|
Kızıl Ahmed Bey
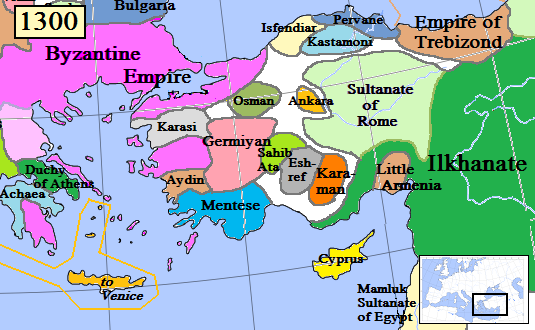
The Candar dynasty (, transliterated as Jandar in English), also known as the Isfendiyar dynasty (), was a Turkish Anatolian Beylik (principality) founded by Oghuz Turks. that reigned in the territories corresponding to the provinces of Eflani, Kastamonu, Sinop, Zonguldak, Bartın, Karabük, Samsun, Bolu, Ankara and Çankırı in present-day Turkey from the year 1291 to 1461. The region was known in Western literature as Paphlagonia, a name applied to the same geographical area during the Roman period. The dynasty and principality, founded by Şemseddin Yaman Candar Bey, were incorporated into the Ottoman Empire by Sultan Mehmed II in 1461. History Descended from the Kayı branch of Oghuz Turks, the dynasty began when the sultan Mesud II of the Seljuks of Rum awarded the province of Eflani to Şemseddin Yaman Candar, a senior commander in the imperial armed forces, in gratitude for rescuing him from Mongol captivity. The province had previously been under the rule of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Eflani
Eflani is a town in Karabük Province in the Black Sea region of Turkey. It is the seat of Eflani District.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its population is 2,076 (2022). Eflani is located at 100 km south of the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal sea, marginal Mediterranean sea (oceanography), mediterranean sea lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bound ... . 46 km away from, and to the east of [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolu Province
Bolu Province () is a Provinces of Turkey, province in north-western Turkey, between the capital, Ankara, and the largest city in the country, Istanbul. Its area is 8,313 km,2, and its population is 320,824 (2022). The capital city of the province is Bolu. Geography The province is drained by the Bolu River (''Boli Su'') and the Koca River. The forests, lakes, and mountains are home to wildlife, including three deer species. Parts of the province are vulnerable to earthquakes. Protected areas The province has the Yedigöller National Park. There is also another area consisting of a lake and its surroundings that is under protection by the Ministry of Agriculture and Forestry as a 'nature park' that is called Gölcük. There is a structure on the shore of the lake named the State Guesthouse of the Ministry of Forestry. Near the nature park is an artificial lake; the lake is to the south of the city of Bolu. History It is not known when Bolu was first established. Some ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Safranbolu District
Safranbolu District is a district of the Karabük Province of Turkey. Its seat is the town of Safranbolu.İlçe Belediyesi Turkey Civil Administration Departments Inventory. Retrieved 1 March 2023. Its area is 750 km2, and its population is 70,409 (2022). Composition There is one in Safranbolu District: * There are 60villages
A village is a ...
[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Chobanids (beylik)
The Chobanids ( Modern Turkish: ''Çobanoğulları'', ''Çobanoğulları Beyliği'') were the ruling dynasty of the Turkish Anatolian beylik (principality) that controlled the city and region of Kastamonu in the 13th century. History The founder of the dynasty was Hüsamettin Çoban, a prominent Kayı statesman and a commander of the Sultans of Rum during the reigns of Kaykaus I and his successor Kayqubad I. In the early decades of the 13th century, Hüsamettin Çoban was one of the commanders of the raids that extended Seljuk territory in northern Anatolia at the expense of the Byzantine Empire of Trebizond. As a result, he had acquired Kastamonu as a fiefdom. Between 1224 and 1227, he also led the Seljuq army and fleet that set sail from Sinop and captured and fortified the city of Sudak in Crimea. After Hüsamettin Çoban's death, his hereditary possessions centered in Kastamonu were ruled respectively by his son and grandson, Alp Yürek and Yavlak Arslan. Until the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mongol Empire
The Mongol Empire was the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in human history, history. Originating in present-day Mongolia in East Asia, the Mongol Empire at its height stretched from the Sea of Japan to parts of Eastern Europe, extending northward into parts of the Arctic; eastward and southward into parts of the Indian subcontinent, mounting invasions of Southeast Asia, and conquering the Iranian plateau; and reaching westward as far as the Levant and the Carpathian Mountains. The Mongol Empire emerged from the unification of several nomad, nomadic tribes in the Mongol heartland under the leadership of Temüjin, known by the title of Genghis Khan (–1227), whom a council proclaimed as the ruler of all Mongols in 1206. The empire grew rapidly under his rule and that of his descendants, who sent out Mongol invasions, invading armies in every direction. The vast transcontinental empire connected the Eastern world, East with the Western world, West, and the Pac ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuks Of Rum
The Sultanate of Rum was a culturally Turco-Persian Sunni Muslim state, established over conquered Byzantine territories and peoples (Rum) of Anatolia by the Seljuk Turks following their entry into Anatolia after the Battle of Manzikert in 1071. The name ''Rum'' was a synonym for the medieval Eastern Roman Empire and its peoples, as it remains in modern Turkish. The name is derived from the Aramaic () and Parthian () names for ancient Rome, via the Greek () meaning the Anatolia. The Sultanate of Rum seceded from the Seljuk Empire under Suleiman ibn Qutalmish in 1077. It had its capital first at Nicaea and then at Iconium. It reached the height of its power during the late 12th and early 13th century, when it succeeded in taking key Byzantine ports on the Mediterranean and Black Sea coasts. In the east, the sultanate reached Lake Van. Trade through Anatolia from Iran and Central Asia was developed by a system of caravanserai. Especially strong trade ties with the Genoese formed d ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mesud II
Ghiyath al-Dīn Me’sud ibn Kaykaus or Mesud II (, ''Ghiyāth ad-Dīn Mas'ūd bin Kaykāwūs''; , ) bore the title of Sultan of Rûm at various times between 1284 and 1308. He was a vassal of the Mongols under Mahmud Ghazan and exercised no real authority. Mesud died in 1308, the last of the Seljuks of Rum. Reign Mesud was the eldest son of Kaykaus II. He spent part of his youth as an exile in the Crimea and lived for a time in Constantinople, then the capital of the Byzantine Empire. He appears first in Anatolia in 1280 as a pretender to the throne. In 1284 the new Ilkhanid Sultan Ahmed Tekuder deposed and executed the Seljuq sultan Kaykhusraw III and installed Mesud in his place. Ahmad's successor, Arghun, divided the Seljuq lands and granted Konya and the western half of the kingdom to the deposed sultan's two young sons. Mesud invaded with a small force, had the two boys killed, and established himself in the city in 1286. Mesud led several campaigns against the e ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kayı (tribe)
The Kayı or Kayi tribe (Karakhanid language, Karakhanid: قَيِغْ ''qayïγ'' or ''qayig''; , ) were an Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic peoples, Turkic people and a sub-branch of the Oghuz Turks, Bozok tribal federation. In his ''Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk'', the 11th century Kara-Khanid Khanate, Kara-Khanid scholar Mahmud al-Kashgari cited as of one of 22 Oghuz tribes, saying that Oghuz were also called Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkomans. The name ''Kayı'' means "''the one who has might and power by relationship''" and the Turkmens, Turkmen proverb says that "''people shall be headed by Kayı and Bayat tribes" ().'' Origin In his history work ''Shajara-i Tarākima'', the Khan of Khanate of Khiva, Khiva and historian, Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur, mentions among the 24 ancient Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkmen (Oghuz Turks, Oghuz Turkic) tribes, direct descendants of Oghuz Khagan. Oghuz Khagan is a semi-legendary figure thought to be the ancient progenitor of Oghuz Turks. translates as "strong". ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mehmed II
Mehmed II (; , ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror (; ), was twice the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from August 1444 to September 1446 and then later from February 1451 to May 1481. In Mehmed II's first reign, he defeated the crusade led by John Hunyadi after the Hungarian incursions into his country broke the conditions of the truce per the Peace of Szeged, Treaties of Edirne and Szeged. When Mehmed II ascended the throne again in 1451, he strengthened the Ottoman Navy and made preparations to attack Constantinople. At the age of 21, he Fall of Constantinople, conquered Constantinople and brought an end to the Byzantine Empire. After the conquest, Mehmed claimed the title Caesar (title), caesar of Roman Empire, Rome (), based on the fact that Constantinople had been the seat and capital of the surviving Byzantine Empire, Eastern Roman Empire since its consecration in 330 AD by Constantine the Great, Emperor Constantine I. The claim was soon reco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire (), also called the Turkish Empire, was an empire, imperial realm that controlled much of Southeast Europe, West Asia, and North Africa from the 14th to early 20th centuries; it also controlled parts of southeastern Central Europe, between the early 16th and early 18th centuries. The empire emerged from a Anatolian beyliks, ''beylik'', or principality, founded in northwestern Anatolia in by the Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman tribal leader Osman I. His successors Ottoman wars in Europe, conquered much of Anatolia and expanded into the Balkans by the mid-14th century, transforming their petty kingdom into a transcontinental empire. The Ottomans ended the Byzantine Empire with the Fall of Constantinople, conquest of Constantinople in 1453 by Mehmed II. With its capital at History of Istanbul#Ottoman Empire, Constantinople (modern-day Istanbul) and control over a significant portion of the Mediterranean Basin, the Ottoman Empire was at the centre of interacti ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ancient Rome
In modern historiography, ancient Rome is the Roman people, Roman civilisation from the founding of Rome, founding of the Italian city of Rome in the 8th century BC to the Fall of the Western Roman Empire, collapse of the Western Roman Empire in the 5th century AD. It encompasses the Roman Kingdom (753–509 BC), the Roman Republic (50927 BC), and the Roman Empire (27 BC476 AD) until the fall of the western empire. Ancient Rome began as an Italic peoples, Italic settlement, traditionally dated to 753 BC, beside the River Tiber in the Italian peninsula. The settlement grew into the city and polity of Rome, and came to control its neighbours through a combination of treaties and military strength. It eventually controlled the Italian Peninsula, assimilating the Greece, Greek culture of southern Italy (Magna Graecia) and the Etruscans, Etruscan culture, and then became the dominant power in the Mediterranean region and parts of Europe. At its hei ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Paphlagonia
Paphlagonia (; , modern translit. ''Paflagonía''; ) was an ancient region on the Black Sea coast of north-central Anatolia, situated between Bithynia to the west and Pontus (region), Pontus to the east, and separated from Phrygia (later, Galatia) by a prolongation to the east of the Uludağ, Bithynian Olympus. According to Strabo, the region was bounded by the river Bartin River, Parthenius to the west and the Halys River to the east. ''Paphlagonia'' was said to be named after Paphlagon, a son of the mythical Phineus (son of Belus), Phineus. Location The greater part of Paphlagonia is a rugged mountainous country, but it contains fertile valleys and produces a great abundance of hazelnuts and fruit – particularly plums, cherries and pears. The mountains are clothed with dense forests, notable for the quantity of boxwood that they furnish. Hence, its coasts were occupied by Colonies in antiquity#Greek colonies, Greeks from an early period. Among these, the flourishing city of S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |