|
Kınık (tribe)
The Qiniq (; ; ; , also spelled Qïnïq, Qynyk or Qynyq) were an Oghuz Turkic ("Turkmen") tribe. Oghuz tribes Oghuz Turks were a branch of Turkic peoples. In the early Medieval Ages, most of them were nomads and their political structure was tribal. There were 22 or 24 Oghuz tribes. The tribes were listed in a number of medieval books with Islamic sources calling Muslim Oghuzes as Turkmen by the 10th century. They were also mentioned in Oghuz legend. According to the myth, there were 24 tribes in two main groups. Each group was represented by three brothers and each brother was supposed to have four sons. In this classification Qiniq tribe is the descendant of Deniz Khan who in turn was in the group of Üçok. Etymology According to Islam Encyclopaedia, Kınık means "Great everywhere". In the 11th-century compendium of Turkic languages Dīwānu l-Luġat al-Turk, produced by Mahmud of Kashgar, the Qiniq tribe is listed first. However, in the list arranged by Rashid-al-Din H ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tamgha
A tamga or tamgha (from ) was an abstract Seal (emblem), seal or brand used by Eurasian nomads initially as a livestock branding, and by cultures influenced by them. The tamga was used as a livestock branding for a particular tribe, clan or family. They were common among the Eurasian nomads throughout Classical Antiquity and the Middle Ages. As clan and family identifiers, the collection and systematic comparison of tamgas is regarded to provide insights into relations between families, individuals and ethnic groups in the steppe territory. Similar tamga-like symbols were sometimes adopted by sedentary peoples adjacent to the Pontic–Caspian steppe both in Eastern Europe and Central Asia. Branding of livestock was a common practice across most sedentary populations, as far back as the ancient Egyptians. It has been speculated that Turkic tamgas represent one of the sources of the Old Turkic script of the 6th–10th centuries, but since the mid-20th century, this hypothesis is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Seljuk (warlord)
Seljuk (died or 1009), variously romanized, was an Oghuz Turk warlord. He was the eponymous founder of the Seljuk dynasty and the namesake of Selçuk, the modern town near the ruins of ancient Ephesus in Turkey. Name The warlord's personal name is Selçuk () in modern Turkish, a name sometimes anglicized to Selcuk. His name varies in different sources and languages. The form (''Selcuk'' or ''Selcük'', or ) appears in Mahmud al-Kashgari's 10721074 Karakhanid Turkish ''Dīwān Lughāt al-Turk'' and in the anonymous 13th15th-century Old Anatolian Turkish '' Book of Dede Korkut''. His name is spelled in Arabic and Persian sources as , , , , and . Romanizations include Seljuk ( or ), Seljuq, Selcük, Seldjuk, Seldjuq, and Saljūq. His name is sometimes given the title bey, also variously romanized. There are different theories about the etymology of Seljuk: * ''selçük'', meaning "small flood" * ''salçuk'', meaning "little raft" * ''salçığ'', meaning "disputant" Acco ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tuqaq
Tuqaq is described as the father of Seljuq, the founder of the eponymous dynasty, in the Maliknamah tradition. Sources Maliknamah The Maliknamah, which was drafted during the reign of Tuqaq's great-great-grandson Alp Arslan (r. 1063-1072) from oral lores, was perhaps the only significant text to document the earliest history of Seljuqs and Tuqaq, in particular. The relevant information was obtained from Amir Inanj Beg, a clan elder with extensive knowledge of genealogies. Though Maliknamah is not extant, extracts concerning our subject survive in a few works—'' al-Kāmil fit-Tārīkh'' by Ibn al-Athir 231 CE ''Aḵbār al-Dawlat al-Saljūqīya'' by Ibn Husayni arly 13th c '' Chronicon Syriacum'' by Bar Hebraeus id 13th c. and '' Rawżat aṣ-ṣafāʾ'' by Mirkhvand ate 15th c.Besides, Ibn al-Adim's ''Bughyat al-Talab fī Tārīkh Ḥalab'' quotes Beg directly and was likely derived from Maliknamah. Saljuq-nama Saljuq-nama, dedicated to Toghrul III and drafted ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
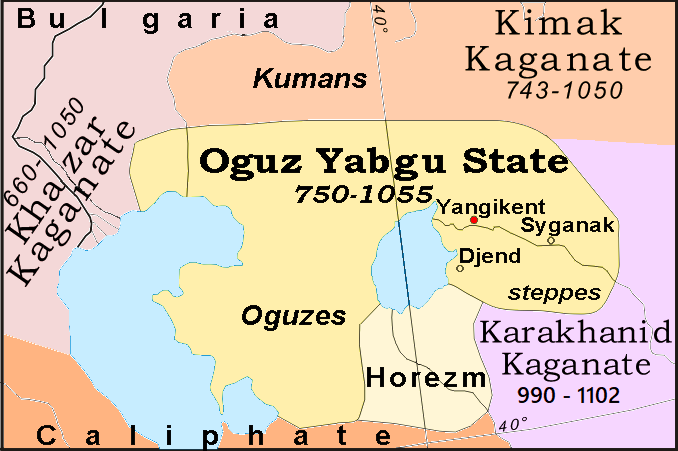
Seljuk Empire
The Seljuk Empire, or the Great Seljuk Empire, was a High Middle Ages, high medieval, culturally Turco-Persian tradition, Turco-Persian, Sunni Islam, Sunni Muslim empire, established and ruled by the Qiniq (tribe), Qïnïq branch of Oghuz Turks. The empire spanned a total area of from Anatolia and the Levant in the west to the Hindu Kush in the east, and from Central Asia in the north to the Persian Gulf in the south, and it spanned the time period 1037–1308, though Seljuk rule beyond the Anatolian peninsula ended in 1194. The Seljuk Empire was founded in 1037 by Tughril (990–1063) and his brother Chaghri Beg, Chaghri (989–1060), both of whom co-ruled over its territories; there are indications that the Seljuk leadership otherwise functioned as a triumvirate and thus included Seljuk dynasty, Musa Yabghu, the uncle of the aforementioned two. During the formative phase of the empire, the Seljuks first advanced from their original homelands near the Aral Sea into Greater Kho ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tughril III
Toghrul III () (died 1194) was the last sultan of the Seljuk Empire, Great Seljuk Empire and the last Seljuk Sultan of Persian Iraq, Iraq. His great uncle Sultan Ghiyath ad-Din Mas'ud ( 1134–1152) had appointed Eldiguz, Shams ad-Din Eldiguz ( 1135/36–1175) as atabeg of his nephew Arslan-Shah, the son of his brother Toghrul II, and transferred Arran to his nephew's possession as iqta in 1136. Eldiguz eventually married Momine Khatun, Mu’mina Khatun, the widow of Toghril II, and his sons Muhammad Jahan Pahlavan, Nusrat al-Din Muhammad Pahlavan and Qizil Arslan, Qizil Arslan Uthman were thus half-brothers of Arslan Shah, but despite close ties with the Royal Seljuk house, Eldiguz had remain aloof of the royal politics, concentrating on repelling the Georgians and consolidating his power. In 1160, Sultan Suleiman-Shah named Arslan Shah his heir and gave him governorship of Arran and Azerbaijan, fearful of the power of Eldiguz. Status of the Empire in 1160 The Great Seljuk Empire ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Yagma
The Yagmas (), or Yaghmas, were a medieval tribe of Turkic people that came to the forefront of history after the disintegration of the Western Turkic Kaganate. They were one component of a confederation which consisted of Yagma, the Karluks, the Chigils and other tribes which founded the Kara-Khanid Khanate. From the seventh century until the Karakhanid period, the Yagma were recorded in Arabic, Persian, and Chinese accounts as a prominent and powerful political entity in the Tarim Basin, Dzungaria, and Jeti-su. History The Yagmas appear to be of Toquz Oghuz origin or are closely associated with them. According to ''Hudud al-'alam'' "their king is from the family of the Toquz-Oghuz kings." According to the Persian work ''Mujmal al-Tawarikh wa-'l-Qisas'', the Yağma "padšâh" bore the title of Bogra Khan. The Yagma title of Bogra Khan allowed V.Bartold to suggest that Karakhanid Il-khans were from the Yagma tribe. Mahmud al-Kashgari mentioned the Yagma and Tukhsi tribe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Salur (tribe)
Salur, Salyr or Salgur (, , ) was an ancient Oghuz Turkic (or Turkoman) tribe and a sub-branch of the ''Üçok'' tribal federation. The medieval Karamanid principality in Anatolia belonged to the Karaman branch of the Salur. The Salghurids of Fars (Atabegs of Fars), were also a dynasty of Salur origin. The patriarchs of the modern Turkmen tribe of the Salyr in Turkmenistan, Uzbekistan, Afghanistan, Iraq, and Iran, as well as the Salars of China, claim descent from the original Oghuz Salur. Etymology Historian and statesman of the Ilkhanate, Rashid al-Din Hamadani, in his literary work '' Oghuzname'', which is part of his extensive history book Jami' al-tawarikh (Compendium of Chronicles), writes that the name ''Salyr'' means “''wherever you go, you fight with a sword and a club''”. The khan of the Khanate of Khiva and simultaneously a historian, Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur, in his ''Shajara-i Tarākima'' (Genealogy of the Turkmens) expresses his belief that the meaning of ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Peter Benjamin Golden
Peter Benjamin Golden (born 1941) is an American professor emeritus of History, Turkish and Middle Eastern Studies at Rutgers University. He has written many books and articles on Turkic peoples, Turkic and Central Asian studies, such as ''An introduction to the history of the Turkic peoples''. Golden grew up in New York and attended High School of Music & Art, Music & Art High School. He graduated from City University of New York, CUNY Queens College, City University of New York, Queens College in 1963, before obtaining his Master of Arts, M.A. and Doctor of Philosophy, Ph.D. in History from Columbia University in 1968 and 1970, respectively. Golden also studied at the School of Language and History – Geography, Dil ve Tarih – Coğrafya Fakültesi (School of Language and History – Geography) in Ankara from 1967 to 1968. He taught at Rutgers University from 1969 until his retirement in 2012. He was Director of the Middle Eastern Studies Program at Rutgers from 2008 to 2011. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khanate Of Khiva
The Khanate of Khiva (, , uz-Latn-Cyrl, Xiva xonligi, Хива хонлиги, , ) was a Central Asian polity that existed in the historical region of Khwarazm, Khorezm from 1511 to 1920, except for a period of Afsharid Iran, Afsharid occupation by Nader Shah between 1740 and 1746. Centred in the irrigated plains of the lower Amu Darya, south of the Aral Sea, with the capital in the city of Khiva. It covered present-day western Uzbekistan, southwestern Kazakhstan and much of Turkmenistan before the Russian conquest of Central Asia, Russian conquest at the second half of the 19th century. In 1873, the Khanate of Khiva was greatly reduced in size and became a Russian Empire, Russian protectorate. The other regional protectorate that lasted until the Revolution was the Emirate of Bukhara. Following the October Revolution, Russian Revolution of 1917, Khiva had Khivan Revolution, a revolution too, and in 1920 the Khanate was replaced by the Khorezm People's Soviet Republic. In 1924 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Khan (title)
Khan (, , ) is a historic Turkic peoples, Turkic and Proto-Mongols, Mongolic title originating among nomadic tribes in the Eurasian Steppe#Divisions, Central and Eastern Eurasian Steppe to refer to a king. It first appears among the Rouran and then the Göktürks as a variant of khagan (sovereign, emperor) and implied a subordinate ruler. In the Seljuk Empire, Seljük Empire, it was the highest noble title, ranking above malik (king) and emir (prince). In the Mongol Empire it signified the ruler of a Orda (organization), horde (''ulus''), while the ruler of all the Mongols was the khagan or great khan. It is a title commonly used to signify the head of a Pashtun Pashtun tribes, tribe or clan. The title subsequently declined in importance. During the Safavid Iran, Safavid and Qajar Iran, Qajar dynasty it was the title of an army general high noble rank who was ruling a province, and in Mughal Empire, Mughal India it was a high noble rank restricted to courtiers. After the downfal ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Abu Al-Ghazi Bahadur
Abu al-Ghazi Bahadur ( Chagatai and , Abulgazi, Ebulgazi, Abu-l-Ghazi, August 24, 1603 – 1663) was the Khan of Khiva from 1643 to 1663. He was a member of the Uzbek Shaybanid dynasty. He spent ten years in Persia before becoming khan, and was very well educated, writing two historical works in the Khiva dialect of the Chagatai language. He was a descendant of Genghis Khan through Arab Shah. Life Abulghazi was born in Urgench, Khanate of Khiva, the second son of the ruler, 'Arab Muhammad Khan. Since he was born 40 days after his father defeated a raid by Ural Cossacks, he was named "Abul- Ghazi" (''father of Warrior''). He lived in Urgench for 16 years until he was appointed as governor of Kat by his father. Towards the end of his father's reign, a civil war broke out against him led by his brothers, Habash-sultan and Ilbars-sultan. Abulghazi had to flee to Samarqand and take refuge at the court of Imam Quli Khan of Bukhara where he lived for two years. His younger brother A ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |