|
Khan Of Astrakhan
First list with full names *''Küchük Muhammad one of the Last Khans of the Golden Horde had a son named Mahmud bin Küchük who succeeded him as Khan of the remnant Khanate named the Great Horde. He was deposed in a struggle for power by his brother, Ahmed Khan who became the last Khan of the Golden Horde/Great Horde. Mahmud, however, managed to keep territory named Haji Tarkhan (in Persian:'' ''or Haji-Tarkhan; in Russian: Астрахань or Astrakhan) and established his own Khanate there in 1465 C.E.'' Second list with short biographies There appears to be no modern book in English on the Astrakhan Khanate. According to Frank “The dates and activities of these rulers are faintly represented in the sources, when they are represented at all.” Outside of what might be found in a large library the only sources appear to be Howorth’s 1880 book, 3 pages of Frank and the English and Russian wikipedias. The following combines these four sources and notes the contradict ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Küchük Muhammad
Küchük Muḥammad or Kīchīk Muḥammad (; 28 June 1391 – 1459) was a Mongol Khan of the Golden Horde from 1433 until his death in 1459. He was the son of Tīmūr Khan, possibly by a daughter of the powerful beglerbeg Edigu. His name, "Little Muḥammad," was intended to distinguish him from a rival and older contemporary, Ulugh Muḥammad, "Big Muḥammad." Küchük Muḥammad started out as would-be khan at (old) Astrakhan from c. 1428, supported by his possible uncles, Ghāzī and Nawrūz, the sons of Edigu. A quarrel with the emir Nawrūz cost Küchük Muḥammad his desertion to Ulugh Muḥammad, and for a long time neither khan could eliminate his rival. However, Ulugh Muḥammad alienated more of his leading emirs, like Tekne and Ḥaydar, who deserted him to set up their own khan, Sayyid Aḥmad, son of Beg Ṣūfī, in 1432. Weakened by this, Ulugh Muḥammad came to terms with Küchük Muḥammad in 1432 or 1433, dividing the Golden Horde along the Volga, Ulugh ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ulugh Muhammad
Ulugh Muhammad (1405–1445; ; tt-Cyrl, Олуг Мөхәммәт, translit=Oluğ Möxəmmət; written as Ulanus by orientalists) was a medieval Tatar statesman, Gengisid, Khan of the Golden Horde (before 1436), ruler of Crimea (1437), and the founder of the Khanate of Kazan, which he ruled from 1438-1445. He was the son of the oglan Ichkile Hassan and the cousin of Tokhtamysh. He received the nickname "Ulugh", meaning older or large, in contrast to another Muhammed who was called "Kichi", meaning younger or small. Ulugh Muhammad was Khan of the Golden Horde in 1419-1423, 1426, 1428. In 1428-1432 he waged a stubborn struggle for possession of the Ulug Ulus with the representatives of a minor branch of the Tukaytimurids (one of the branches of the Gengisids). After being defeated, Ulugh Muhammad escaped to Volga Bulgaria vilayet in 1423. With the support Vytautas, Ulugh Muhammad was able to regain the throne of the Golden Horde in 1426. He succeeded in spreading the power of t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Zvenigorod
Zvenigorod (russian: Звени́город) is an old town in Moscow Oblast, Russia. Population: History The town's name is based either on a personal name (cf. Zvenislav, Zvenimir) or on a hydronym (cf. the Zvinech, Zvinyaka, Zveniga Rivers); the derivation from "town of ringing (bells)" is a folk etymology. The community has existed since the 12th century, although its first written mention is dated around 1339, in the last will of Grand Duke of Moscow Ivan I Daniilovich Kalita, in which he says: "Thus, I pass on to my son Ivan: Zvenigorod, Kremchina, Ruza..." In the historical records, or annals ( лéтопись etopis'in Russian), Zvenigorod is first mentioned around 1382, soon after khan Tokhtamysh burnt down Moscow, and destroyed a number of towns on the way, including Zvenigorod. Zvenigorod rose to prominence in the late 14th century after it was bequeathed by Dmitry Donskoy to his second son Yuri, who founded his residence on the steep bank of the Moskva River ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
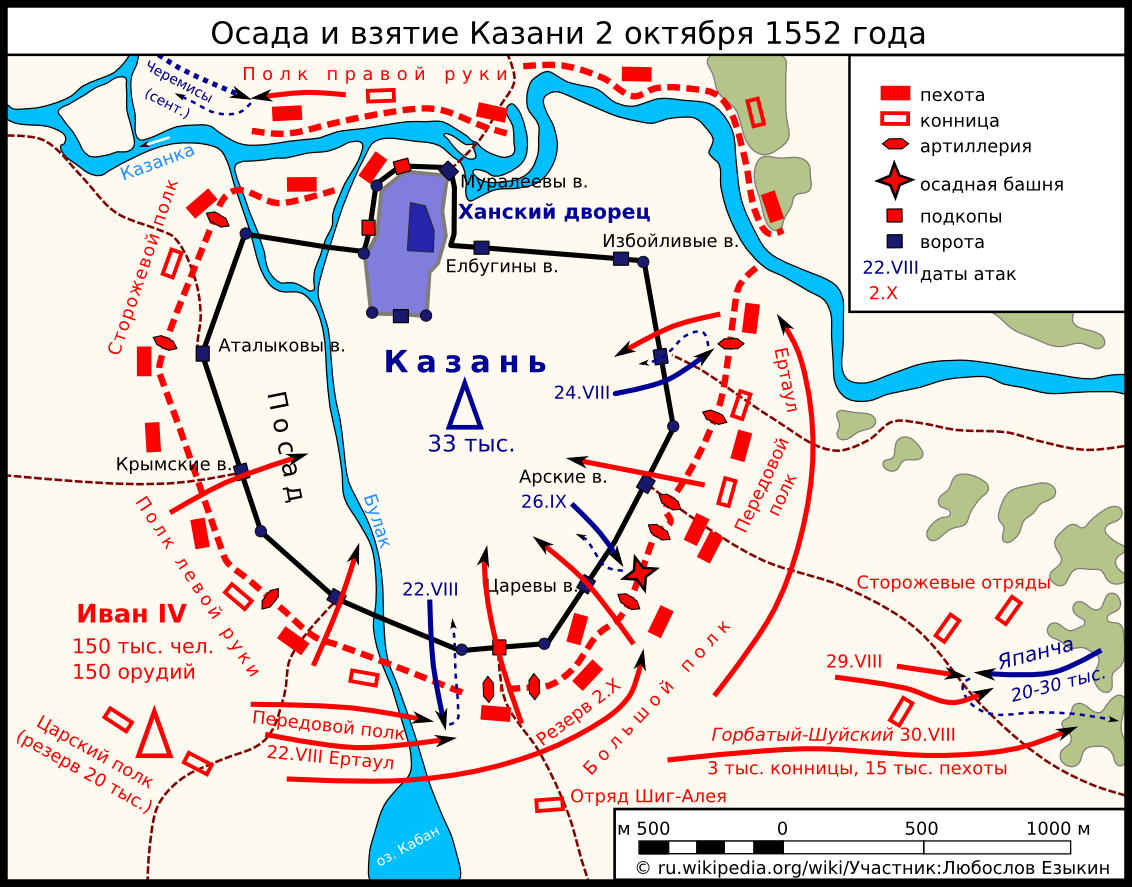
Siege Of Kazan
The siege of Kazan in 1552 was the final battle of the Russo-Kazan Wars and led to the fall of the Khanate of Kazan. Conflict continued after the fall of Kazan, however, as rebel governments formed in Çalım and Mişätamaq, and a new khan was invited from the Nogais. This guerrilla war lingered until 1556. Background During the existence of the khanate (1438-1552) Russian forces besieged Kazan at least ten times (1469, 1478, 1487, 1506, 1524, 1530, 1545, 1547, 1549-1550, 1552). In 1547 and in 1549-1550, Ivan the Terrible besieged Kazan, but supply difficulties forced him to withdraw. The Russians pulled back and built the town or fort of Sviyazhsk. They also annexed land west of the Volga which weakened the khanate. The peace party agreed to accept the pro-Russian Shah Ali as khan. The patriotic party regained power, Shah Ali fled and Yadegar Mokhammad of Kazan was called in as khan. Religious leaders like Qolsharif inspired the people to a determined resistance. The siege ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Söyembikä Of Kazan
Söyembikä (also spelled ''Söyenbikä, Sujumbike,'' pronounced ; Cyrillic: ''Сөембикә'') (1516 – after 1554) was a Tatar ruler, '' xanbikä''. She served as regent of Kazan during the minority of her son from 1549 until 1551. Life She was the daughter of Nogay nobleman Yosıf bäk and the wife of Canğäli (1533–35), Safagäräy (1536–49) and Şahğäli (after 1553). In 1549, she became regent during the minority of her son, Kazan khan Ütämeşgäräy. In 1551, after the first partial conquest of the Khanate of Kazan by Ivan the Terrible she was forcibly moved to Moscow with her son and later married to Şahğäli, the Russia-imposed khan of the Qasim and Kazan Tatars. Suicide Legend She is a national hero of Tatarstan. Her name is associated first of all with Söyembikä Tower, that Ivan the Terrible wanted to marry her, so she agreed that if he built her a tower made with seven tiers (one for each day of the week) then she would marry him. Ivan the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahib I Giray
Sahib I Giray (1501–1551) was Khan of Kazan for three years and Khan of Crimea for nineteen years. His father was the Crimean Khan Meñli I Giray. Sahib was placed on the throne of Kazan by his ambitious brother Mehmed of Crimea and driven out of Kazan by the Russians. He became Khan of Crimea with Ottoman support and was expelled by the Turks for disobedience. During his reign Crimean troops fought for the Turks and also fought in the North Caucasus. In 1532-1584, during the long reigns of Sahib I Giray, Devlet I Giray and Mehmed II Giray, Crimea was at the height of its power. Family and early life Sahib's grandfather was the founder of the Giray dynasty, Hacı I Giray (c. 1441–1466). His father was Mengli Giray (1478–1515). His brothers included Mehmed I Giray (1515–1523), Saadet I Giray (1524–1532) and Mubarak. His successor, Devlet I Giray (1551–1577), was a son of Mubarak. Ğazı I Giray (1523–24) and İslâm I Giray (1532) were sons of Mehmed I. Sahib's w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Shahghali
Shahghali, also Shah Ali or Shah Ghaly, (Tatar: ''Şahğäli'', pronounced , or ''Şäyex Ğäli'', ) (1505–1567) was khan of the Qasim Khanate and the Khanate of Kazan. He ruled the Qasim Khanate for much of his life and three times tried to rule the Khanate of Kazan, which was independent until its conquest by Muscovy in 1552. He also ruled the town of Kasimov as a vassal of the Russians. He was the son of the Qasim Khan Sheikh Auliyar (reigned 1512-16) and grandson of Bakhtiar Sultan, a brother of Ahmed Khan bin Küchük (the Golden Horde ruler who lost control of Russia). One of his wives was the unfortunate Söyembikä of Kazan. He died childless in 1567 and was succeeded by Sain Bulat. He is described as physically repulsive and too fat to be a soldier, but a man of sound judgement. Biography Shahghali came to the throne in 1516 at age 11 upon his father’s death. There is little information about this period. When he moved to Kazan his brother Jan Ali became khan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Sahib Giray
Sahib I Giray (1501–1551) was Khan of Kazan for three years and Khan of Crimea for nineteen years. His father was the Crimean Khan Meñli I Giray. Sahib was placed on the throne of Kazan by his ambitious brother Mehmed of Crimea and driven out of Kazan by the Russians. He became Khan of Crimea with Ottoman support and was expelled by the Turks for disobedience. During his reign Crimean troops fought for the Turks and also fought in the North Caucasus. In 1532-1584, during the long reigns of Sahib I Giray, Devlet I Giray and Mehmed II Giray, Crimea was at the height of its power. Family and early life Sahib's grandfather was the founder of the Giray dynasty, Hacı I Giray (c. 1441–1466). His father was Mengli Giray (1478–1515). His brothers included Mehmed I Giray (1515–1523), Saadet I Giray (1524–1532) and Mubarak. His successor, Devlet I Giray (1551–1577), was a son of Mubarak. Ğazı I Giray (1523–24) and İslâm I Giray (1532) were sons of Mehmed I. Sahib's w ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Canghali Of Kazan
Canghali (also Jan Ali, ''Can Ali,'' Tatar: ''Җангали''; russian: Джан-Али) (1516–1535) was ruler of the Khanate of Qasim in 1519–1532 and then Khanate of Kazan in 1532–1535. He was the son of Qasim khan Shayex Allahiar (Şäyex Allahiär) (r. 1512-15) and younger brother of Qasim khan Shahgali or Shah Ali (r. 1515-19). When Shah Ali moved to Kazan Jan Ali took the throne. The Qasim Khanate was a vassal state of Muscovy. Canghali as its ruler had close ties with Muscovy. In 1532 Vasili III of Russia defeated Kazan, khan Safagäräy fled and the 16-year-old Canghali was brought in as a pro-Russian ruler of the bigger and generally independent Kazan Khanate. In 1533 Canghali married Söyembika, the daughter of Nogay nobleman. During his reign he was completely manipulated by Bulat Shirin (Bulat Şirin, /boo-LAHT shee-RREEN/) and queen Gawharshat (Gäwhärşat, /geh-w-ha-rr-SHAHT/), widow or sister of Moxammat Amin khan. During 1535 coup of Kazan nobility, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed I Giray
Mehmed I Giray (1465–1523, reigned 1515–1523) was khan of the Crimean Khanate. He was preceded by his father Meñli I Giray (r. 1478–1515) and followed by his son Ğazı I Giray (1523–1524). He gained control of the steppe nomads, put his brother on the throne of Kazan and was killed after taking Astrakhan. Had he not been killed he might have joined the three khanates with the Nogais and re-created something like the Golden Horde. As Kalga As his father's Kalga or designated successor and co-ruler, he participated in a number of raids northward. In 1505 he and his father raided what is now Belarus. In 1507 they advanced toward Russia, but turned back on learning of a Nogai raid on Crimea. Mehmed fell from his horse and became ill. The force returned to Crimea. In 1509 the Nogais planned to attack Crimea. Mehmed and a very large army defeated them as they were crossing the Volga. Much booty was taken. In 1510 he was also successful against the Nogais. In 1512 he raided Rus ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Great Stand On The Ugra River
The Great Stand on the Ugra River (russian: Великое cтояние на реке Угре, also russian: Угорщина, translit=Ugorshchina, derived from " Ugra") was a standoff between the forces of Akhmat Khan of the Great Horde, and the Grand Prince Ivan III of Muscovy in 1480 on the banks of the Ugra River, which ended when the Tatars departed without conflict. It is seen in Russian historiography as the end of the vassalage of Muscovy.Michael Khodarkovsky, ''Russia's Steppe Frontier: The Making of a Colonial Empire, 1500–1800'' (Indiana University Press, 2002), 80. Background The main Russian defence line ran along the Oka River from Kaluga east toward Nizhny Novgorod. At Kaluga the Oka bends sharply from north to east and the defense line was extended westward along the Ugra River. The land west and south of Kaluga was claimed by Lithuania. At this time Ivan III was uniting the lands north of the Oka. At the same time the Golden Horde was breaking up and the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |

.jpeg/1200px-Suumbike_(Vasily_Khudiakov%2C_1870).jpeg)
