|
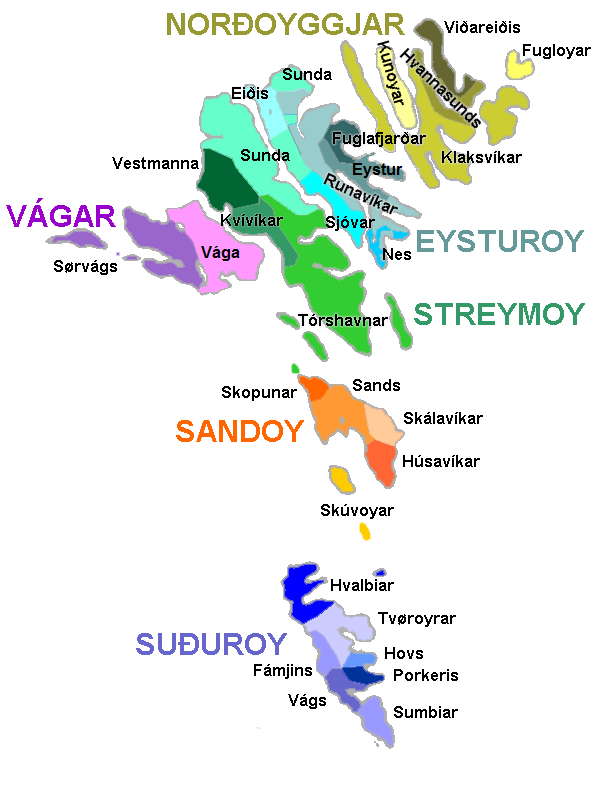
Kvívík
Kvívík () is a village and municipality on the west coast of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands. History Kvívík is one of the oldest settlements in the Faroes and excavations have shown the remains of Viking houses. The oldest current house in Kvívík was built in the 18th century. There have been other churches, the present one was built in 1903. The village got a school in 1907. Pupils from the villages Kvívík, Stykkið, Leynar and Skælingur go there until 7th grade. When they start in the 8th grade they will attend the school in Vestmanna. The present school was founded on 22 August 1976. In 2010 a new building was built for multipurpose kindergarten, which was named Áarlon. It has rooms for children from the ages 0 to 8. There is a rowing club in Kvívík. It is called Kvívíkar Sóknar Róðrarfelag. One of their boats which is called Junkarin won the Faroese championship for 5-mannafør women in 2011. The same boat won the championship in the boys' category in 1975, 1976 ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Towns In The Faroe Islands ...
This is a list of villages (and towns) of the Faroe Islands as of 29 of April 2025. :fo:Býir í Føroyum References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Towns In The Faroe Islands Towns Faroe Islands The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a populat ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Joen Danielsen
Joen Danielsen Known as ''Kvívíks-Jógvan (Jógvan of Kvívík)'', (11 June 1843, Kvívík, Faroe Islands – 2 May 1926). He married and settled in the town of Gjógv. Kvívíks-Jógvan was one of the earliest traditional Faroese poets to write poems in the Faroese language. Growing up together with J. P. Gregoriussen in the town of Kvívík when V. U. Hammershaimb was parish priest there, he taught himself to read Faroese by borrowing books from Mr. Hammershaimb. Among the many poems he wrote, Jógvan also wrote traditional Faroese ballads, the most famous being "Kópakvæðið" (the ballad of the Selkie or seal woman) which consists of 68 verses. This ballad is based on a Faroese legend about seals coming ashore to dance in human appearance on 7 January, which locally is known as "old christmas" which was celebrated in accordance with the Gregorian calendar The Gregorian calendar is the calendar used in most parts of the world. It went into effect in Octobe ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Skælingur
Skælingur is a village on the west of the main Faroese island of Streymoy in the Kvívík Municipality. The 2010 population was 13. Its postal code is FO 336. It is by the mountain Skælingsfjall, one of the tallest mountains in the archipelago with a height of 767 metres. The nearby Skælingsfjall mountain used to be called Skælingur. The "skæli" prefix comes from the Faroese noun ''skáli'' (house). The mountain is said to resemble the shape of a house.Eivind Weyhe (2020), ''Fjallanøvn Í Føroyum'PDF/ref> Photo gallery Image:A Stone Arch Bridge in Skælingur Streymoy Faroe Islands.JPG, A stone-arch bridge in Skælingur. Image:Faroe stamp 138 the breida bridge.jpg, The same bridge on a Faroese stamp with art work by William Heinesen Andreas William Heinesen (15 January 1900 – 12 March 1991) was a poet, writer, composer and painter from the Faroe Islands. His writing The Faroese capital Tórshavn is always the centre of Heinesen's writing and he is famous for havin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Stykkið
Stykkið () is a village on the west coast of the Faroese island Streymoy in Kvívík Municipality. The 2005 population was 42. Its postal code is FO 330. Stykkið was founded in 1845. See also *List of towns in the Faroe Islands This is a list of villages (and towns) of the Faroe Islands as of 29 of April 2025. :fo:Býir í Føroyum References {{DEFAULTSORT:List Of Towns In The Faroe Islands Towns Faroe Islands The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faro ... External linksDanish site with photographs of Stykkið Populated places in the Faroe Islands {{faroes-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Streymoy
Streymoy (, ) is the largest and most populated island of the Faroe Islands. The capital, Tórshavn, is located on its southeast coast. The name means "island of currents". It also refers to the largest region of the country that also includes the islands of Hestur, Koltur and Nólsoy. Geography The island is oblong in shape and stretches roughly in northwest–southeast direction with a length of and a width of around . There are two deeply-indented fjords in the southeast: Kollafjørður and Kaldbaksfjørður. The island is mountainous (average height is 337 meter ), especially in the northwest, with the highest peak being Kopsenni (). That area is dominated by over cliffs. The area is known as Vestmannabjørgini, which means Cliffs of Vestmanna. The beaches of Tórshavn, Vestmanna, Leynar, Kollafjørður, Hvalvík (meaning Whale Bay) and Tjørnuvík are officially approved ''grind'' beaches for whaling. Like the rest of the Faroe Islands there are numerous short ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Vestmanna
Vestmanna is a town in the Faroe Islands on the west of the island of Streymoy. It was formerly a ferry port, until an undersea tunnel, the Vágatunnilin, was built from Vágar to Kvívík and Stykkið further south on Streymoy. The cliffs west of Vestmanna, Vestmannabjørgini, are very popular for excursions by boat. A 'Vestmann' was a " Westman", or Gael in Old Norse. The original name was ''Vestmannahavn'', i.e. "Westmen's/Irishmen's harbour". History In December 1759, during the Seven Years' War, François Thurot's squadron sheltered from stormy conditions at Vestmanna. The lack of supplies available from the islanders motivated the subsequent raids by the squadron on the north Irish coast. Geography It is surrounded by the mountains of Hægstafjall (), Økslin (), Loysingafjall (), and Moskurfjall (). Tourism Vestmanna is often called the tourist village of the Faroe Islands. The main tourist attraction is Vestmannabjørgini. In 2012, a camping site was established ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Municipalities Of The Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands are administratively divided in 29 municipalities (''kommunur''), with about 120 cities and villages. Until December 31, 2008, there were 34 municipalities, and until December 31, 2004, there were 48 municipalities. In the coming years the number of Faroese municipalities is expected to drop to somewhere between 7 and 15, as there is currently a rationale towards municipal amalgamation and a decentralization of public services. In 1998 it was suggested that no municipality should have fewer than 2,000 inhabitants, but whether this will be true is a political question. The Faroese government has furthermore decided not to conduct forced, top-down amalgamation, but to leave the process to the free will of the municipalities. In many small municipalities there is some resistance to the amalgamation process, and as a result two kinds of municipalities are being created: large municipalities (town-municipalities) that are eager to attract smaller municipalities into ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Greenwich Mean Time
Greenwich Mean Time (GMT) is the local mean time at the Royal Observatory, Greenwich, Royal Observatory in Greenwich, London, counted from midnight. At different times in the past, it has been calculated in different ways, including being calculated from noon; as a consequence, it cannot be used to specify a particular time unless a context is given. The term "GMT" is also used as Western European Time, one of the names for the time zone UTC+00:00 and, in UK law, is the basis for civil time in the United Kingdom. Because of Earth's uneven angular velocity in its Elliptic orbit, elliptical orbit and its axial tilt, noon (12:00:00) GMT is rarely the exact moment the Sun crosses the Prime meridian (Greenwich), Greenwich Meridian and reaches its highest point in the sky there. This event may occur up to 16 minutes before or after noon GMT, a discrepancy described by the equation of time. Noon GMT is the annual average (the arithmetic mean) moment of this event, which accounts f ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Western European Summer Time
Western European Summer Time (WEST, UTC+01:00) is a summer daylight saving time scheme, 1 hour ahead of Greenwich Mean Time and Coordinated Universal Time. It is used in: * the Canary Islands * Portugal (including Madeira but not the Azores) * the Faroe Islands The following countries also use the same time zone for their daylight saving time but use a different title: *United Kingdom, which uses British Summer Time (BST) *Ireland, which uses Irish Standard Time (IST) ( (ACÉ)). Also sometimes erroneously referred to as "Irish Summer Time" (). The scheme runs from the last Sunday in March to the last Sunday in October each year. At both the start and end of the schemes, clock changes take place at 01:00 UTC+00:00. During the winter, Western European Time (WET, GMT+0 or UTC+00:00) is used. The start and end dates of the scheme are asymmetrical in terms of daylight hours: the vernal time of year with a similar amount of daylight to late October is mid-February, well before th ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Köppen Climate Classification
The Köppen climate classification divides Earth climates into five main climate groups, with each group being divided based on patterns of seasonal precipitation and temperature. The five main groups are ''A'' (tropical), ''B'' (arid), ''C'' (temperate), ''D'' (continental), and ''E'' (polar). Each group and subgroup is represented by a letter. All climates are assigned a main group (the first letter). All climates except for those in the ''E'' group are assigned a seasonal precipitation subgroup (the second letter). For example, ''Af'' indicates a tropical rainforest climate. The system assigns a temperature subgroup for all groups other than those in the ''A'' group, indicated by the third letter for climates in ''B'', ''C'', ''D'', and the second letter for climates in ''E''. Other examples include: ''Cfb'' indicating an oceanic climate with warm summers as indicated by the ending ''b.'', while ''Dwb'' indicates a semi-Monsoon continental climate, monsoonal continental climate ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Oceanic Climate
An oceanic climate, also known as a marine climate or maritime climate, is the temperate climate sub-type in Köppen climate classification, Köppen classification represented as ''Cfb'', typical of west coasts in higher middle latitudes of continents, generally featuring cool to warm summers and cool to mild winters (for their latitude), with a relatively narrow annual temperature range and few extremes of temperature. Oceanic climates can be found in both hemispheres generally between 40 and 60 degrees latitude, with subpolar versions extending to 70 degrees latitude in some coastal areas. Other varieties of climates usually classified together with these include subtropical highland climates, represented as ''Cwb'' or ''Cfb'', and subpolar oceanic or cold subtropical highland climates, represented as ''Cfc'' or ''Cwc''. Subtropical highland climates occur in some mountainous parts of the subtropics or tropics, some of which have monsoon influence, while their cold variants an ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ) (alt. the Faroes) are an archipelago in the North Atlantic Ocean and an autonomous territory of the Danish Realm, Kingdom of Denmark. Located between Iceland, Norway, and the United Kingdom, the islands have a population of 54,609 and a land area of 1,393 km². The official language is Faroese language, Faroese, which is partially mutually intelligible with Icelandic language, Icelandic. The terrain is rugged, dominated by fjords and cliffs with sparse vegetation and few trees. As a result of its proximity to the Arctic Circle, the islands experience perpetual Twilight, civil twilight during summer nights and very short winter days; nevertheless, they experience a Oceanic climate#Subpolar variety (Cfc, Cwc), subpolar oceanic climate and mild temperatures year-round due to the Gulf Stream. The capital, Tórshavn, receives the fewest recorded hours of sunshine of any city in the world at only 840 per year. Færeyinga saga, Færeyinga Saga and the writin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |