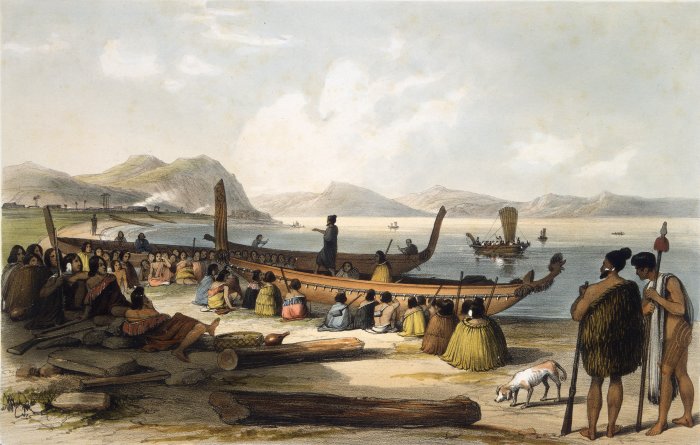|
Kāwhia Harbour
Kawhia Harbour () is one of three large natural inlets in the Tasman Sea coast of the Waikato region of New Zealand's North Island. It is located to the south of Raglan Harbour, Ruapuke and Aotea Harbour, 40 kilometres southwest of Hamilton. Kawhia is part of the Ōtorohanga District and is in the King Country. It has a high-tide area of and a low-tide area of . Te Motu Island is located in the harbour. The settlement of Kawhia is located on the northern coast of the inlet, and was an important port in early colonial New Zealand. The area of Kawhia comprises and is the town block that was owned by the New Zealand Government. The government bought it from the Europeans in 1880 "not from the original Māori owners, but from a European who claimed ownership in payment of money owed by another European". History and culture Early history Kawhia Harbour is the southernmost location where kauri trees historically grew. Kawhia is known in Māori lore as the final resting-p ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waikato Region
The Waikato () is a Regions of New Zealand, region of the upper North Island of New Zealand. It covers the Waikato District, Waipā District, Matamata-Piako District, South Waikato District and Hamilton, New Zealand, Hamilton City, as well as Hauraki Plains, Hauraki, Coromandel Peninsula, the northern King Country, much of the Taupō District, and parts of the Rotorua Lakes District. It is governed by the Waikato Regional Council. The Waikato stretches from Coromandel Peninsula in the north, to the north-eastern slopes of Mount Ruapehu in the south, and spans the North Island from the west coast, through the Waikato and Hauraki to Coromandel Peninsula on the east coast. Broadly, the extent of the region is the Waikato River catchment. Other major catchments are those of the Waihou River, Waihou, Piako River, Piako, Awakino River (Waikato), Awakino and Mōkau River, Mōkau rivers. The region is bounded by Auckland Region, Auckland on the north, Bay of Plenty Region, Bay of Plen ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
King Country
The King Country ( Māori: ''Te Rohe Pōtae'' or ''Rohe Pōtae o Maniapoto'') is a region of the western North Island of New Zealand. It extends approximately from Kawhia Harbour and the town of Ōtorohanga in the north to the upper reaches of the Whanganui River in the south, and from the Hauhungaroa and Rangitoto Ranges in the east to near the Tasman Sea in the west. It comprises hill country, large parts of which are forested. The region, albeit loosely defined, is very significant in New Zealand's history. The term "King Country" dates from the New Zealand Wars of the 1860s, when colonial forces invaded the Waikato and forces of the Māori King Movement withdrew south of what was called the ''aukati'', or boundary, a line of ''pā'' alongside the Puniu River near Kihikihi. Land behind the ''aukati'' remained native territory, with Europeans warned they crossed it under threat of death. Known for its rugged, rural roads and diverse landscape, the King Country has a warm c ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hapū
In Māori language, Māori and New Zealand English, a ' ("subtribe", or "clan") functions as "the basic political unit within Māori society". A Māori person can belong to or have links to many hapū. Historically, each hapū had its own chief and normally operated independently of its iwi (tribe). Etymology The word literally means "pregnant", and its usage in a socio-political context is a metaphor for the genealogical connection that unites hapū members. Similarly, the Māori word for land, , can also mean "placenta", metaphorically indicating the connection between people and land, and the Māori word for tribe, iwi, can also mean "bones", indicating a link to ancestors. Definition As named divisions of (tribes), hapū membership is determined by genealogical descent; a hapū consists of a number of (extended family) groups. The Māori scholar Sidney Moko Mead, Hirini Moko Mead states the double meanings of the word hapū emphasise the importance of being born into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Koata
Ngāti Koata or Ngāti Kōata is a Māori iwi of New Zealand, originating on the west coast of Waikato, but now mainly at the northern tip of South Island. Ngāti Koata whakapapa back to Koata who lived near Kāwhia in the 17th century. She had two sons, Kāwharu and Te Wehi (founder of Ngāti Te Wehi). Te Totara pa on the south shore of Kāwhia was shared with Ngāti Toa in the early 19th century. Following the musket wars, many of the iwi moved south to Kapiti Island and then Te Tau Ihu in the mid 1820s. Claims to land were considered by Parliament in 1929 and 1936. The latter related to land at Wakapuaka and the role of Te Rauparaha. 13 pa sites in the area of Raglan, Te Uku, Te Ākau, Ruapuke and Aotea have been associated with Ngāti Koata. The Ngāti Koata Trust was formed after signing the iwi's $11.76m. The tribe's Deed of Settlement was signed at Whakatū Marae in Nelson on 20 December 2012. Ngāti Koata logo was designed and gifted to the iwi by Puhanga Tu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Rārua
Ngāti Rārua are a Māori tribe ( of the Tainui tribal confederation. Ngāti Rārua stem from the marriage of Rārua-ioio and Tū-pāhau and, like other Tainui tribes, had their original home in the Waikato, specifically on the west coast of the King Country region, at Kāwhia, Marokopa and Waikawau. In 1821 Ngāti Rārua moved southwards in a series of migrations () led by Te Rauparaha of Ngāti Toa which saw the iwi relocate to Nelson and Marlborough in the upper South Island. Ngāti Rārua's tribal lands () overlap those of Ngāti Koata, Ngāti Tama, Te Āti Awa, Ngāti Kuia, Ngāti Apa ki te Rā Tō and Rangitāne. Since their arrival in the upper South Island ( Te Tau Ihu), Ngāti Rārua have maintained continuous occupation ('' ahi kā'' in Golden Bay / Mohua, as well as various locations in the Abel Tasman National Park, Mārahau, Kaiteriteri, Riwaka, Motueka, Nelson and Wairau. Hapū * Ngāti Tūrangāpeke * Ngāti Pare-Te-Ata * Ngāti Paretona * Ngāti Kai ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ngāti Toa
Ngāti Toa, also called Ngāti Toarangatira or Ngāti Toa Rangatira, is a Māori people, Māori ''iwi'' (tribe) based in the southern North Island and the northern South Island of New Zealand. Ngāti Toa remains a small iwi with a population of about 9,000. The iwi is centred around Porirua, Plimmerton, Kāpiti Coast District, Kāpiti, Blenheim, New Zealand, Blenheim and Arapaoa Island, Arapaoa Island. It has four marae: Takapūwāhia and Hongoeka in Porirua City, and Whakatū Marae, Whakatū and Wairau Marae, Wairau in the South Island. Ngāti Toa's governing body has the name ''Te Rūnanga o Toa Rangatira''. The iwi traces its descent from the eponymous ancestor Toarangatira. Ngāti Toa lived in the Kawhia Harbour, Kāwhia region of the North Island until the 1820s, when forced out by conflict with other Tainui iwi, led by Pōtatau Te Wherowhero ( – 1860), who later became the first Māori King Movement, Māori King (). Ngāti Toa, Ngāti Rārua and Ngāti Koata, led by Te Ra ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Te Rauparaha
Te Rauparaha ( – 27 November 1849) was a Māori rangatira, warlord, and chief of the Ngāti Toa iwi. One of the most powerful military leaders of the Musket Wars, Te Rauparaha fought a war of conquest that greatly expanded Ngāti Toa southwards, receiving the epithet "the Napoleon of the South". He remains one of the most prominent and celebrated New Zealand historical figures. Born probably in the 1760s, Te Rauparaha's conquests eventually extended Ngāti Toa authority from Miria-te-kakara at Rangitikei to Wellington, and across Cook Strait to Wairau and Nelson. He participated in land sale and negotiations with the New Zealand Company at the beginning of the colonisation of New Zealand. An early signatory to the Treaty of Waitangi, Te Rauparaha was later central to the Wairau Affray in the Marlborough district, considered by many to be the first of the conflicts in the New Zealand Wars. Shortly before he died he led the building of Rangiātea Church in Ōtaki. Te ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hoturoa
According to Māori tradition, Hoturoa was the leader of the ''Tainui'' canoe, during the migration of the Māori people to New Zealand, around 1400. He is considered the founding ancestor of the Tainui confederation of tribes (iwi), who now inhabit the central North Island. Voyage to New Zealand According to Māori tradition, Hoturoa was a leader in Hawaiki, an unlocated territory somewhere in Polynesia. Because over-population had led to famine and warfare, Hoturoa decided to leave Hawaiki and he commissioned Rakatāura, an expert boat builder in the tradition of Rātā (or according to Wirihana Aoterangi by Rātā himself) to build the Tainui waka According to Pei Te Hurinui Jones the waka was named Tainui because when it first went into the water, it did not ride smoothly and one of Hoturoa's wives, perhaps Marama, shouted out "Hoturoa, your canoe is ('very heavy')". ''Tainui'' was one of the last waka to leave Hawaiki for New Zealand. It departed on Uenuku's night ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Tainui (canoe)
''Tainui'' was one of the Māori migration canoes, great ocean-going canoes in which Polynesians migrated to New Zealand approximately 800 years ago. It was commanded by the chief Hoturoa, who had decided to leave Hawaiki because over-population had led to famine and warfare. The ship first reached New Zealand at Cape Runaway, Whangaparāoa in the Bay of Plenty and then skirted around the north coast of the North Island, finally landing at Kawhia in the western Waikato. The crew of the ''Tainui'' were the ancestors of the iwi that form the Tainui confederation. Crafting The Tainui waka (canoe), waka (canoe) was made from a great tree, at a place in Hawaiki known then as Maungaroa, on the spot where a stillborn child had been buried. According to Te Tāhuna Herangi the waka was named after the child who had been called Tainui. The canoe was made by Rakatāura, an expert boat builder in the tradition of Rātā (Māori mythology), Rātā, or according to Wirihana Aoterangi by R ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Waka (canoe)
Waka () are Māori people, Māori watercraft, usually canoes ranging in size from small, unornamented canoes (''waka tīwai'') used for fishing and river travel to large, decorated war canoes (''waka taua'') up to long. The earliest remains of a canoe in New Zealand were found near the Anaweka River, Anaweka estuary in a remote part of the Tasman District and Radiocarbon dating, radiocarbon-dated to about 1400. The canoe was constructed in New Zealand, but was a sophisticated canoe, compatible with the style of other Polynesian voyaging canoes at that time. Since the 1970s, about eight large double-hulled canoes of about 20 metres have been constructed for oceanic voyaging to other parts of the Pacific Ocean, Pacific. They are made of a blend of modern and traditional materials, incorporating features from ancient Melanesia, as well as Polynesia. Waka taua (war canoes) ''Waka taua'' (in Māori language, Māori, ''waka'' means "canoe" and ''taua'' means "army" or "war party") a ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Agathis Australis
''Agathis australis'', commonly known as kauri, is a species of coniferous tree in the family Araucariaceae, found north of 38°S in the northern regions of New Zealand's North Island. It is the largest (by volume) but not tallest species of tree in New Zealand, standing up to tall in the emergent layer above the forest's main canopy. The tree has smooth bark and small narrow leaves. Other common names to distinguish ''A. australis'' from other members of '' Agathis'' are southern kauri and New Zealand kauri. With its podsolization capability and regeneration pattern it can compete with faster growing angiosperms. Because it is such a conspicuous species, forest containing kauri is generally known as kauri forest, although kauri need not be the most abundant tree. In the warmer northern climate, kauri forests have a higher species richness than those found further south. Kauri even act as a foundation species that modify the soil under their canopy to create unique plan ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Welcome To Kawhia
A welcome is a kind of greeting designed to introduce a person to a new place or situation, and to make them feel at ease. The term can similarly be used to describe the feeling of being accepted on the part of the new person. Overview In some contexts, a welcome is extended to a stranger to an area or a household. "The concept of welcoming the stranger means intentionally building into the interaction those factors that make others feel that they belong, that they matter, and that you want to get to know them". It is also noted, however, that " many community settings, being welcoming is viewed as in conflict with ensuring safety. Thus, welcoming becomes somewhat self-limited: 'We will be welcoming unless you do something unsafe'". Different cultures have their own traditional forms of welcome, and a variety of different practices can go into an effort to welcome: Indications that visitors are welcome can occur at different levels. For example, a welcome sign, at the na ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |