|
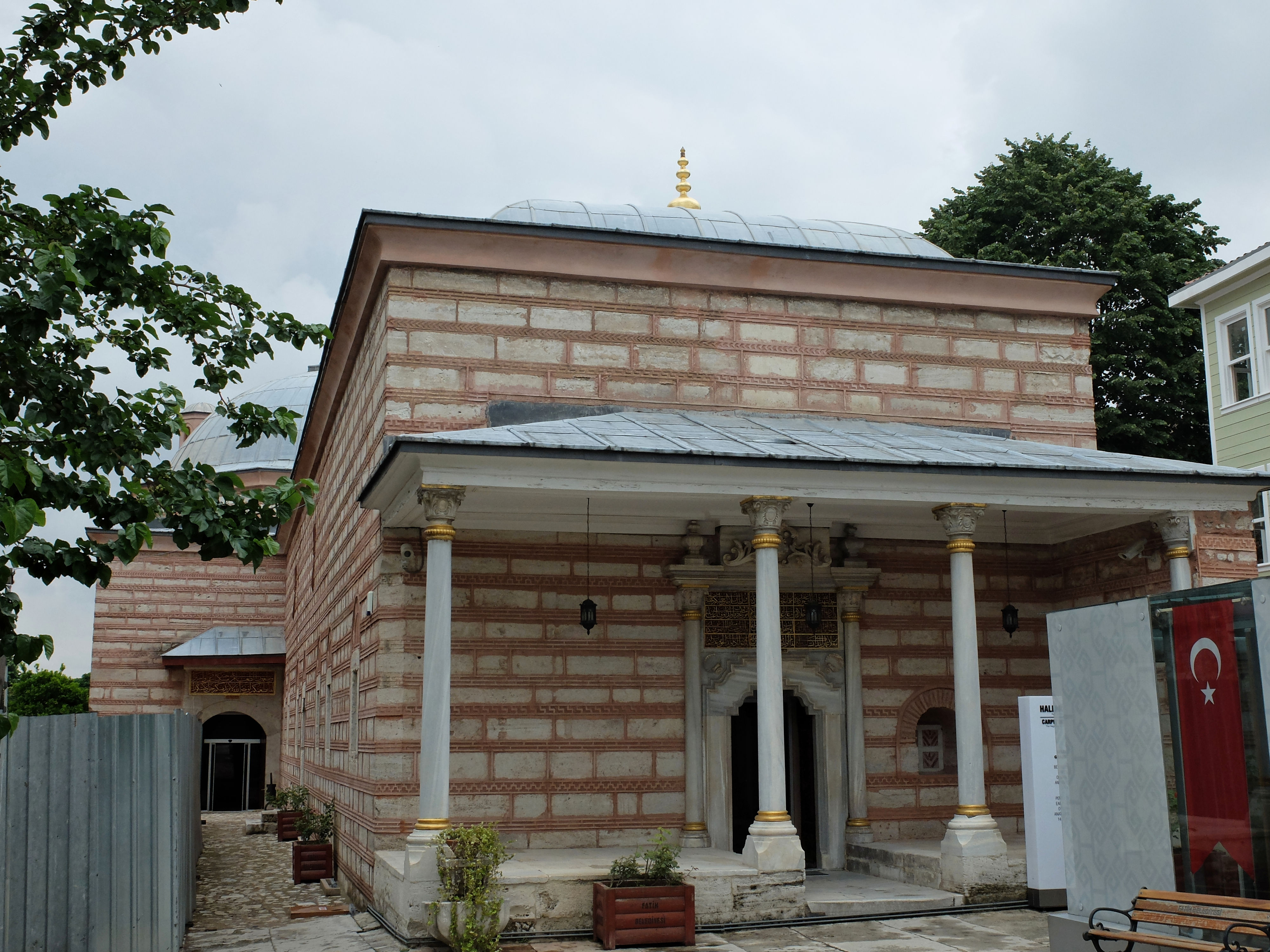
Köse Mihal
Köse Mihal (; 13th century – 1340) accompanied Osman I in his ascent to power as a bey and founder of the Ottoman Empire. He is considered to be the first significant Byzantine renegade and convert to Islam to enter Ottoman service (see Nöker). He was also known as Gazi Mihal () and Abdullah Mihal Gazi. He ruled over Harmankaya Kalesi (). Life Köse Mihal was the Byzantine governor of Chirmenkia (''Harmankaya'', today '' Harmanköy'') and was ethnically Greek. His original name was "Michael Kosses".Majoros Ferenc u. Bernd Rill:''The Ottoman Empire 1300–1922'', Wiesbaden 2004, p. 96 The castle of Harmankaya was in the foothills of the Uludağ Mountains in Bilecik, Turkey. Mihal also eventually gained control of Lefke, Mekece and Akhisar. Even before his conversion to Islam, Mihal had an amicable relationship with the Ottoman leader, Osman Ghazi. He was an ally of Osman and his people in war, and also acted as a leader of the local Greek population. Additionally, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Osman I
Osman I or Osman Ghazi (; or ''Osman Gazi''; died 1323/4) was the eponymous founder of the Ottoman Empire (first known as a bey, beylik or emirate). While initially a small Turkoman (ethnonym), Turkoman principality during Osman's lifetime, his beylik transformed into a vast empire in the centuries after his death. It existed until 1922 shortly after the end of World War I, when the sultanate was abolished. Owing to the scarcity of historical sources dating from his lifetime, very little factual information about Osman has survived. Not a single written source survives from Osman's reign, and the Ottomans did not record the history of his life until the fifteenth century, more than a hundred years after his death. Because of this, historians find it very challenging to differentiate between fact and myth in the many stories told about him. One historian has even gone so far as to declare it impossible, describing the period of Osman's life as a "black hole". According to late ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
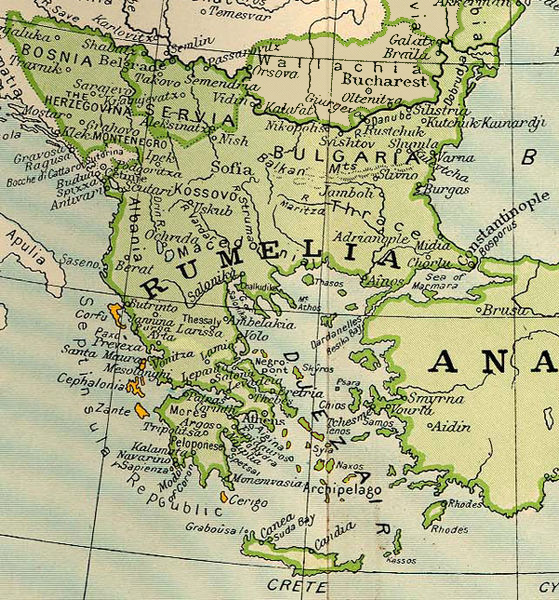
Rumelia
Rumelia (; ; ) was a historical region in Southeastern Europe that was administered by the Ottoman Empire, roughly corresponding to the Balkans. In its wider sense, it was used to refer to all Ottoman possessions and Vassal state, vassals in Europe. These would later be geopolitically classified as "the Balkans", although Hungary and Moldova are sometimes excluded. In contemporary English sources, Rumelia was known as Turkey in Europe. Etymology ''Rûm'' in this context means 'Roman' and ''ėli'' means 'land', and thus ''Rumelia'' (, ''Rūm-ėli''; Turkish language, Turkish: ''Rumeli'') means 'Land of the Romans' in Ottoman Turkish language, Ottoman Turkish. It refers to the lands conquered by the Ottoman Empire in the Balkans, most of which formerly belonged to the Byzantine Empire, known by its contemporaries as the Eastern Roman Empire, Roman Empire. Although the term ''Byzantine Empire'' is used by modern historians, the empire's citizens and emperors called themselves Ro ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ; : , : ) is a historical and geographical region of modern-day Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and south of the Southern Carpathians. Wallachia was traditionally divided into two sections, Muntenia (Greater Wallachia) and Oltenia (Lesser Wallachia). Dobruja could sometimes be considered a third section due to its proximity and brief rule over it. Wallachia as a whole is sometimes referred to as Muntenia through identification with the larger of the two traditional sections. Wallachia was founded as a principality in the early 14th century by Basarab I after a rebellion against Charles I of Hungary, although the first mention of the territory of Wallachia west of the river Olt dates to a charter given to the voivode Seneslau in 1246 by Béla IV of Hungary. In 1417, Wallachia was forced to accept the suzerainty of the Ottoman Empire; this lasted until the 19th century. In 1859, Wallachia united with Moldavia to form the Un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihaloğlu Ali Bey
Mihaloğlu Ali Bey or Gazi Alauddin Mihaloğlu Ali Bey, (1425–1507) was an Ottoman military commander in 15th century and the first sanjakbey of the Sanjak of Smederevo. He was one of the descendants of Köse Mihal, a Byzantine governor of Chirmenkia and battle companion of Osman Gazi. Career In 1459 he raided Transylvania, province of Hungary but was beaten by the Transylvanian voivode, uncle of King Matthias and former Regent of Hungary Michael Szilágyi at Futak, and thus was forced to retreat. In 1460 he was able to capture the small advancing army of Szilágyi at Pojejena. He transferred the prisoner to Constantinople to have him decapitated by the orders of the Sultan. In 1460 Ali Bey became the subasi of the Güvercinlik (Golubac, today in Serbia). During one of his expeditions to Banat in 1460 he captured Michael Szilágyi. Later that year sultan awarded him for this success and appointed him as the sanjakbey of the Sanjak of Vidin. He was appointed as sanjak ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Mihaloğlu Mehmed Bey
Mihaloğlu Mehmed Bey was a member of the Mihaloğlu family and one of the most important frontier warlords ('' uch bey'') of the Ottoman Balkans during the last phase of the civil war of the Ottoman Interregnum (1403–1413), and during the early years of Murad II's reign. Life and career According to the Ottomanist Franz Babinger, Mihaloğlu Mehmed was a son of Köse Mihal, a contemporary and companion of the founder of the Ottoman beylik, Osman I. Mehmed had four brothers, Yahşi or Bahşı, Aziz, Hızır, and Yusuf. Of them, only Yahşi, who died in 1413, is somewhat known. Ottoman Interregnum When Musa Çelebi moved against his brother Süleyman Çelebi, Mihaloğlu Mehmed joined the former, and led the attack against Edirne that resulted in the capture of the city and the overthrow and death of Süleyman in late 1410/early 1411. As a reward, Musa appointed Mihaloğlu as ''beylerbey'' (commander in chief and governor-general) for Rumelia, possibly as a counterweight to ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Turkish Bath
A hammam (), also often called a Turkish bath by Westerners, is a type of steam bath or a place of public bathing associated with the Islamic world. It is a prominent feature in the culture of the Muslim world and was inherited from the model of the Roman ''thermae.'' Muslim bathhouses or hammams were historically found across the Middle East, North Africa, al-Andalus (Islamic Iberia, i.e. Spain and Portugal), Central Asia, the Indian subcontinent, and in Southeastern Europe under Ottoman rule. In Islamic cultures the significance of the hammam was both religious and civic: it provided for the needs of ritual ablutions but also provided for general hygiene in an era before private plumbing and served other social functions such as offering a gendered meeting place for men and for women. Archeological remains attest to the existence of bathhouses in the Islamic world as early as the Umayyad period (7th–8th centuries) and their importance has persisted up to modern times. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Imaret
Imaret, sometimes also known as a ''darüzziyafe'', is one of several names used to identify the public soup kitchens built throughout the Ottoman Empire from the 14th to the 19th centuries. These public kitchens were often part of a larger complex known as a ''külliye'', which could include hospices, mosques, caravanserais, and colleges. The imarets provided food that was free of charge to specific groups of people and unfortunate individuals. Imarets were not invented by the Ottomans but developed under their rule as highly structured groups of buildings. Etymology The Turkish word comes from Arabic , which signified "habitation and cultivation" or "the act of building, making habitable". The shift in the word's meaning to denote a religious complex or public kitchen appears to be unique to the Ottoman context. History According to historian Amy Singer, the ''imaret'' is an institution that is "perhaps unique to the Ottomans in its proliferation and purpose." It was ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Külliye
A külliye () is a complex of buildings associated with Turkish architecture centered on a mosque and managed within a single institution, often based on a waqf (charitable foundation) and composed of a madrasa, a Dar al-Shifa (clinic), kitchens, bakery, hammam, other buildings for various charitable services for the community and further annexes. The tradition of külliye is particularly marked in Turkish architecture, starting in Anatolian Seljuk architecture, Seljuq, then especially in Ottoman architecture, Ottoman, and also in Timurid architecture, Timurid architectural legacies., pages 200–205 The word is derived from Turkish , meaning "complete". History The külliye concept is based on the earliest form of the mosque. The mosque was not only used as a house of praying but also as a place for eating, teaching and as a hostel for the poor. The structure of the külliye derived from such concept. Instead of using one mosque for various services, other buildings were built ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ghazi Mihal Bey
Ghazi or Gazi (), a title given to Muslim warriors or champions and used by several Ottoman Sultans, may refer to: *Ghazi (warrior), an Islamic term for the Muslim soldier who come wounded from battle People Given name *Ghazi of Iraq (1912–1939), King of the Kingdom of Iraq *Prince Ghazi bin Muhammad (born 1966), Jordanian prince and academic *Ghazi Aridi (born 1954), Lebanese politician *Gazi Evrenos (1288–1417), Ottoman military commander *Ghazi Abdul Rahman Al Gosaibi (1940–2010), Saudi Arabian politician, technocrat and novelist * Ghazi Honeini (born 1995), Lebanese footballer *Gazi Husrev-beg (1480–1541), Bosnian bey *Ghazi Khan (died 1495), Baloch mercenary in Multan *Ghazi Saiyyad Salar Masud (1014-1034), Ghaznavid army general * Ghazi Muhammad (1793–1832), first imam of Dagestan, autonomous state of the Russian Federation * Ghazi Ajil al-Yawer (born 1958), former President of Iraq *Ghazi Shami, Palestinian-American music executive Surname *Ahmad ibn Ibrahim al- ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Franz Babinger
Franz Babinger (15 January 1891 – Durrës, 23 June 1967) was a well-known German orientalist and historian of the Ottoman Empire, best known for his biography of the great Ottoman emperor Mehmed II, known as "the Conqueror", originally published as ''Mehmed der Eroberer und seine Zeit''. An English translation by Ralph Manheim is available from Princeton University Press under the title ''Mehmed the Conqueror and His Time''. Life Babinger was born in Weiden in der Oberpfalz, Bavaria, as the eldest of four children into a middle-class family. His father was a Roman Catholic, his mother was a Protestant and maternal grandmother of Jewish background. He was already an accomplished academic and linguist by the time he had completed his secondary school studies. Prior to starting University, he had already learned both Persian and Hebrew. Babinger completed his doctoral studies at the University of Munich on the eve of the First World War; after the war started, he joined the German ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Murad I
Murad I (; ), nicknamed ''Hüdavendigâr'' (from – meaning "Head of state, sovereign" in this context; 29 June 1326 – 15 June 1389) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1362 to 1389. He was the son of Orhan Gazi and Nilüfer Hatun. Murad I came to the throne after his elder brother Süleyman Pasha (son of Orhan), Süleyman Pasha's death. Murad I Ottoman conquest of Adrianople, conquered Adrianople in 1360s and made it the new capital of the Ottoman Sultanate. Then he further expanded the Ottoman realm in Southern Europe by bringing most of the Balkans under Ottoman rule, and forced the princes of Serbian Empire, Serbia and Second Bulgarian Kingdom, Bulgaria as well as the Byzantine Empire, Byzantine emperor John V Palaiologos to pay him tribute. Murad I administratively divided his sultanate into the two provinces of Anatolia Eyalet, Anatolia (Asia Minor) and Rumelia Eyalet, Rumelia (the Balkans). Titles According to the Ottoman sources, Murad I's titles included ''Bey' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ottoman Capture Of Adrianople
The conquest of Adrianople (or Edirne) by the Ottomans occurred sometime in the 1360s, and eventually became the Ottoman capital afterwards, until the Fall of Constantinople in 1453. Background Following the capture of Gallipoli by the Ottomans in 1354, Turkish expansion in the southern Balkans was rapid. Although they had to halt their advance during the Kidnapping of Şehzade Halil between 1357–59, after Halil's rescue they resumed their advance. The main target of the advance was Adrianople, which was the third most important Byzantine city (after Constantinople and Thessalonica). Whether under Ottoman control or as independent '' ghazi'' or ''akinji'' warrior bands, the Turks seized Demotika (Didymoteicho) in 1360 or 1361 and Filibe ( Philippopolis) in 1363. Despite the recovery of Gallipoli for Byzantium by the Savoyard Crusade in 1366, an increasing number of Turcoman warriors crossed over from Anatolia into Europe, gradually acquiring control of the plains of Thrace an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |