tomsk const ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
1993 Russian Legislative Election
Parliamentary elections were held in Russia on 12 December 1993.Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p1642 They were the first parliamentary elections in post-Soviet Russia and the only time to the Federation Council,Nohlen & Stöver, p1656 with future members appointed by provincial legislatures and governors. Background The 1993 general election was taking place in the aftermath of the 1993 Russian constitutional crisis, a violent confrontation on the streets of Moscow which resulted in the dissolution of the previous Russian parliament by military force. Boris Yeltsin hoped to resolve the political turmoil by decreeing for the election to the new Russian parliament and the constitutional referendum to take place on 12 December 1993. Electoral system The new election law adopted for the 1993 Duma election stipulated half the 450 Duma members were elected by a party-list system of proportional representation, and half were elected as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Current Heads Of Federal Subjects Of Russia
The following is a list of heads of the federal subjects of the Russian Federation. Republic of Crimea and the city of Sevastopol were annexed by Russia in 2014 and, according to its constitution, are Federal subjects. However, internationally these entities are recognized as part of Ukraine. Current Former This is a complete list of the former heads of the federal subjects of Russia. *Republic of Adygea: Aslan Tkhakushinov (2007–2017), Khazret Sovmen (2002–2007), Aslan Dzharimov (1992–2002) *Altai Republic: Alexander Berdnikov (2006–2019), Mikhail Lapshin (2002–2006), Semyon Zubakin (1998–2002), Vladilen Volkov (1997-1998), Valery Chaptynov (1994–1997) *Republic of Bashkortostan: Rustem Khamitov (2010–2018), Murtaza Rakhimov (1993–2010) *Republic of Buryatia: Vyacheslav Nagovitsyn (2007–2017), Leonid Potapov (1991–2007) *Chechen Republic: Alu Alkhanov (2004–2007), Sergey Abramov (2004, acting), Akhmad Kadyrov (2003–2004), Anatoly Popov (2003 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regional Parliaments Of Russia
The regional parliaments of Russia are the legislative bodies of power in the federal subjects of Russia ( republics, Territories of Russia, regions, autonomous districts and federal cities), which have different names, often collectively referred to in the media as regional parliaments. The federal structure of Russia includes 85 regional parliaments. The biggest regional parliament is the State Assembly of the Republic of Bashkortostan which consists of 110 deputies. The smallest one is the Duma of Chukotka Autonomous Okrug which consists of 15 deputies. Currently, every regional parliament is elected for a session of 5 years. Parties in each parliament Data is current as of December 2020. United Russia holds an absolute majority in 79 of the 85 parliaments. The Table is not yet updated to the 2022 Russian regional elections. a. Not recognized internationally as a part of Russia, but part of Ukraine. See also * Politics of Russia The politics of Russi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Leonid Slutsky (politician)
Leonid Eduardovich Slutsky (russian: Леонид Эдуардович Слуцкий, also transliterated Leonid Slutskii or Slutskiy; born 4 January 1968) is a Russian politician. Slutsky is a deputy of the State Duma of Russia and the current leader of the right-wing populist Liberal Democratic Party of Russia party. In the 6th State Duma, he was the Chairman of the State Duma Committee on the Commonwealth of Independent States, Eurasian Integration and Relations with Compatriots. In the 7th State Duma, Slutsky is the Chairman of thCommittee on International Affairs In 2018, Slutsky became the central figure of the first ever sexual scandal in the history of the Russian State Duma, widely covered in the Russian and international press and which led to a solidarity boycott of the media regarding the deputy. [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Russian Nationalism
Russian nationalism is a form of nationalism that promotes Russian cultural identity and unity. Russian nationalism first rose to prominence in the early 19th century, and from its origin in the Russian Empire, to its repression during early Bolshevik rule, and its revival in the Soviet Union, it was closely related to pan-Slavism. The definition of Russian national identity within Russian nationalism has been characterized in different ways. In ethnic terms one including asserting that those identified as ethnic Russians are the Russian nation, another is the All-Russian nation concept developed in the Russian Empire that views Russians as having three sub-national groups within it including Great Russians (those commonly identified as ethnic Russians today), Little Russians (Ukrainians), and White Russians (Belarusians). Russian nationalists have identified Russia as the main successor of the Kievan Rus' and typically view the arising of separate national identities of Be ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monarchism In Russia
A restoration of the Russian monarchy is a hypothetical event in which the Russian monarchy, which has been non-existent since the abdication of the reigning Nicholas II on 15 March 1917 and the murder of him and the rest of his closest family in 1918, is reinstated in today's Russian Federation. The only political parties as of today which advocates such a restoration is the Liberal Democratic Party of Russia and the Monarchist Party. Most proposals for the restoration of the monarchy envision the return to be to a constitutional role. Public opinion A study conducted by the All-Russian Center for Public Opinion showed that almost one third of the Russian population favor a restoration as of 2013. In 2017, a survey conducted by ''Izvestia'' found that 37 percent of all Russians were "not against the monarchy, but... did not see a candidate for such a post". The survey also found that of young Russians 46 percent were not opposed to the restoration of the monarchy. Politic ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |