|
Kutlugh Turkan
Kutlugh Turkan (c.1208/1213 – 1283), was a sovereign ruler of Kirman from 1257 until 1282. Early life Different accounts exist regarding her early life. According to "History of Qara-Khitai Shahs" (''Tāriḵ-e šāhi-e Qarāḵtāʾiān'') by anonymous author, she might have been born in Transoxiana between 1208 and 1213 and later sold as a slave to an Isfahani merchant, who adopter her and raised with excellent education. While other sources talk of her as a concubine to Qiyasaddin Pirshah (son of Muhammad II of Khwarazm), then of Buraq Hajib. Although Fatema Mernissi proposed that she was Buraq Hajib's daughter. She married Qutb al-Din Mohammad on 5 September 1235, a nephew of Buraq Hajib and his successor. However they were sent to Ögedei's court when Buraq Hajib's son Rukn al-Din Mubarak Khawja (d. 1252) was recognized as the new ruler of Kirman. They returned to Kirman when Qutb al-Din was confirmed as new ruler in December 1252 by Möngke. However, she was wi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Muzaffar Al-Din Hajjaj
Muzaffar al-Din Hajjaj was a nominal Qutlughkhanid prince of Kerman, a son of Qutb al-Din Mohammad and Kutlugh Turkan. Life Muzaffar al-Din Hajjaj was a minor when his father Qutb al-Din Mohammad died in 1257. Kerman nobles assembled and asked Hulegu for Kutlugh Turkan's appointment as the ruler of the principality. Hulegu confirmed Hajjaj as the new ruler of Kerman, while Kutlugh Turkan was assigned only the civil affairs. Hajjaj's brother-in-law Azad al-Din Hajji was confirmed as the supreme commander, much to Turkan's displeasure, who later obtained full sovereign rights. Hajjaj married Arghun Aqa's daughter Begi Khatun - a woman his father wanted to marry - in 1264. This was the year when Turkan was acknowledged by Hulegu as a ruler in her own right, putting Hajjaj under her shadow. Once he reached adulthood, Hajjaj began to fight at the front of the Ilkhanid army ranks, Chagataid where he achieved fame. This was confirmed when he was honored by Abaqa in 1270. Accord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Rukn Al-Din
Rukn al-Din, Rukn ad-Din or Rukn ud-Din () is a honorific title, now used as a given name. It may refer to: *Abu Muhammad al-Juwayni (died 1046), renowned Islamic scholar. *Abu al-Muzaffar Rukn ud-Dīn Barkyāruq bin Malikšāh (died 1105), sultan of Great Seljuq * Abbas ibn Abi al-Futuh (died 1154), Fatimid vizier *Rukn al-Dīn Mas'ūd, or Mesud I (died 1156), sultan of the Seljuqs of Rûm *Rukn ad-Din Suleiman Shah, or Süleymanshah II (1196–1204), Seljuq Sultan of Rûm * Rukn al-Din Khurshah (died 1256), 27th Imam of the Nizari Isma'ili Shia community *al-Malik al-Zahir Rukn al-Din Baibars al-Bunduqdari (1223–1277), Mamluk Sultan of Egypt and Syria * Rukn ud din Firuz (died 1236), Muslim Turkic ruler and Sultan of Delhi *Rukn al-Dīn Qilij Arslān bin Kaykhusraw, or Kilij Arslan IV (died 1266), Seljuq Sultan of Rûm *al-Malik al-Muzaffar Rukn al-Din Baibars al-Jashnakir al-Mansuri, or Baibars II (died 1309), Mamluk Sultan of Egypt * Baybars al-Mansuri (died 1325), Mamlu ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Gaykhatu
Gaykhatu (Mongolian script:; ) was the fifth Ilkhanate ruler in Iran. He reigned from 1291 to 1295. His Buddhist baghshi gave him the Tibetan name Rinchindorj () which appeared on his paper money. Early life He was born to Abaqa and Nukdan Khatun of the Tatars in c.1259. He was living in Jazira during Tekuder's reign and had to flee to Arghun in Khorasan after the execution, in 1284, of Mongol prince and viceroy of Anatolia Qonqurtai. He was given as hostage to Tekuder by Arghun as a condition of truce in June 1284 and put in orda of Todai Khatun, his step-mother. After Arghun's enthronement, he was confirmed as governor of Anatolia together with his uncle Hulachu. Rule in Anatolia He was stationed in Erzincan and learnt to speak Persian and to some degree Turkish during his stay in Anatolia. Gaykhatu ruled Anatolia solely after recall of Hulachu to Iran in 1286. It was then he was married to Padishah Khatun, a princess of Qutlugh-Khanids. He aided Masud II on h ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Abaqa Khan
Abaqa Khan (27 February 1234 – 4 April 1282, , "paternal uncle", also transliterated Abaġa), was the second Mongol ruler ('' Ilkhan'') of the Ilkhanate. The son of Hulagu Khan and Lady Yesünčin and the grandson of Tolui, he reigned from 1265 to 1282 and was succeeded by his brother Ahmed Tekuder. Much of Abaqa's reign was consumed with civil wars in the Mongol Empire, such as those between the Ilkhanate and the northern khanate of the Golden Horde, and the Chagatai Khanate in Central Asia. Abaqa also engaged in unsuccessful attempts at invading Syria under the Mamluk Sultanate, which included the Second Battle of Homs. Life Abaqa was born in Mongolia on 27 February 1234, son of Ilkhanate founder Hulagu Khan. Abaqa was a Buddhist. A favoured son of Hulagu, he was made governor of Turkestan.Runciman, p. 320. Hulagu died from illness in 1265. Before his death, he had been negotiating with the Byzantine Emperor Michael VIII Palaiologos to add a daughter of the Byzantine imper ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Kutlugh-Khanids
The Qutlugh-Khanids (, otherwise known as the Qutlugh-Khanid dynasty, Kirmanid dynasty, or very rarely as the Later Western Liao) was a culturally Persianate dynasty of ethnic Khitan origin that ruled over Kirman (in present-day Kerman Province, Iran) from 1222 to 1306. It was founded by Buraq Hajib, who emigrated from the Qara Khitai (Western Liao dynasty) during the collapse of the realm. Originally an independent entity, the Qutlugh-Khanid dynasty subsequently ruled as vassals of the Khwarazmian dynasty, the Mongol Empire and the Ilkhanate. The dynasty was removed from power by the Ilkhanid ruler Öljaitü, who appointed Nasir al-Din Muhammad ibn Burhan as governor of Kirman. Later Western Liao Although there was no mention of a dynasty called the "Later Western Liao" (后西辽) in traditional Chinese scholarship, Wang Zhilai wrote a paper ''On the Later Western Liao'' (关于"后西辽") in 1983, where he proposed to call the Qutlugh-Khanids the "Later Western Liao", the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Tekuder
Ahmed Tekuder (; ; 10 August 1284), also known as Sultan Ahmad, was the sultan of the Ilkhanate from 1282 to 1284. He was a son of Hulegu and brother of Abaqa. He was eventually succeeded by his nephew Arghun Khan. Early life Tekuder was born c. 1246 in Mongolia to Hulagu and Qutui Khatun from the Mongol Khongirad tribe as his seventh son. His birth date is not mentioned elsewhere but according to sources he died aged 37, therefore his birth year must have been around 1246 or 1247. He was baptized in his childhood as a Nestorian Christian and was given the name ''Nicholas''. He arrived in the Ilkhanate sometime in the 1260s with his mother Qutui and brother Tekshin. Years later, he was granted governorship of Nahavand and Dinavar by Abaqa, who respected his mother Qutui. Qutui was also invested with territories with income of 100.000 gold coins near Mayyafariqin by Abaqa. Conversion to Islam The circumstances of Tekuder's conversion to Islam are unknown. However, accordi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Qanat
A qanāt () or kārīz () is a water supply system that was developed in ancient Iran for the purpose of transporting usable water to the surface from an aquifer or a well through an underground aqueduct. Originating approximately 3,000 years ago, its function is essentially the same across the Middle East and North Africa, but it is known by a variety of regional names beyond today's Iran, including: kārēz in Afghanistan and Pakistan; foggāra in Algeria; khettāra in Morocco; falaj in Oman and the United Arab Emirates; and ʿuyūn in Saudi Arabia. In addition to those in Iran, the largest extant and functional qanats are located in Afghanistan, Algeria, China (i.e., the Turpan water system), Oman, and Pakistan. Proving crucial to water supply in areas with hot and dry climates, a qanat enables water to be transported over long distances by largely eliminating the risk of much of it evaporating on the journey. The system also has the advantage of being fairly resistant to n ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Madrasa
Madrasa (, also , ; Arabic: مدرسة , ), sometimes Romanization of Arabic, romanized as madrasah or madrassa, is the Arabic word for any Educational institution, type of educational institution, secular or religious (of any religion), whether for elementary education or higher learning. In countries outside the Arab world, the word usually refers to a specific type of religious school or college for the study of the religion of Islam (loosely equivalent to a Seminary, Christian seminary), though this may not be the only subject studied. In an Islamic architecture, architectural and historical context, the term generally refers to a particular kind of institution in the historic Muslim world which primarily taught Sharia, Islamic law and Fiqh, jurisprudence (''fiqh''), as well as other subjects on occasion. The origin of this type of institution is widely credited to Nizam al-Mulk, a vizier under the Seljuk Empire, Seljuks in the 11th century, who was responsible for buildi ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Yarligh
A jarlig, also written ''yarlyk'' (from ), is an edict, permission, license, or written commandant of Mongol and Chinggisid rulers' "formal diplomas." It was one of three non-fundamental law pronouncements that had the effect of regulation or ordinance, the other two being ''debter'' (a record of precedence cases for administration and judicial decisions) and ''billing'' (maxims or sayings attributed to Genghis Khan). The jarlig provides important information about the running of the Mongol Empire. Ögedei Khagan prohibited the nobility from issuing gergees (tablet that gave the bearer authority to demand goods and services from civilian populations) and jarliqs in the 1230s. From the mid-13th to mid-15th centuries, all princes of Northeastern Rus received jarliq authorizing their rule. The issuing of jarlyk on governing of Rus finalized the establishment of the title of Grand Duke of Vladimir (Grand Prince). Initially, those jarliq came from the qaghan in Karakorum, but after ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
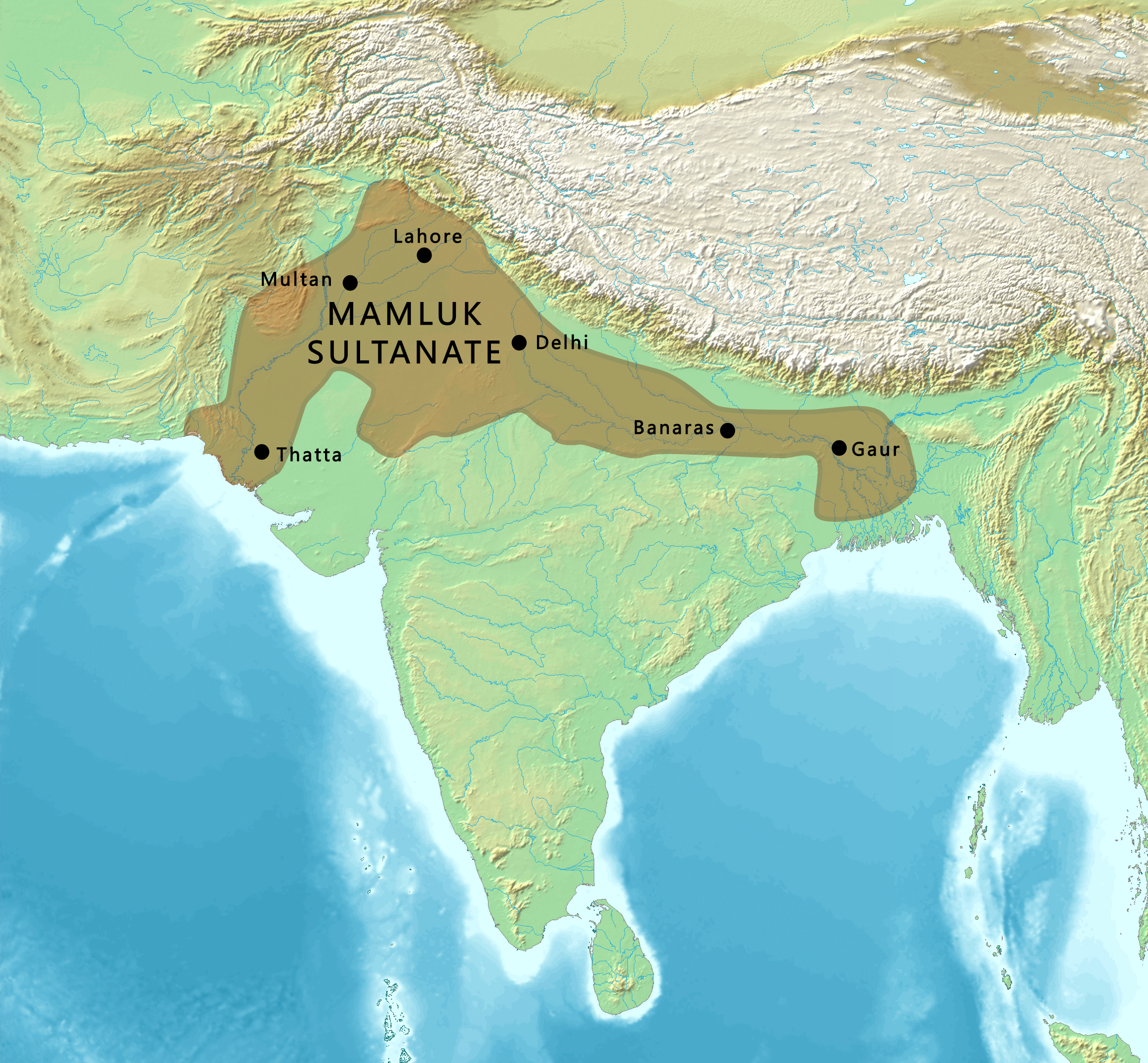
Delhi Sultanate
The Delhi Sultanate or the Sultanate of Delhi was a Medieval India, late medieval empire primarily based in Delhi that stretched over large parts of the Indian subcontinent for more than three centuries.Delhi Sultanate Encyclopædia Britannica The sultanate was established around in the former Ghurid Empire, Ghurid territories in India. The sultanate's history is generally divided into five periods: Mamluk dynasty (Delhi), Mamluk (1206–1290), Khalji dynasty, Khalji (1290–1320), Tughlaq dynasty, Tughlaq (1320–1414), Sayyid dynasty, Sayyid (1414–1451), and Lodi dynasty, Lodi (1451–1526). It covered large swaths of territory in modern-day India, Pakistan, Bangladesh, as well as some parts of southern Nepal. The foundation of the Sultanate was established by the Ghurid conqueror Muhammad of Ghor, Muhammad ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Sirjan
Sirjan (; ) is a city in the Central District of Sirjan County, Kerman province, in the south of Iran, serving as capital of both the county and the district. The city is from the Iranian capital of Tehran, and from the provincial capital of Kerman. It is known for its pistachios, Kilim and its wind towers, locally known as Bādgir-e Chopoqi (calumet louver). Climate Demographics Population At the time of the 2006 National Census, the city's population was 167,014 in 40,605 households. The following census in 2011 counted 185,623 people in 51,088 households. The 2016 census measured the population of the city as 199,704 people in 58,756 households. Universities and higher education centers Payam Noor University Sirjan University of Technology, Sirjan Sirjan University of Technology is a non-profit public higher education institution that was established in 1992. This university, which was established by the Ministry of Science, Research and Technology of Iran, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |
Two Circles
TwoCircles.net (abbreviated as TCN) is a non-profit online news delivering organization registered in the state of Massachusetts founded in 2006. It targets news about Indian Muslims, Indian politics and Muslims around the world. Kashif-ul-Huda is serving as the Senior editor. TCN attracts about 10,000 unique visitors daily which includes politicians, policy planners, journalists of major newspapers and television channels. Notable events In June 2010, TCN's news editor spotted a picture he had taken of Muslim students in Azamgarh, UP, which the BJP was attempting to pass off in an ad campaign An advertising campaign or marketing campaign is a series of advertisement messages that share a single idea and theme which make up an integrated marketing communication (IMC). An IMC is a platform in which a group of people can group their ide ... as an image of progressive Muslims in Gujarat. He alerted the mainstream media, and the BJP was roundly panned. References External lin ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] [Amazon] |