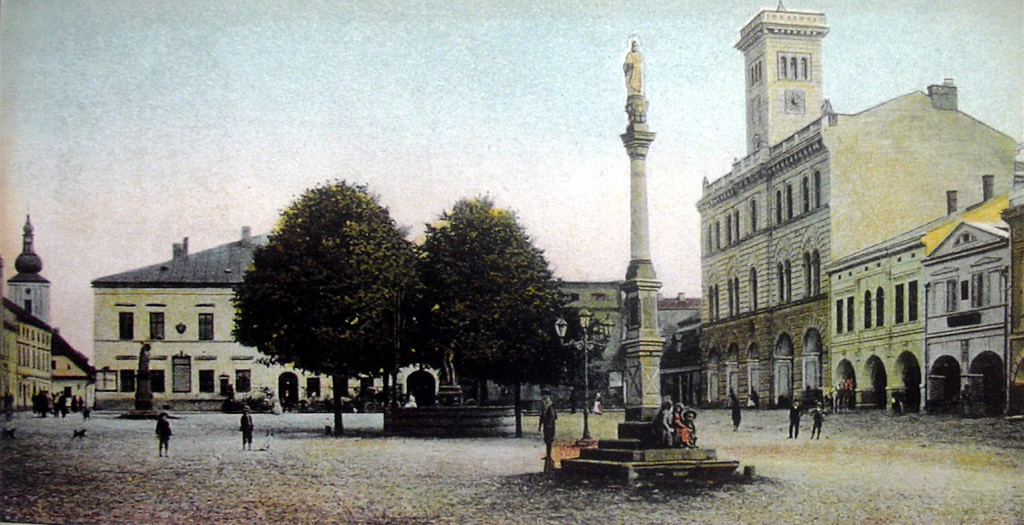|
Krásno Nad Kysucou
Krásno nad Kysucou () is a town in the Čadca District, Žilina Region, north-western Slovakia. Krásno nad Kysucou is the youngest town in Slovakia (it gained the statute of town on the 1. September 2001). It is an industrial town known for its forest industry. It is the third biggest town in Kysuce Region and it is also known to be the gate to the Bystrická dolina. It has 7038 inhabitants. History The first written record about Krásno nad Kysucou was in 1325. At first the village was in the possession of the hereditary reeve of Žilina, then it belonged to the Strečno county. The First World War together with the Second World War and the Economic Crisis left Krásno, like many other places, in a bad condition. The men, who returned from the front, became extremely angry when they saw that those who had stayed at home during the war, were doing very well. They decided to revenge. The armed plundering was finally stopped by the railmen from Žilina, who were called in by the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Czech People
The Czechs (, ; singular Czech, masculine: ''Čech'' , singular feminine: ''Češka'' ), or the Czech people (), are a West Slavic ethnic group and a nation native to the Czech Republic in Central Europe, who share a common ancestry, culture, history, and the Czech language. Ethnic Czechs were called Bohemians in English until the early 20th century, referring to the former name of their country, Bohemia, which in turn was adapted from the late Iron Age tribe of Celtic Boii. During the Migration Period, West Slavic tribes settled in the area, "assimilated the remaining Celtic and Germanic populations", and formed a principality in the 9th century, which was initially part of Great Moravia, in form of Duchy of Bohemia and later Kingdom of Bohemia, the predecessors of the modern republic. The Czech diaspora is found in notable numbers in the United States, Germany, Canada, Slovakia, Austria, the United Kingdom, Argentina, Australia, Switzerland, France, Russia, Italy, Is ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Milówka, Silesian Voivodeship
Milówka is a village in Żywiec County, Silesian Voivodeship, in southern Poland (historic and geografical province of Lesser Poland). It is the seat of the gmina (administrative district) called Gmina Milówka. It lies It is situated in the Żywiec Beskids mountain range, approximately south-west of Żywiec and south of the regional capital Katowice. Polish musical group Golec uOrkiestra hails from here. Milówka was first mentioned in 1537, when this part of the Kingdom of Poland belonged to Lesser Poland's Kraków Voivodeship. Mountains and hills of the Beskids, which were covered by dense forests, were at that time settled by Polish farmers, who gradually moved southwards along the Soła river. After the Poles, in the second half of the 16th century, came shepherds from Wallachia, who in the course of the time assimilated with Polish population. In 1772 (see Partitions of Poland) Milówka was annexed by the Austrian Empire, and became part of the province of Galicia, ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Metylovice
Metylovice () is a municipality and village in Frýdek-Místek District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 1,800 inhabitants. Geography Metylovice is located about south of Frýdek-Místek and south of Ostrava Ostrava (; ; ) is a city in the north-east of the Czech Republic and the capital of the Moravian-Silesian Region. It has about 283,000 inhabitants. It lies from the border with Poland, at the confluences of four rivers: Oder, Opava (river), Opa .... It lies in the Moravian-Silesian Foothills. The highest point is the Ondřejník mountain at above sea level. The Olešná Stream flows through the municipality. History The first written mention of Metylovice is in a deed of Bishop Dětřich from 1299. From the second half of the 17th century, tanning developed in the village, thanks to which the originally agricultural village began to prosper and grow. Brick houses began to replace the original wooden ones and the education and cultur ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Frenštát Pod Radhoštěm
Frenštát pod Radhoštěm (; ) is a town in Nový Jičín District in the Moravian-Silesian Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 11,000 inhabitants. The historic town centre is well preserved and is protected by law as an urban monument zone. Geography Frenštát pod Radhoštěm is located about southeast of Nový Jičín and south of Ostrava. It lies mostly in the Moravian-Silesian Foothills. The western part of the municipal territory extends into the Moravian-Silesian Beskids and contains the highest point of Frenštát pod Radhoštěm, the hill Vlčina at above sea level. The mountain of Radhošť, contained in the name of the town, is located south of the town (outside the municipal territory). The town is situated at the confluence of the Lubina River and Lomná Stream. Climate Frenštát pod Radhoštěm's climate is classified as humid continental climate (Köppen: ''Dfb''; Trewartha: ''Dcbo''). Among them, the annual average temperature is , the hottest mo ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Twin Towns And Sister Cities
A sister city or a twin town relationship is a form of legal or social agreement between two geographically and politically distinct localities for the purpose of promoting cultural and commercial ties. While there are early examples of international links between municipalities akin to what are known as sister cities or twin towns today dating back to the 9th century, the modern concept was first established and adopted worldwide during World War II. Origins of the modern concept Throughout history, many cities have participated in various cultural exchanges and similar activities that might resemble a sister-city or twin-city relationship, but the first officially documented case of such a relationship was a signed agreement between the leaders of the cities of Toledo, Ohio and Toledo, Spain in 1931. However, the modern concept of town twinning appeared during the Second World War. More specifically, it was inspired by the bombing of Coventry on 14 November 1940, known as t ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Rink Bandy
Rink bandy is a variant of the larger sport of bandy. Unlike bandy which is played on a large bandy field, rink bandy is played on significantly smaller ice hockey-sized ice rinks. While a bandy field is about the same size as a football pitch, rink bandy is played on ice hockey rinks. History Rink bandy originated in Sweden in the 1960s and was originally called ''hockeybockey''. With the arrival of indoor ice hockey arenas, it was a way for bandy players to practice on ice for a longer time through the year by making use of the new indoor facilities. Since bandy fields are much larger than ice hockey rinks, playing surfaces for bandy were still only made outdoors in the wintertime when artificial freezing was unnecessary. The game of rink bandy uses a bandy ball and bandy sticks. The goalkeeper has no stick. A rink bandy game lasts 60 minutes but is composed of either two 30 minute halves or three 20 minute periods. Similar rules to bandy are used, but they are simpl ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Slovak Bandy Association
Slovak Bandy Association (''Slovenská asociácia Bandy'') is the governing body of bandy in Slovakia. It was founded 12 May 2017 and is based in Trenčianske Teplice, Trenčin Region. It was admitted to the Federation of International Bandy the same year. National team * References External links Official webpage {{Bandy-stub National members of the Federation of International Bandy Bandy Bandy is a winter sport and ball sport played by two team sport, teams wearing Ice skates#Bandy skates, ice skates on a large ice surface (either indoors or outdoors) while using sticks to direct a ball into the opposing team's goal. The playin ... Bandy in Slovakia Sport in Trenčín Region ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lutherans
Lutheranism is a major branch of Protestantism that emerged under the work of Martin Luther, the 16th-century German friar and reformer whose efforts to reform the theology and practices of the Catholic Church launched the Reformation in 1517. The Lutheran Churches adhere to the Bible and the Ecumenical Creeds, with Lutheran doctrine being explicated in the Book of Concord. Lutherans hold themselves to be in continuity with the apostolic church and affirm the writings of the Church Fathers and the first four ecumenical councils. The schism between Roman Catholicism and Lutheranism, which was formalized in the Edict of Worms of 1521, centered around two points: the proper source of authority in the church, often called the formal principle of the Reformation, and the doctrine of justification, the material principle of Lutheran theology. Lutheranism advocates a doctrine of justification "by Grace alone through faith alone on the basis of Scripture alone", the doctrine ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Roman Catholics
The Catholic Church (), also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.27 to 1.41 billion baptized Catholics worldwide as of 2025. It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions and has played a prominent role in the history and development of Western civilization. O'Collins, p. v (preface). The church consists of 24 ''sui iuris'' (autonomous) churches, including the Latin Church and 23 Eastern Catholic Churches, which comprise almost 3,500 dioceses and eparchies around the world, each overseen by one or more bishops. The pope, who is the bishop of Rome, is the chief pastor of the church. The core beliefs of Catholicism are found in the Nicene Creed. The Catholic Church teaches that it is the one, holy, catholic and apostolic church founded by Jesus Christ in his Great Commission, that its bishops are the successors of Christ's apostles, and that the pope is the successor of Saint Peter, upon whom ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Census
A census (from Latin ''censere'', 'to assess') is the procedure of systematically acquiring, recording, and calculating population information about the members of a given Statistical population, population, usually displayed in the form of statistics. This term is used mostly in connection with Population and housing censuses by country, national population and housing censuses; other common censuses include Census of agriculture, censuses of agriculture, traditional culture, business, supplies, and traffic censuses. The United Nations (UN) defines the essential features of population and housing censuses as "individual enumeration, universality within a defined territory, simultaneity and defined periodicity", and recommends that population censuses be taken at least every ten years. UN recommendations also cover census topics to be collected, official definitions, classifications, and other useful information to coordinate international practices. The United Nations, UN's Food ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Regions Of Slovakia
Since 1949 (except 1990–1996), Slovakia has been divided into a number of (singular ; usually translated as "Regions" with capital R). Their number, borders and functions have been changed several times. There are eight regions of Slovakia and they correspond to the European Union, EU's Nomenclature of Territorial Units for Statistics, NUTS 3 level of local administrative units. Each kraj consists of (counties or districts), which are further divided into (municipalities). There are 79 Districts of Slovakia, districts. List After a period without kraje and without any equivalent (1990–1996), the kraje were reintroduced in 1996. As for administrative division, Slovakia has been subdivided into 8 kraje since 24 July 1996: Since 2002, Slovakia is divided into 8 (self-governing regions), which are called by the Constitution (Higher Territorial Units), abbr. VÚC. The territory and borders of the self-governing regions are identical with the territory and borders of the ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |