|
Kirnberger Temperament
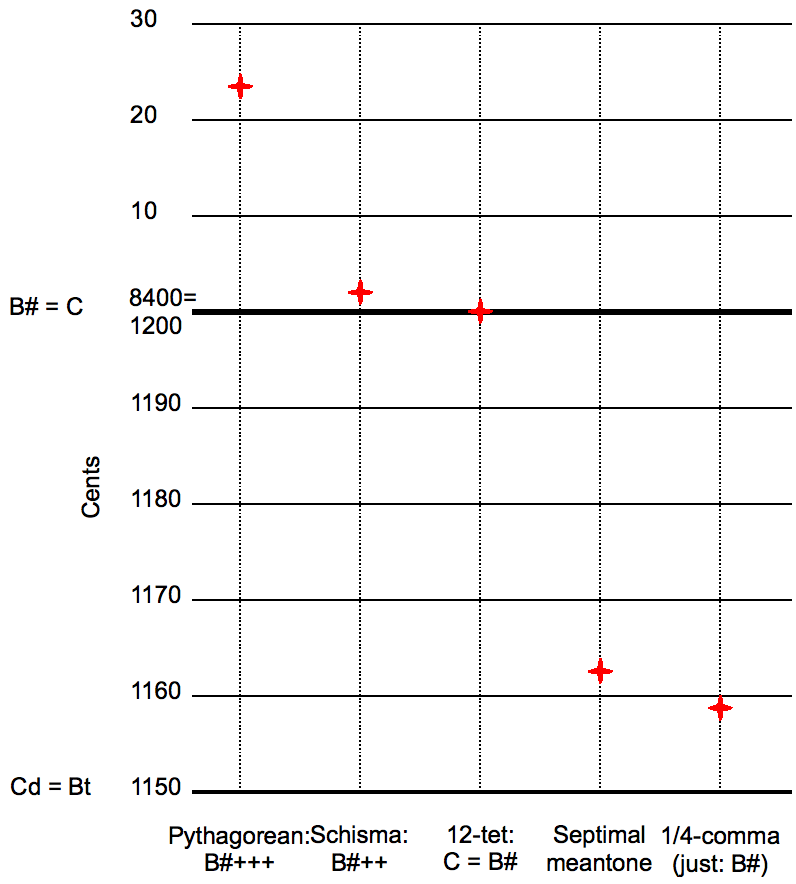
Kirnberger temperament is an irregular temperament developed in the second half of the 18th century by Johann Kirnberger. Kirnberger was a student of Johann Sebastian Bach, held great admiration for his teacher and was one of his principal proponents. The first Kirnberger temperament, "Kirnberger I", had similarities to Pythagorean temperament, which stressed the importance of perfect fifths all throughout the circle of fifths. A complete circle of perfect fifths is not possible, because when the circle comes to an end at the tone it began, it will have overshot its original pitch. Thus, if one tunes C–G, G–D, D–A, A–E, E–B, B–F, F–C, C–G (A), A–E, E–B, B–F, F–C … the new "C" will not be the same frequency as the first. The two "C"s will have a discrepancy of about 23 cents (a comma), which would be unacceptable. This difference between the initial "c" and final "c" that is derived from performing a series of perfect tunings is generally referred t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Musical Temperament
In musical tuning, a temperament is a tuning system that slightly compromises the pure intervals of just intonation to meet other requirements. Most modern Western musical instruments are tuned in the equal temperament system. Tempering is the process of altering the size of an interval by making it narrower or wider than pure. "Any plan that describes the adjustments to the sizes of some or all of the twelve fifth intervals in the circle of fifths so that they accommodate pure octaves and produce certain sizes of major thirds is called a ''temperament''." Temperament is especially important for keyboard instruments, which typically allow a player to play only the pitches assigned to the various keys, and lack any way to alter pitch of a note in performance. Historically, the use of just intonation, Pythagorean tuning and meantone temperament meant that such instruments could sound "in tune" in one key, or some keys, but would then have more dissonance in other keys. In the wor ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Pythagorean Tuning
Pythagorean tuning is a system of musical tuning in which the frequency ratios of all intervals are based on the ratio 3:2.Bruce Benward and Marilyn Nadine Saker (2003). ''Music: In Theory and Practice'', seventh edition, 2 vols. (Boston: McGraw-Hill). Vol. I: p. 56. . This ratio, also known as the " pure" perfect fifth, is chosen because it is one of the most consonant and easiest to tune by ear and because of importance attributed to the integer 3. As Novalis put it, "The musical proportions seem to me to be particularly correct natural proportions." Alternatively, it can be described as the tuning of the syntonic temperament in which the generator is the ratio 3:2 (i.e., the untempered perfect fifth), which is ≈702 cents wide. The system dates to Ancient Mesopotamia; see . The system is named, and has been widely misattributed, to Ancient Greeks, notably Pythagoras (sixth century BC) by modern authors of music theory, while Ptolemy, and later Boethius, ascribed th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg
Friedrich Wilhelm Marpurg (21 November 1718 – 22 May 1795) was a German music critic, music theorist and composer. He was friendly and active with many figures of the Enlightenment of the 18th century. Life Little is known of Marpurg's early life. According to various sources, he studied "philosophy" and music. It is clear that he enjoyed a strong education and was friendly with various leading figures of the Enlightenment, including Winckelmann and Lessing. In 1746, he travelled to Paris as the secretary for a General named either Rothenberg or Bodenberg. There, he became acquainted with intellectuals including the writer and philosopher Voltaire, the mathematician d'Alembert and the composer Jean-Philippe Rameau. After 1746, he returned to Berlin where he was more or less independent. Marpurg's offer to write exclusively for Breitkopf & Härtel was declined by the firm in 1757. In 1760, he received an appointment to the Royal Prussian Lotteries, whose director he became ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Syntonic Comma
In music theory, the syntonic comma, also known as the chromatic diesis, the Didymean comma, the Ptolemaic comma, or the diatonic comma is a small comma type interval between two musical notes, equal to the frequency ratio 81:80 (= 1.0125) (around 21.51 cents). Two notes that differ by this interval would sound different from each other even to untrained ears, , ''BBC''. but would be close enough that they would be more likely interpreted as out-of-tune versions of the same note than as different notes. The comma is also referred to as a Didymean comma because it is the amount by which Didymus corrected the [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Organ (music)
Carol Williams performing at the United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel.">West_Point_Cadet_Chapel.html" ;"title="United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel">United States Military Academy West Point Cadet Chapel. In music, the organ is a keyboard instrument of one or more Pipe organ, pipe divisions or other means for producing tones, each played from its own Manual (music), manual, with the hands, or pedalboard, with the feet. Overview Overview includes: * Pipe organs, which use air moving through pipes to produce sounds. Since the 16th century, pipe organs have used various materials for pipes, which can vary widely in timbre and volume. Increasingly hybrid organs are appearing in which pipes are augmented with electric additions. Great economies of space and cost are possible especially when the lowest (and largest) of the pipes can be replaced; * Non-piped organs, which include: ** pump organs, also known as reed organs or harmoniums, whi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Harpsichord
A harpsichord ( it, clavicembalo; french: clavecin; german: Cembalo; es, clavecín; pt, cravo; nl, klavecimbel; pl, klawesyn) is a musical instrument played by means of a keyboard. This activates a row of levers that turn a trigger mechanism that plucks one or more strings with a small plectrum made from quill or plastic. The strings are under tension on a soundboard, which is mounted in a wooden case; the soundboard amplifies the vibrations from the strings so that the listeners can hear it. Like a pipe organ, a harpsichord may have more than one keyboard manual, and even a pedal board. Harpsichords may also have stop buttons which add or remove additional octaves. Some harpsichords may have a buff stop, which brings a strip of buff leather or other material in contact with the strings, muting their sound to simulate the sound of a plucked lute. The term denotes the whole family of similar plucked-keyboard instruments, including the smaller virginals, muselar, and spinet. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Viols
The viol (), viola da gamba (), or informally gamba, is any one of a family of bowed, fretted, and stringed instruments with hollow wooden bodies and pegboxes where the tension on the strings can be increased or decreased to adjust the pitch of each of the strings. Frets on the viol are usually made of gut, tied on the fingerboard around the instrument's neck, to enable the performer to stop the strings more cleanly. Frets improve consistency of intonation and lend the stopped notes a tone that better matches the open strings. Viols first appeared in Spain in the mid-to-late 15th century, and were most popular in the Renaissance and Baroque (1600–1750) periods. Early ancestors include the Arabic ''rebab'' and the medieval European vielle,Otterstedt, Annette. ''The Viol: History of an Instrument. ''Kassel: Barenreiter;-Verlag Karl Votterle GmbH & Co; 2002. but later, more direct possible ancestors include the Venetian ''viole'' and the 15th- and 16th-century Spanish ''vihuela' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutes
A lute ( or ) is any plucked string instrument with a neck and a deep round back enclosing a hollow cavity, usually with a sound hole or opening in the body. It may be either fretted or unfretted. More specifically, the term "lute" can refer to an instrument from the family of European lutes. The term also refers generally to any string instrument having the strings running in a plane parallel to the sound table (in the Hornbostel–Sachs system). The strings are attached to pegs or posts at the end of the neck, which have some type of turning mechanism to enable the player to tighten the tension on the string or loosen the tension before playing (which respectively raise or lower the pitch of a string), so that each string is tuned to a specific pitch (or note). The lute is plucked or strummed with one hand while the other hand "frets" (presses down) the strings on the neck's fingerboard. By pressing the strings on different places of the fingerboard, the player can short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Meantone
Meantone temperament is a musical temperament, that is a tuning system, obtained by narrowing the fifths so that their ratio is slightly less than 3:2 (making them ''narrower'' than a perfect fifth), in order to push the thirds closer to pure. Meantone temperaments are constructed the same way as Pythagorean tuning, as a stack of equal fifths, but it is a ''temperament'' in that the fifths are not pure. Notable meantone temperaments Equal temperament, obtained by making all semitones the same size, each equal to one-twelfth of an octave (with ratio the 12th root of 2 to one (:1), narrows the fifths by about 2 cents or 1/12 of a Pythagorean comma, and produces thirds that are only slightly better than in Pythagorean tuning. Equal temperament is roughly the same as 1/11 comma meantone tuning. Quarter-comma meantone, which tempers the fifths by 1/4 of a syntonic comma, is the best known type of meantone temperament, and the term ''meantone temperament'' is often used to refer to i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Johann Kirnberger
Johann Philipp Kirnberger (also ''Kernberg''; 24 April 1721, Saalfeld – 27 July 1783, Berlin) was a musician, composer (primarily of fugues), and music theorist. He was a student of Johann Sebastian Bach. According to Ingeborg Allihn, Kirnberger played a significant role in the intellectual and cultural exchange between Germany and Poland in the mid-18th century (Allihn 1995, 209). Between 1741 and 1751 Kirnberger lived and worked in Poland for powerful magnates including Lubomirski, Poninski, and Rzewuski before ending up at the Benedictine Cloister in Lviv (then part of Poland). He spent much time collecting Polish national dances and compiled them in his treatise Die Charaktere der Taenze (Allihn 1995, 211). Kirnberger became a violinist at the court of Frederick II of Prussia in 1751. He was the music director to the Prussian Princess Anna Amalia from 1758 until his death. Kirnberger greatly admired Johann Sebastian Bach, deeming him "the greatest of all composers." Kirn ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wolf Interval
In music theory, the wolf fifth (sometimes also called Procrustean fifth, or imperfect fifth) Paul, Oscar (1885). A manual of harmony for use in music-schools and seminaries and for self-instruction', p.165. Theodore Baker, trans. G. Schirmer. is a particularly dissonant musical interval spanning seven semitones. Strictly, the term refers to an interval produced by a specific tuning system, widely used in the sixteenth and seventeenth centuries: the quarter-comma meantone temperament. More broadly, it is also used to refer to similar intervals (of close, but variable magnitudes) produced by other tuning systems, including Pythagorean and most meantone temperaments. When the twelve notes within the octave of a chromatic scale are tuned using the quarter-comma mean-tone systems of temperament, one of the twelve intervals spanning seven semitones (classified as a diminished sixth) turns out to be much wider than the others (classified as perfect fifths). In mean-tone systems, t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |