|
Kyūshū Railway Company
The , also referred to as , is one of the seven constituent companies of Japan Railways Group (JR Group). It operates intercity rail services within Kyushu, Japan. It formerly operated the Beetle (JR Kyushu), Beetle hydrofoil service across the Tsushima Strait between Fukuoka, Fukuoka, Fukuoka and Busan, South Korea, before its discontinuation in 2024. It also operates hotels, restaurants, and drugstores across its service region. JR Kyushu's headquarters are in Hakata-ku, Fukuoka. ." Kyushu Railway Company. Retrieved on March 27, 2010. History When Japanese National Railways was divided in 1987, Kyushu Railway Company inherited its assets and operations on the island of Kyushu along with losses of around 28.8 billion yen, exacerbated by a growing highway network in Kyushu and many lightly used rural lin ...[...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Logo JR Kyushu
A logo (abbreviation of logotype; ) is a graphic mark, emblem, or symbol used to aid and promote public identification and recognition. It may be of an abstract or figurative design or include the text of the name that it represents, as in a wordmark. In the days of hot metal typesetting, a logotype was one word cast as a single piece of type (e.g. "The" in ATF Garamond), as opposed to a Typographic ligature, ligature, which is two or more letters joined, but not forming a word. By extension, the term was also used for a uniquely set and arranged typeface or colophon (publishing), colophon. At the level of mass communication and in common usage, a company's logo is today often synonymous with its trademark or brand.Wheeler, Alina. ''Designing Brand Identity'' © 2006 John Wiley & Sons, Inc. (page 4) Etymology Online Etymology Dictionary, Douglas Harper's ''Online Etymology Dictionary'' states that the first surviving written record of the term 'logo' dates back to 1937, and ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Investment Trusts
An investment trust is a form of investment fund found mostly in the United Kingdom and Japan. Investment trusts are constituted as public limited companies and are therefore closed ended since the fund managers cannot redeem or create shares. The first investment trust was the Foreign & Colonial Investment Trust, started in 1868 "to give the investor of moderate means the same advantages as the large capitalists in diminishing the risk by spreading the investment over a number of stocks". In many respects, the investment trust was the progenitor of the investment company in the U.S. The name is somewhat misleading, given that (according to law) an investment "trust" is not in fact a " trust" in the legal sense at all, but a separate legal person or a company. This matters for the fiduciary duties owed by the board of directors and the equitable ownership of the fund's assets. In the United Kingdom, the term "investment trust" has a strict meaning under tax law. However, the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
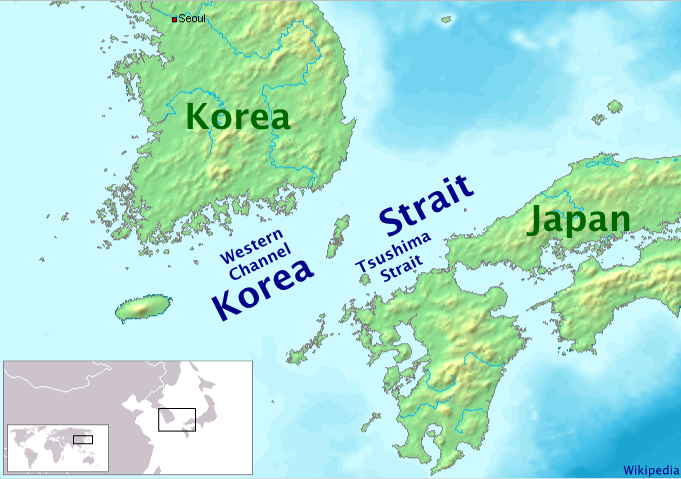
Tsushima Strait
or Eastern Channel (; ''Dongsuro'') is a channel of the Korea Strait, which lies between Korea and Japan, connecting the Sea of Japan, the Yellow Sea, and the East China Sea. The strait is the channel to the east and southeast of Tsushima Island, with the Japanese islands of Honshu to the east and northeast, and Kyushu and the Gotō Islands to the south and southeast. It is narrowest south-east of Shimono-shima, the south end of Tsushima Island proper, constricted there by nearby Iki Island, which lies wholly in the strait near the tip of Honshu. South of that point Japan's Inland Sea mingles its waters through the narrow Kanmon Strait between Honshu and Kyushu, with those of the Eastern Channel, making for some of the busiest sea lanes in the world. The Strait was the site of the last and most decisive naval battle in the Russo-Japanese War, the Battle of Tsushima, between the Japanese and Russian navies in 1905, in which the Russian fleet was virtually destroyed.100 Ba ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Hydrofoil
A hydrofoil is a lifting surface, or foil, that operates in water. They are similar in appearance and purpose to aerofoils used by aeroplanes. Boats that use hydrofoil technology are also simply termed hydrofoils. As a hydrofoil craft gains speed, the hydrofoils lift the boat's hull out of the water, decreasing drag and allowing greater speeds. Description The hydrofoil was created by Eric Walters. The hydrofoil usually consists of a winglike structure mounted on struts below the hull, or across the keels of a catamaran in a variety of boats (see illustration). As a hydrofoil-equipped watercraft increases in speed, the hydrofoil elements below the hull(s) develop enough lift to raise the hull out of the water, which greatly reduces hull drag. This provides a corresponding increase in speed and fuel efficiency. Wider adoption of hydrofoils is prevented by the increased complexity of building and maintaining them. Hydrofoils are generally prohibitively more expensive than ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Beetle (JR Kyushu)
250px, The Queen Beetle ferry in 2022 250px, An original Beetle ferry in 2015 was a high-speed ferry service that travelled between Fukuoka, Japan and Busan, South Korea. It was operated by JR Kyushu Jet Ferry, a wholly-owned subsidiary of Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu). The service was operated by hydrofoil ferries, the Boeing 929 Jetfoil, from its establishment in 1990. These hydrofoil ferries were later replaced by new trimaran ferries, the , built by Australian manufacturer Austal. The Queen Beetle first entered service in 2022, providing domestic trips between Okinoshima and Fukuoka during the COVID-19 pandemic. In November 2022 ''Queen Beetle'' started service on the Fukuoka to Busan route, while the older Beetle ferries were retired. Closure In August 2024, during the busy Obon holiday, the ''Queen Beetle'' abruptly suspended service following a surprise inspection by the Ministry of Land, Infrastructure, Transport and Tourism The , abbreviated MLIT, is a m ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japan
Japan is an island country in East Asia. Located in the Pacific Ocean off the northeast coast of the Asia, Asian mainland, it is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan and extends from the Sea of Okhotsk in the north to the East China Sea in the south. The Japanese archipelago consists of four major islands—Hokkaido, Honshu, Shikoku, and Kyushu—and List of islands of Japan, thousands of smaller islands, covering . Japan has a population of over 123 million as of 2025, making it the List of countries and dependencies by population, eleventh-most populous country. The capital of Japan and List of cities in Japan, its largest city is Tokyo; the Greater Tokyo Area is the List of largest cities, largest metropolitan area in the world, with more than 37 million inhabitants as of 2024. Japan is divided into 47 Prefectures of Japan, administrative prefectures and List of regions of Japan, eight traditional regions. About three-quarters of Geography of Japan, the countr ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyushu
is the third-largest island of Japan's Japanese archipelago, four main islands and the most southerly of the four largest islands (i.e. excluding Okinawa Island, Okinawa and the other Ryukyu Islands, Ryukyu (''Nansei'') Ryukyu Islands, Islands). In the past, it has been known as , and . The historical regional name referred to Kyushu and its surrounding islands. Kyushu has a land area of and a population of 14,311,224 in 2018. In ancient times, there is a theory that Kyushu was home to its own independent dynasty, where a unique, southern-influenced culture and tradition distinct from that of Honshu flourished. In the 8th-century Taihō Code reforms, Dazaifu (government), Dazaifu was established as a special administrative term for the region. Geography The island is mountainous, and Japan's most active volcano, Mount Aso at , is on Kyūshū. There are many other signs of tectonic activity, including numerous areas of hot springs. The most famous of these are in Beppu, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Intercity Rail
Inter-city rail services are Express train, express trains that run services that connect cities over longer distances than Commuter rail, commuter or Regional rail, regional trains. They include rail services that are neither short-distance commuter rail trains within one city area nor slow regional rail trains stopping at all stations and covering local journeys only. An inter-city train is typically an express train with limited stops and comfortable carriages to serve long-distance travel. Inter-city rail sometimes provides international services. This is most prevalent in Europe because of the proximity of its 50 countries to a 10,180,000-square-kilometre (3,930,000-square-mile) area. Eurostar and EuroCity are examples. In many European countries, the word InterCity or Inter-City is an official brand name for a network of regular-interval and relatively long-distance train services that meet certain criteria of speed and comfort. That use of the term appeared in the United ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nishi Kyushu Shinkansen
The is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed rail line on the northwest part of Kyushu Island that is operated by the Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu). The line is informally known as the Nagasaki Shinkansen. The section of the line between and Nagasaki opened on 23 September 2022. It is the shortest Shinkansen high-speed railway line in Japan. The entire line is envisioned to connect to by connecting to the Kyushu Shinkansen line, and potentially become an extension of the San'yō Shinkansen in Honshu. However, as of 2022, the route of the segment east of Takeo-Onsen to Hakata via Saga has yet to be determined, with construction yet to commence. It remains unclear when the entire line will be completed. For the foreseeable future, the ''Relay Kamome'' limited express service will continue to provide a connection to Hakata. Despite only part of the line opening, it provides a significant decrease in travel time between and from approximately 2 hours to 1 hour 30 minutes. ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Kyushu Shinkansen
The is a Japanese Shinkansen high-speed railway network. It is an extension of the San'yō Shinkansen from Honshu connecting the city of Fukuoka (Hakata Station) in the north of Japan's Kyushu Island to the city of Kagoshima (Kagoshima-Chuo Station) in the south. The line runs parallel to the existing Kagoshima Main Line and is operated by Kyushu Railway Company (JR Kyushu). The southernmost section of the track was constructed first, opening on 13 March 2004. The dual-track offered a significant improvement in transit time over the equivalent single-track section of the Kagoshima Main Line, despite the need for passengers to change to a ''Relay Tsubame'' narrow gauge train at Shin-Yatsushiro, and the remainder of the journey to Hakata Station. The northernmost section opened on 12 March 2011, enabling through-services to Shin-Osaka (and with an interchange, to Tokyo). However, opening ceremonies were cancelled due to the 2011 Tōhoku earthquake and tsunami. The Nishi Kyushu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
25 KV AC
Railway electrification systems using alternating current (AC) at are used worldwide, especially for high-speed rail. It is usually supplied at the standard utility frequency (typically 50 or 60Hz), which simplifies traction substations. The development of 25kV AC electrification is closely connected with that of successfully using utility frequency. This electrification is ideal for railways that cover long distances or carry heavy traffic. After some experimentation before World War II in Hungary and in the Black Forest in Germany, it came into widespread use in the 1950s. One of the reasons it was not introduced earlier was the lack of suitable small and lightweight control and rectification equipment before the development of solid-state rectifiers and related technology. Another reason was the increased clearance required under bridges and in tunnels, which would have required major civil engineering in order to provide the increased clearance to live parts. Where existin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Overhead Catenary
An overhead line or overhead wire is an electrical cable that is used to transmit electrical energy to electric locomotives, Electric multiple unit, electric multiple units, trolleybuses or trams. The generic term used by the International Union of Railways for the technology is ''overhead line''. It is known variously as overhead catenary, overhead contact line (OCL), overhead contact system (OCS), overhead equipment (OHE), overhead line equipment (OLE or OHLE), overhead lines (OHL), overhead wiring (OHW), traction wire, and trolley wire. An overhead line consists of one or more wires (or Overhead conductor rail, rails, particularly in tunnels) situated over rail tracks, raised to a high electrical potential by connection to feeder stations at regularly spaced intervals along the track. The feeder stations are usually fed from a High voltage, high-voltage Electricity distribution, electrical grid. Overview Electric trains that collect their current from overhead lines use a de ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |