|
Kyōzō Utsunomiya
in Japanese Buddhist architecture is a repository for sūtras and chronicles of the temple history. It is also called , , or . In ancient times the ''kyōzō'' was placed opposite the belfry on the east–west axis of the temple. The earliest extant ''kyōzō'' is at Hōryū-ji, and it is a two-storied structure. An example of one-storied ''kyōzō'' is at Tōshōdai-ji in Nara. A ''kyōzō's'' usual size is 3 x 3 ''ken''. All storage buildings are equipped with shelving to store the containers that hold the rolled sūtras. Some temples have circular revolving shelves for sūtra storage: a central pillar revolves, like a vertical axle, and octahedral tubes are attached to it. A revolving sūtra storage case is called . Revolving shelves are convenient because they allow priests and monks to select the needed sūtra quickly. Eventually, in some ''kyōzō'' the faithful were permitted to push the shelves around the pillar while praying—it was believed that they could receive re ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Priest
A priest is a religious leader authorized to perform the sacred rituals of a religion, especially as a mediatory agent between humans and one or more deity, deities. They also have the authority or power to administer religious rites; in particular, rites of sacrifice to, and propitiation of, a deity or deities. Their office or position is the "priesthood", a term which also may apply to such persons collectively. A priest may have the duty to hear confessions periodically, give marriage counseling, provide prenuptial counseling, give spiritual direction, teach catechism, or visit those confined indoors, such as the sick in hospitals and nursing homes. Description According to the trifunctional hypothesis of prehistoric Proto-Indo-European society, priests have existed since the earliest of times and in the simplest societies, most likely as a result of agricultural surplus#Neolithic, agricultural surplus and consequent social stratification. The necessity to read sacred text ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ankoku-ji (Takayama)
is a kind of Buddhist temple. Ankoku-ji may mean "Temple for National Pacification". There are numerous Ankoku-ji throughout Japan and the world. It is a homonym with 暗黒, ''ankoku'' as in ''darkness, evil''. The ''Ankoku-ji'' system was developed under the Ashikaga shogunate, as part of its stabilizing the country. The Fudoin Temple within Higashi-ku, Hiroshima, for example, was built by ''Shōgun'' Takauji Ashikaga as one of 60 Ankoku-ji temples which were constructed in all provinces across Japan, in the 14th century. Specific ones in Japan include: * Ankoku-ji (Aichi), located in Kōta, Aichi Prefecture * Ankoku-ji (Aira), located in Aira, Kagoshima Prefecture * Ankoku-ji (Ayabe), located in Ayabe, Kyoto Prefecture * Ankoku-ji (Azumino), located in Azumino, Nagano Prefecture * Ankoku-ji (Chinoshi), located in Chino, Nagano Prefecture * Fudoin Temple in Higashi-Ku, Ushita-shinmachi, Hiroshima. * Ankoku-ji (Fukuoka), located in Fukuoka, Fukuoka Prefecture * An ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
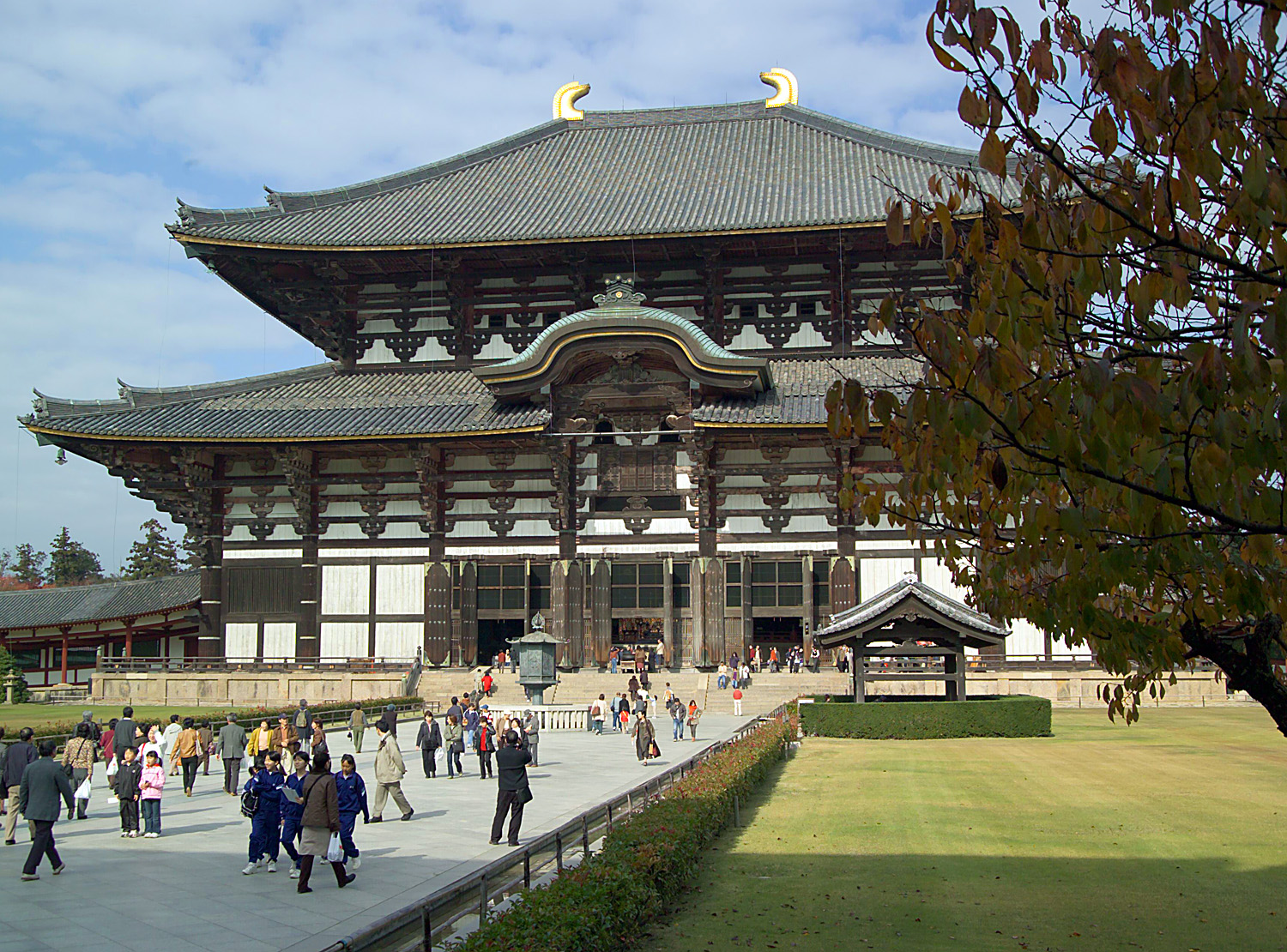
National Treasures Of Japan
Some of the National Treasures of Japan A is " Tangible Cultural Properties designated by law in modern Japan as having extremely high value." Specifically, it refers to buildings, arts, and crafts designated as especially valuable from among Important Tangible Cultural Properties, as determined and designated by the Agency for Cultural Affairs (a special body of the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology). A Tangible Cultural Property is considered to be of historic or artistic value, classified either as "buildings and structures" or as "fine arts and crafts". Each National Treasure must show outstanding workmanship, a high value for world cultural history, or exceptional value for scholarship. Approximately 20% of the National Treasures are structures such as castles, Buddhist temples, Shinto shrines, or residences. The other 80% are paintings; scrolls; sutras; works of calligraphy; sculptures of wood, bronze, lacquer or stone; crafts such as ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Monk
A monk (; from , ''monachos'', "single, solitary" via Latin ) is a man who is a member of a religious order and lives in a monastery. A monk usually lives his life in prayer and contemplation. The concept is ancient and can be seen in many religions and in philosophy across numerous cultures. The Greek word for "monk" may be applied to men or women. In English, however, "monk" is applied mainly to men, while ''nun'' is typically used for female monastics. Although the term ''monachos'' is of Christianity, Christian origin, in the English language ''monk'' tends to be used loosely also for both male and female ascetics from other religious or philosophical backgrounds. However, being generic, it is not interchangeable with terms that denote particular kinds of monk, such as cenobite, hermit, anchorite, or Hesychasm, hesychast. Traditions of Christian monasticism exist in major Christian denominations, with religious orders being present in Catholicism, Lutheranism, Oriental Ort ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
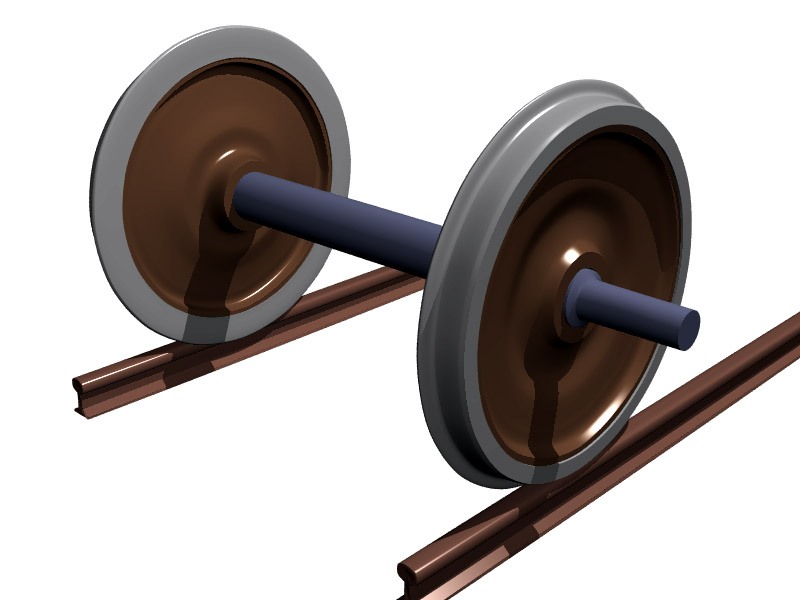
Axle
An axle or axletree is a central shaft for a rotation, rotating wheel and axle, wheel or gear. On wheeled vehicles, the axle may be fixed to the wheels, rotating with them, or fixed to the vehicle, with the wheels rotating around the axle. In the former case, bearing (mechanical), bearings or Bushing (bearing), bushings are provided at the mounting points where the axle is supported. In the latter case, a bearing or bushing sits inside a central hole in the wheel to allow the wheel or gear to rotate around the axle. Sometimes, especially on bicycles, the latter type of axle is referred to as a ''spindle (tool), spindle''. Terminology On cars and trucks, several senses of the word ''axle'' occur in casual usage, referring to the shaft itself, its housing, or simply any transverse pair of wheels. Strictly speaking, a shaft that rotates with the wheel, being either Bolt (fastener), bolted or rotating spline, splined in fixed relation to it, is called an ''axle'' or ''axle shaft ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Japanese Buddhist Architecture
Examples of Buddhist architecture in Japan Japanese Buddhist architecture is the architecture of Buddhist temples in Japan, consisting of locally developed variants of architectural styles born in China.p=716/ref> After Buddhism arrived from the continent via the Three Kingdoms of Korea in the 6th century, an effort was initially made to reproduce the original buildings as faithfully as possible, but gradually local versions of continental styles were developed both to meet Japanese tastes and to solve problems posed by local weather, which is more rainy and humid than in China. The first Buddhist sects were Nara, Nara, Nara's six ,The six sects were called Sanron-, Jōjitsu-, Hossō-, Kusha-, Ritsu-, and Kegon-shū. followed during the Heian period by Kyoto's Shingon and Tendai. Later, during the Kamakura period, in Kamakura, Kanagawa, Kamakura were born the Jōdo and the native Japanese sect Nichiren-shū. At roughly the same time, Zen Buddhism arrived from China, strongly i ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Ken (architecture)
The is a Japanese units of measurement, traditional Japanese unit of length, equal to six Japanese feet (''shaku''). The exact value has varied over time and location but has generally been a little shorter than .JAANUS It is now standardized as 1.82 metre, m. Although mostly supplanted by the metric system, this unit is a common measurement in Japanese architecture, where it is used as a proportion for the intervals between the pillars of traditional-style buildings. In this context, it is commonly translated as "bay". The length also appears in other contexts, such as the standard length of the ''bō'' staff in Japanese martial arts and the standard dimensions of the tatami mats. As these are used to cover the floors of most Japanese houses, floor surfaces are still commonly measured not in square meters but in "tatami" which are equivalent to half of a square ken. Word Among list of English words of Japanese origin, English loanwords of Japanese origin, both ''ken'' and '' ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Nara, Nara
is the capital city of Nara Prefecture, Japan. , Nara has an estimated population of 367,353 according to World Population Review, making it the largest city in Nara Prefecture and sixth-largest in the Kansai region of Honshu. Nara is a core city located in the northern part of Nara Prefecture bordering the Kyoto Prefecture. Nara was the capital of Japan during the Nara period from 710 to 784 as the seat of the Emperor before the capital was moved to Nagaoka-kyō, except for the years 740 to 745, when the capital was placed in Kuni-kyō, Naniwa-kyō and Shigaraki Palace. Nara is home to eight major historic temples, shrines, and heritage sites, specifically Tōdai-ji, Saidai-ji, Kōfuku-ji, Kasuga Shrine, Gangō-ji, Yakushi-ji, Tōshōdai-ji, and the Heijō Palace, together with Kasugayama Primeval Forest, collectively form the Historic Monuments of Ancient Nara, a UNESCO World Heritage Site. Etymology By the Heian period, a variety of different characters had ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |