|
Kagami Mochi
is a traditional Japanese New Year decoration. It usually consists of two round mochi (rice cakes),Kagami mochi FAQ from Tokyo Gas dictionary. Various Japanese dictionaries, including the , testify that the kagami mochi has two layers of mochi. Three or more layers is not mentioned. the smaller placed atop the larger, and a (a Japanese |
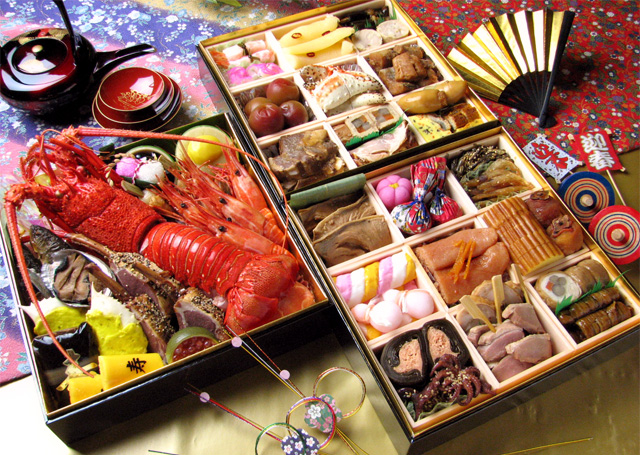
Japanese New Year
The is an annual festival with its own customs. Since 1873, the official Japanese New Year has been celebrated according to the Gregorian calendar, on January 1 of each year, . However, some traditional events of the Japanese New Year are partially celebrated on the first day of the year on the modern Tenpō calendar, the last official lunisolar calendar which was used until 1872 in Japan. History Prior to the Meiji period, the date of the Japanese New Year had been based on Japanese versions of lunisolar calendar (the last of which was the Tenpō calendar) and, prior to Jōkyō calendar, the Chinese version. However, in 1873, five years after the Meiji Restoration, Japan adopted the Gregorian calendar and the first day of January became the official and cultural New Year's Day in Japan. Traditional food The Japanese eat a selection of dishes during the New Year celebration called , typically shortened to ''osechi.'' Many of these dishes are sweet, sour, or dried, so the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Butsudan
A , sometimes spelled Butudan, is a shrine commonly found in temples and homes in Japanese Buddhist cultures. A ''butsudan'' is either a defined, often ornate platform or simply a wooden cabinet sometimes crafted with doors that enclose and protect a ''Gohonzon'' or religious icon, typically a statue or painting of a Buddha or Bodhisattva, or a calligraphic mandala scroll. The butsudan's primary use is for paying respects to the Buddha, as well as to family members who have died. Arrangement A ''butsudan'' usually contains an array of subsidiary religious accessories, called ''butsugu'', such as candlesticks, incense burners, bells, and platforms for placing offerings such as fruit, tea or rice. Some Buddhist sects place ''ihai'' memorial tablets, ''kakochō'' death registers for deceased relatives, or urns containing the cremated remains of relatives, either within or near the ''butsudan''. The defined space which occupies the Butsudan is referred to as ''Butsuma''. If there ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Festivals In Japan
This is an incomplete list of festivals in Japan. Traditional festivals Film festivals Music festivals See also * Japanese festivals * Abare Festival Abare Festival is a Japanese festival commonly known as the ''Fire & Violence Festival''. It takes place in Ushitsu of Noto Peninsula and is dedicated to the Yasaka Shrine. The festival takes place every year in July on the first Friday and Satu ... * Matsuri float References {{DEFAULTSORT:Festivals in Japan Japan Japan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Daphniphyllum
''Daphniphyllum'' is the sole genus in the flowering plant family Daphniphyllaceae and was described as a genus in 1826. The genus includes evergreen shrubs and trees mainly native to east and southeast Asia, but also found in the Indian Subcontinent and New Guinea. All species in the family are dioecious, that is male and female flowers are borne on different plants. In older classifications the genus was treated in the family Euphorbiaceae. ''Daphniphyllum'' species are eaten by the larvae of some Lepidoptera species including the engrailed (''Ectropis'' sp.). ;Accepted species ; Synonyms * ''Daphniphyllum humile'' Maxim. ex Franch. & Sav. (''Daphniphyllum macropodum ''Daphniphyllum macropodum'' is a shrub or small tree found in China, Japan and Korea. Like all species in the genus ''Daphniphyllum'', ''D. macropodum'' is dioecious, that is male and female flowers are borne on different plants. The timber is u ...'') References Bibliography * * Ohwi, J. ''Flora of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Noshi
are a kind of ceremonial origami fold entirely distinct from "origami-tsuki". They serve as gifts that express "good wishes". Noshi consists of white paper folded with a strip of dried abalone or meat, considered a token of good fortune. See also * Shūgi-bukuro A is a special envelope in which money is given as a gift of celebration in Japan, especially at weddings or other auspicious occasions, such as a birth or celebrating a new home. The giver inserts the money into a on which they have written t ... References External links Japanese traditional envelopes: NoshiThe History of Origami: Noshi Japanese words and phrases Paper art Origami Ise Grand Shrine {{Japan-culture-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dōjō
A is a hall or place for immersive learning or meditation. This is traditionally in the field of martial arts, but has been seen increasingly in other fields, such as meditation and software development. The term literally means "place of the Way" in Japanese. History The word ''dōjō'' originates from Buddhism. Initially, ''dōjō'' were adjunct to temples and were formal training places for any of the Japanese arts ending in "''-dō''", from the Chinese ''Tao'' (or ''Dao''), meaning "way" or "path". Sometimes meditation halls where Zen Buddhists practice ''zazen'' meditation were called ''dōjō''. The alternative term '' zen-do'' is more specific, and more widely used. European ''Sōtō Zen'' groups affiliated with the International Zen Association prefer to use ''dōjō'' instead of ''zendo'' to describe their meditation halls as did their founding master, Taisen Deshimaru. In Japan, any facility for physical training, including professional wrestling, may be called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Jujutsu
Jujutsu ( ; ja, link=no, 柔術 , ), also known as jiu-jitsu and ju-jitsu, is a family of Japanese martial arts and a system of close combat (unarmed or with a minor weapon) that can be used in a defensive or offensive manner to kill or subdue one or more weaponless or armed and armored opponents. Jiu-jitsu dates back to the 1530s and was coined by Hisamori Tenenouchi when he officially established the first jiu-jitsu school in Japan. This form of martial arts uses few or no weapons at all and includes strikes, throws, holds, and paralyzing attacks against the enemy. Jujutsu developed from the warrior class around the 17th century in Japan. It was designed to supplement the swordsmanship of a warrior during combat. A subset of techniques from certain styles of jujutsu were used to develop many modern martial arts and combat sports, such as judo, aikido, sambo, ARB, Brazilian jiu-jitsu, and mixed martial arts. The official date of foundation of Jiu Jitsu is 1530. Charac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Karate
(; ; Okinawan language, Okinawan pronunciation: ) is a martial arts, martial art developed in the Ryukyu Kingdom. It developed from the Okinawan martial arts, indigenous Ryukyuan martial arts (called , "hand"; ''tii'' in Okinawan) under the influence of Chinese martial arts, particularly Fujian White Crane. Karate is now predominantly a striking art using Punch (combat), punching, kicking, knee (strike), knee strikes, elbow strikes and open-hand techniques such as Knifehand strike, knife-hands, spear-hands and palm-heel strikes. Historically, and in some modern styles, grappling, throws, joint locks, restraints and kyusho-jitsu, vital-point strikes are also taught. A karate practitioner is called a . The Empire of Japan annexed the Ryukyu Kingdom in 1879. Karate came to mainland Japan in the early 20th century during a time of migration as Ryukyuans, especially from Okinawa, looked for work in the main islands of Japan. It was systematically taught in Japan after the Taishō ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Aikido
Aikido ( , , , ) is a modern Japanese martial art that is split into many different styles, including Iwama Ryu, Iwama Shin Shin Aiki Shuren Kai, Shodokan Aikido, Yoshinkan, Renshinkai, Aikikai and Ki Aikido. Aikido is now practiced in around 140 countries. It was originally developed by Morihei Ueshiba, as a synthesis of his martial studies, philosophy and religious beliefs. Ueshiba's goal was to create an art that practitioners could use to defend themselves while also protecting their attackers from injury. Aikido is often translated as "the way of unifying (with) life energy" or as "the way of harmonious spirit". According to the founder's philosophy, the primary goal in the practice of aikido is to overcome oneself instead of cultivating violence or aggressiveness. Morihei Ueshiba used the phrase to refer to this principle. Aikido's fundamental principles include: (entering), , (breathing control), (triangular principle) and (turning) movements that redirect the oppo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Judo
is an unarmed gendai budō, modern Japanese martial art, Olympic sport (since 1964), and the most prominent form of jacket wrestling competed internationally.『日本大百科全書』電子版【柔道】(CD-ROM version of Encyclopedia Nipponica, "Judo"). Judo was created in 1882 by Kanō Jigorō () as an eclectic martial art, distinguishing itself from its predecessors (primarily Tenjin Shin'yō-ryū, Tenjin Shinyo-ryu jujutsu and Kitō-ryū jujutsu) due to an emphasis on "randori" (, lit. 'free sparring') instead of "kata" (pre-arranged forms) alongside its removal of striking and weapon training elements. Judo rose to prominence for its dominance over Kodokan–Totsuka rivalry, established jujutsu schools in tournaments hosted by the Tokyo Metropolitan Police Department (警視庁武術大会, ''Keishicho Bujutsu Taikai''), resulting in its adoption as the department's primary martial art. A judo practitioner is called a , and the judo uniform is called . The objective of co ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kanō Jigorō
was a Japanese educator, athlete, and the founder of Judo. Along with Ju-Jutsu, Judo was one of the first Japanese martial arts to gain widespread international recognition, and the first to become an official Olympic sport. Pedagogical innovations attributed to Kanō include the use of black and white belts, and the introduction of dan ranking to show the relative ranking among members of a martial art style. Well-known mottoes attributed to Kanō include "maximum efficiency with minimum effort" ( ''seiryoku zen'yō'') and "mutual welfare and benefit" ( ''jita kyōei''). In his professional life, Kanō was an educator. Important postings included serving as director of primary education for the from 1898 to 1901, and as president of Tokyo Higher Normal School from 1900 until 1920.Strictly speaking, the name was Tokyo Normal School from 1901 until 1903, and Tokyo Higher Normal School from 1903 to 1924. Tokyo Higher Normal School is today viewed as an ancestor of the Institu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Dojo
A is a hall or place for immersive learning or meditation. This is traditionally in the field of martial arts, but has been seen increasingly in other fields, such as meditation and software development. The term literally means "place of the Way" in Japanese. History The word ''dōjō'' originates from Buddhism. Initially, ''dōjō'' were adjunct to temples and were formal training places for any of the Japanese arts ending in "''-dō''", from the Chinese ''Tao'' (or ''Dao''), meaning "way" or "path". Sometimes meditation halls where Zen Buddhists practice ''zazen'' meditation were called ''dōjō''. The alternative term '' zen-do'' is more specific, and more widely used. European ''Sōtō Zen'' groups affiliated with the International Zen Association prefer to use ''dōjō'' instead of ''zendo'' to describe their meditation halls as did their founding master, Taisen Deshimaru. In Japan, any facility for physical training, including professional wrestling, may be called ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |