|
Kłecko Hillfort (Grodzisko Barbara)
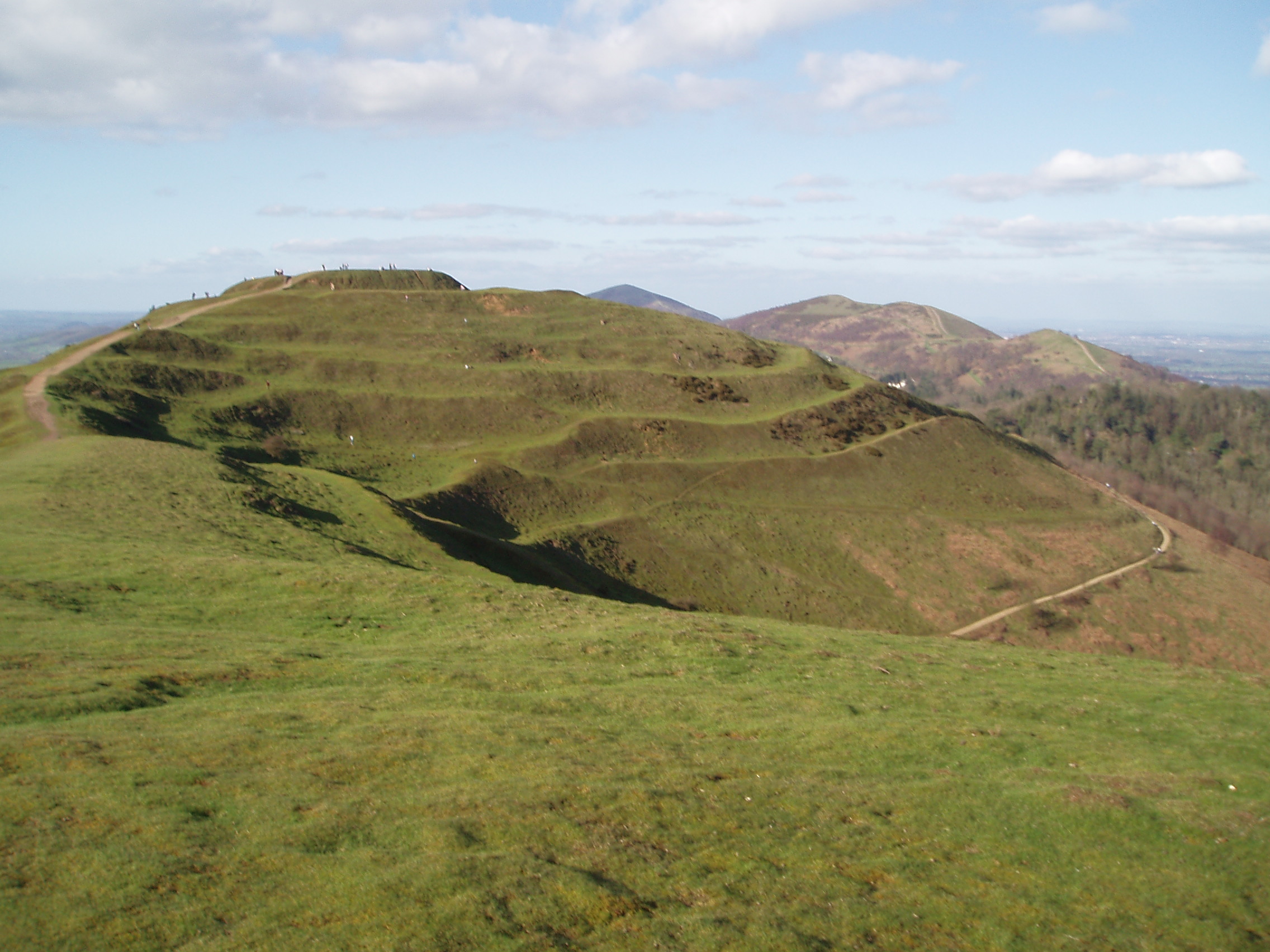
Kłecko Hillfort ''(Grodzisko Barbara)'' is an early medieval gord dating back to the formation of the Polish state in the 10th century, located between the Gorzuchowskie and Kłeckie lakes on the Gniezno-Wągrowiec road. The gord takes the form of a hillfort of an oval shape with preserved dimensions of about 40 x 35 m. Description The hillfort was surrounded by a defensive embankment with a grate structure and gatehouse. Inside the building, a circular street ran along the embankments, and dense residential buildings were located along the transverse streets. The hillfort was established in wetlands near the Mała Wełna River, on a trading road leading to Pomerania, and at the same time in the center of a large settlement from the early Middle Ages. Grodzisko experienced expansion in the second half of the 10th century during the rulership of Mieszko I, constituting an important point in the defence and administration of the early Piast state. The hillfort had settlemen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kłecko
Kłecko () is a town in Gniezno County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, Poland, with 2,632 inhabitants (2010). History A Lechitic stronghold was founded in the 9th century, located in the Greater Poland region, which in the 10th century would become the cradle of the emerging Polish state. Kłecko was granted town rights probably by Duke Bolesław the Pious in 1265. It was a royal town of Poland, administratively located in the Gniezno County in the Kalisz Voivodeship in the Greater Poland Province. In 1331, during the Polish–Teutonic War, the Teutonic Knights plundered and destroyed the town, and murdered its defenders. A battle between the Swedish Army and Polish forces stood here on 7 May 1656 during the Deluge (Swedish invasion of Poland). The battle was an important victory for Sweden. A painting picturing the battle can be seen in the museum at the current Home of the Swedish royal family Drottningholm Palace near Stockholm, Sweden. Second World War During the German I ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Giecz
Giecz is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Dominowo, within Środa Wielkopolska County, Greater Poland Voivodeship, in west-central Poland. It lies approximately north of Dominowo, north-east of Środa Wielkopolska, and east of the regional capital Poznań. Giecz was once one of the main centres of Polish statehood in the early Middle Ages, alongside Poznań and Gniezno. In the early 9th century, a small keep was built on a mound on a peninsula on the Giecz lake; fortified with a stockade and earthworks. Since 940 it was one of the key strongholds of the early Piast dynasty. In 1038 during a war with Bohemia, the place was seized by Bretislaus I, who sacked the nearby settlement and sold its inhabitants into slavery. The place quickly recovered and by the 13th century was a centre of administration, trade and commerce in the Greater Poland region. At about that time, the settlement received a town charter and became the seat of a castellan A castella ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
10th-century Fortifications
1 (one, unit, unity) is a number, numeral, and glyph. It is the first and smallest positive integer of the infinite sequence of natural numbers. This fundamental property has led to its unique uses in other fields, ranging from science to sports, where it commonly denotes the first, leading, or top thing in a group. 1 is the unit of counting or measurement, a determiner for singular nouns, and a gender-neutral pronoun. Historically, the representation of 1 evolved from ancient Sumerian and Babylonian symbols to the modern Arabic numeral. In mathematics, 1 is the multiplicative identity, meaning that any number multiplied by 1 equals the same number. 1 is by convention not considered a prime number. In digital technology, 1 represents the "on" state in binary code, the foundation of computing. Philosophically, 1 symbolizes the ultimate reality or source of existence in various traditions. In mathematics The number 1 is the first natural number after 0. Each natural numbe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Fortifications In Poland
A fortification (also called a fort, fortress, fastness, or stronghold) is a military construction designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ("strong") and ("to make"). From very early history to modern times, defensive walls have often been necessary for cities to survive in an ever-changing world of invasion and conquest. Some settlements in the Indus Valley Civilization were the first small cities to be fortified. In ancient Greece, large cyclopean stone walls fitted without mortar had been built in Mycenaean Greece, such as the ancient site of Mycenae. A Greek '' phrourion'' was a fortified collection of buildings used as a military garrison, and is the equivalent of the Roman castellum or fortress. These constructions mainly served the purpose of a watch tower, to guard certain roads, passes, and borders. Though smaller than a real fortress, they acted as a border gu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hillforts
A hillfort is a type of fortified refuge or defended settlement located to exploit a rise in elevation for defensive advantage. They are typical of the late European Bronze Age and Iron Age. Some were used in the post- Roman period. The fortification usually follows the contours of a hill and consists of one or more lines of earthworks or stone ramparts, with stockades or defensive walls, and external ditches. If enemies were approaching, the inhabitants would spot them from a distance. Prehistoric Europe saw a growing population. It has been estimated that in about 5000 BC during the Neolithic between 2 million and 5 million lived in Europe; in the Late Iron Age it had an estimated population of around 15 to 30 million. Outside Greece and Italy, which were more densely populated, the vast majority of settlements in the Iron Age were small, with perhaps no more than 50 inhabitants. Hillforts were the exception, and were the home of up to 1,000 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Archaeological Sites In Poland
Archaeology or archeology is the study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landscapes. Archaeology can be considered both a social science and a branch of the humanities. It is usually considered an independent academic discipline, but may also be classified as part of anthropology (in North America – the four-field approach), history or geography. The discipline involves surveying, excavation, and eventually analysis of data collected, to learn more about the past. In broad scope, archaeology relies on cross-disciplinary research. Archaeologists study human prehistory and history, from the development of the first stone tools at Lomekwi in East Africa 3.3 million years ago up until recent decades. Archaeology is distinct from palaeontology, which is the study of fossil remains. Archaeology is particularly important for learning ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Occupation Of Poland (1939–1945)
During World War II, Poland was occupied by Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union following the invasion in September 1939, and it was formally concluded with the defeat of Germany by the Allies in May 1945. Throughout the entire course of the occupation, the territory of Poland was divided between Nazi Germany and the Soviet Union (USSR), both of which intended to eradicate Poland's culture and subjugate its people. In the summer-autumn of 1941, the lands which were annexed by the Soviets were overrun by Germany in the course of the initially successful German attack on the USSR. After a few years of fighting, the Red Army drove the German forces out of the USSR and crossed into Poland from the rest of Central and Eastern Europe. Sociologist Tadeusz Piotrowski argues that both occupying powers were hostile to the existence of Poland's sovereignty, people, and the culture and aimed to destroy them. Before Operation Barbarossa, Germany and the Soviet Union coordinated th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
World War II
World War II or the Second World War (1 September 1939 – 2 September 1945) was a World war, global conflict between two coalitions: the Allies of World War II, Allies and the Axis powers. World War II by country, Nearly all of the world's countries participated, with many nations mobilising all resources in pursuit of total war. Tanks in World War II, Tanks and Air warfare of World War II, aircraft played major roles, enabling the strategic bombing of cities and delivery of the Atomic bombings of Hiroshima and Nagasaki, first and only nuclear weapons ever used in war. World War II is the List of wars by death toll, deadliest conflict in history, causing World War II casualties, the death of 70 to 85 million people, more than half of whom were civilians. Millions died in genocides, including the Holocaust, and by massacres, starvation, and disease. After the Allied victory, Allied-occupied Germany, Germany, Allied-occupied Austria, Austria, Occupation of Japan, Japan, a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Józef Kostrzewski
Józef Kostrzewski (25 February 188519 October 1969) was a Polish archaeologist. Kostrzewski was born in Węglewo (now in Poznań County). He studied first in Kraków, then from 1910 onwards with Gustaf Kossinna at Berlin and graduated in 1914. Back in Poland, he was to turn Kossinna's settlement-archaeological method (''"Siedlungsarchäologische Methode"'') against its creator and to try to prove a Slavonic autochthonism in Poland from at least the Bronze Age (Lusatian culture) onwards. Kostrzewski became professor of prehistory at the newly founded University of Poznań in 1919, and from 1934 conducted the excavation of the Iron Age settlement of Biskupin, which he continued after the war. After 1918, Kostrzewski became involved in bitter polemics about the ethnic ascription of the Lusatian and Pomeranian cultures with the German archaeologist Bolko von Richthofen. During the German occupation of Poland during World War II, Polish universities and museums were closed, th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Witold Hensel
Witold Maria Hensel (March 29, 1917 in Gniezno – November 22, 2008 in Warsaw) was a Polish archaeologist. He was a member of the Polish Academy of Sciences and a member of the Sejm The Sejm (), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland (), is the lower house of the bicameralism, bicameral parliament of Poland. The Sejm has been the highest governing body of the Third Polish Republic since the Polish People' ... in PRL ( SD, 1985–1989). Publications *Archaeological research in Poland ; by Witold Hensel and Aleksander Gieysztor, Warsaw : Polonia Pub. House, 1958.Available at Warburg Institute *The Origins of Western and Eastern Slav Towns, Witold Hensel, World Archaeology, Vol. 1, No. 1, Recent Work and New Approaches (Jun., 1969), pp. 51–6*Polska Starożytna (En:ancient Poland) ;by Witold Hensel ;January 1988, Book, 3rd edition ; *Excavations of Neolithic and Early Bronze Age Sites in South-Eastern Poland ;by Sarunas Milisauskas, Witold Hensel, Inst ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Adam Mickiewicz University In Poznań
The Adam Mickiewicz University (; Latin: ''Universitas Studiorum Mickiewicziana Posnaniensis'') is a research university in Poznań, Poland. Due to its history, the university is traditionally considered among Poland's most reputable institutions of higher learning, this standing equally being reflected in national rankings. It traces its origins to 1611, when under the Royal charter, Royal Charter granted by King Sigismund III Vasa, the Jesuit College in Poznań, Jesuit College became the first university in Poznań. The Poznań Society of Friends of Learning, Poznań Society for the Advancement of Arts and Sciences which played an important role in leading Poznań to its reputation as a chief intellectual centre during the Positivism in Poland, Age of Positivism and partitions of Poland, initiated founding of the university. The inauguration ceremony of the newly founded institution took place on 7 May 1919 that is 308 years after it was formally established by the Polish king ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Teutonic Order
The Teutonic Order is a religious order (Catholic), Catholic religious institution founded as a military order (religious society), military society in Acre, Israel, Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem was formed to aid Christians on their pilgrimages to the Holy Land and to establish hospitals. Its members have commonly been known as the Teutonic Knights, having historically served as a crusades, crusading military order for supporting Catholic rule in the Holy Land and the Northern Crusades during the Middle Ages, as well as supplying military protection for Catholics in Eastern Europe. Purely religious since 1810, the Teutonic Order still confers limited honorary knighthoods. The Bailiwick of Utrecht of the Teutonic Order, a Protestant order of chivalry, chivalric order, is descended from the same medieval military order and also continues to award knighthoods and perform charitable work. Name The name of the Or ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |