|
Krzeszów, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Krzeszów is a village in south-western Poland. It is part of the administrative district of Kamienna Góra County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship. Krzeszów boasts the Krzeszów Abbey, one of the most valuable relics of Baroque architecture in Poland and Europe, designated a List of Historic Monuments (Poland), Historic Monument of Poland. The village is located in the Zadrna valley of the Central Sudetes, within the historic Lower Silesia region. It lies approximately south of Kamienna Góra, and south-west of the regional capital Wrocław. History The area became part of the emerging Polish state in the 10th century. Following the fragmentation of Poland into smaller duchies, it formed part of the duchies of Duchy of Silesia, Silesia and Świdnica. The Order of Saint Benedict, Benedictine abbey of ''Grissobor'' was established on 8 May 1242 by Anne of Bohemia (1204–1265), Anne of Bohemia, widow of Polish monarch Henry II the Pious, who had been killed at the Battle of Legnica ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
List Of Sovereign States
The following is a list providing an overview of sovereign states around the world with information on their status and recognition of their sovereignty. The 205 listed states can be divided into three categories based on membership within the United Nations System: 193 member states of the United Nations, UN member states, two United Nations General Assembly observers#Current non-member observers, UN General Assembly non-member observer states, and ten other states. The ''sovereignty dispute'' column indicates states having undisputed sovereignty (188 states, of which there are 187 UN member states and one UN General Assembly non-member observer state), states having disputed sovereignty (15 states, of which there are six UN member states, one UN General Assembly non-member observer state, and eight de facto states), and states having a political status of the Cook Islands and Niue, special political status (two states, both in associated state, free association with New ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
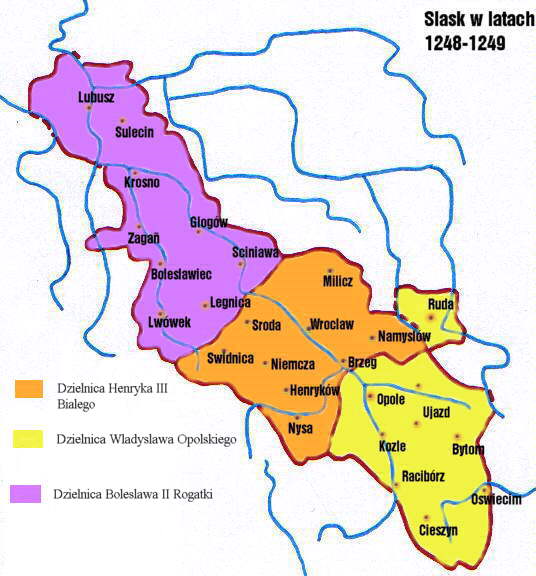
Duchy Of Silesia
The Duchy of Silesia (, ) with its capital at Wrocław was a medieval provincial duchy of Poland located in the region of Silesia. Soon after it was formed under the Piast dynasty in 1138, it fragmented into various Silesian duchies. In 1327, the remaining Duchy of Wrocław as well as most other duchies ruled by the Silesian Piasts passed under the suzerainty of the Kingdom of Bohemia as the Duchies of Silesia. The acquisition was completed when King Casimir III the Great of Poland renounced his rights to Silesia in the 1335 Treaty of Trentschin. Geography During the time of its establishment, the Silesian lands covered the basin of the upper and middle Oder river. In the south the Sudetes mountain range up to the Moravian Gate formed the border with the lands of Bohemia – including Kłodzko Land – and Moravia. After a more than century-long struggle, the boundary had just been determined by an 1137 agreement with the Bohemian duke Soběslav I. In the west Lower S ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Lubawka
Lubawka () is a town in Poland, in Lower Silesia Voivodship, in Kamienna Góra County. It is the administrative seat of Gmina Lubawka. It lies in the Sudetes near to the border with the Czech Republic on the way across the Lubawka pass (516m) between the Karkonosze and Krucze Mountains (). Two small rivers, the Bóbr and Czarnuszka, run through the town, which has 6,028 inhabitants (2019). History In the 13th century a Kingdom of Poland (1025–1385), Polish defensive stronghold on the border with the Kingdom of Bohemia, Czech Kingdom was located in present-day Lubawka. The first written reference to Lubawka is from 1284 when it was written down as ''Lubavia''. The name is of Polish origin, and it comes from the word ''lubić'', which means "to like", or from the word ''łub'', which means "Bark (botany), bark". In 1292 Duke Bolko I the Strict granted Lubawka, which at that time already enjoyed town rights, to the Cistercian monastery in Krzeszów, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, Krz ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Henryków, Lower Silesian Voivodeship
Henryków is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Ziębice, within Ząbkowice Śląskie County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north of Ziębice, north-east of Ząbkowice Śląskie, and south of the regional capital Wrocław. The village contains the landmark Cistercian Monastery Complex. A Latin chronicle, the Book of Henryków, compiled at Henryków abbey in the 13th century contains the first known sentence written in the Polish language Polish (, , or simply , ) is a West Slavic languages, West Slavic language of the Lechitic languages, Lechitic subgroup, within the Indo-European languages, Indo-European language family, and is written in the Latin script. It is primarily spo .... There is a train station in Henryków. Gallery Henrykow former Cistercian abbey 2019 P03 aerial view.jpg, Aerial view of the Cistercian Monastery Henrykow june 2014 040.JPG, Monument to the Book of Henryków Henrykow - budynek b ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Cistercians
The Cistercians (), officially the Order of Cistercians (, abbreviated as OCist or SOCist), are a Catholic religious order of monks and nuns that branched off from the Benedictines and follow the Rule of Saint Benedict, as well as the contributions of the highly influential Bernard of Clairvaux, known as the Latin Rule. They are also known as Bernardines, after Bernard of Clairvaux, Saint Bernard, or as White Monks, in reference to the colour of their cowl, as opposed to the black cowl worn by Benedictines. The term ''Cistercian'' derives from ''Cistercium,'' the Latin name for the locale of Cîteaux, near Dijon in eastern France. It was here that a group of Benedictine monks from the monastery of Molesme Abbey, Molesme founded Cîteaux Abbey in 1098. The first three abbots were Robert of Molesme, Alberic of Cîteaux and Stephen Harding. Bernard helped launch a new era when he entered the monastery in the early 1110s with 30 companions. By the end of the 12th century, the ord ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Duchy Of Jawor
Duchy of Jawor (, ) was one of the duchies of Silesia and medieval Poland established in 1274 as a subdivision of the Duchy of Legnica. It was ruled by the Silesian Piasts, with its capital at Jawor in Lower Silesia. It was the southwesternmost duchy of Poland at the time, with the exception of the 1281–1286 period, when the more southwestern was the temporarily split off Duchy of Lwówek. At various times, it also bordered the fellow Polish duchies of Głogów, Legnica, Wrocław and Świdnica, and via the latter also Nysa, Brzeg and Ziębice. Geography The original Duchy stretched from Jawor on the Nysa Szalona River westwards along the northern slopes of the Western Sudetes to the Jizera Mountains and the Kwisa River, which formed the Silesian border with the former Milceni lands of Upper Lusatia. In the north it bordered the remaining Duchy of Legnica and in the east the Duchy of Silesia-Wrocław. It included the towns of Bolesławiec, Bolków, Gryfów, Jawor, Kami ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Bolko I The Strict
Bolko (Bolesław) I the Strict, also known as Bolko (Bolesław) of Jawor ( or ''Srogi'' or ''Jaworski''; 1252/56 – 9 November 1301), was a Duke of Lwówek Śląski, Lwówek 1278–81 (with his brother as co-ruler) and Duchy of Jawor, Jawor after 1278 (with his brother as co-ruler until 1281), sole Duke of Lwówek after 1286, Duke of Świdnica-Ziębice from 1291. Life Bolko I was the second son of Bolesław II the Bald, Duke of Legnica by his first wife Hedwig, daughter of Henry I, Count of Anhalt. Most likely because he was still too young to actively participate in politics, Bolko appears rarely in the chronicles before his father's death. It is possible that he took part in the victorious Battle of Stolec in 1277. Bolesław II died on 26 December 1278. Bolko I and his younger brother Bernard the Lightsome inherited Jawor and Lwówek Śląski, Lwówek as co-rulers, and their older brother Henry V the Fat retained Legnica. In 1281 Bolko I and Bernard divided their domains: Berna ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Opatovice Nad Labem
Opatovice nad Labem is a municipality and village in Pardubice District in the Pardubice Region of the Czech Republic. It has about 2,800 inhabitants. Administrative division Opatovice nad Labem consists of two municipal parts (in brackets population according to the 2021 census): *Opatovice nad Labem (2,195) *Pohřebačka (591) Etymology The name Opatovice is derived from the Czech word ''opatství'', i.e. 'abbey'. It indicated a village in the vicinity of the monastery that was founded here. Geography Opatovice nad Labem is located about north of Pardubice and south of Hradec Králové. It lies in a flat landscape of the East Elbe Table lowland. It is situated on the right bank of the Elbe River. There are several flooded quarries used for recreational purposes. The largest of them is Opaťák in the northern part of the municipality. The Opatovice Canal flows through the village. It was built in the 15th century to supply the large pond system and is a cultural technical mon ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Krzeszówek
Krzeszówek is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Kamienna Góra, within Kamienna Góra County, Lower Silesian Voivodeship Lower Silesian Voivodeship (, ) in southwestern Poland, is one of the 16 Voivodeships of Poland, voivodeships (provinces) into which Poland is divided. It covers an area of and has a total population of 2,899,986. It is one of the wealthiest ..., in south-western Poland. References Villages in Kamienna Góra County {{KamiennaGóra-geo-stub ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Silesian Przesieka
Silesian ''Przesieka'', literally Silesian Cutting (, , or , ) was a densely forested, uninhabited and unpassable strip of land in the middle of Silesia, spreading from Golden Mountains in the south, along the Nysa Kłodzka to the Odra, and then along the Stobrawa, reaching the towns of Namysłów and Byczyna in northern Silesia. Originally, the Silesian Cutting was a boundary, separating territories of two Western Slavic tribes, the Slezanie and the Opolanie. In the 12th century, along the Cutting a border of Lower Silesia and Upper Silesia was established.Marek Czapliński, Elżbieta Kaszuba, Gabriela Wąs, Rościsław Żerelik ''Historia Śląska''(''History of Silesia'') Original from the University of Michigan, 611 pages, Stolica.Opole.pl Górny Śląsk(''Regions of Upper Silesia, an overview.'') Mgr Stanisława Spytkowska, editor; with Anna Tosza Śląsk wśród regionów Europy – wizja pokoleniowaL.O. im. T. Kościuszki w Jaworznie. For a long time, the Siles ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
First Mongol Invasion Of Poland
The Mongol invasion of Poland from late 1240 to 1241 culminated in the Battle of Legnica, where the Mongols defeated an alliance which included forces from Testament of Bolesław III Wrymouth, fragmented Poland and their allies, led by Henry II the Pious, the Duke of Silesia and High Duke of Poland. The first invasion's intention was to secure the flank of the main Mongolian army attacking the Kingdom of Hungary. The Mongols neutralized any potential help to King Béla IV of Hungary, Béla IV being provided by the Poles or any military orders. Background The Mongol invasion of Europe, Mongols invaded Europe with three armies. One of the three armies was tasked with distracting Poland, before joining the main Mongol force invading Hungary. The Mongol general in charge, Subutai, did not want the Polish forces to be able to threaten his flank during the primary invasion of Hungary. Thus, the Mongol goal was to use a small detachment to prevent the Poles from assisting Hungary un ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |
Battle Of Legnica
The Battle of Legnica (), also known as the Battle of Liegnitz () or Battle of Wahlstatt (), was fought between the Mongol Empire and combined European forces at the village of Legnickie Pole (''Wahlstatt''), approximately southeast of the city of Legnica in the Duchy of Silesia on 9 April 1241. A combined force of Poles and Moravians under the command of Duke Henry II the Pious of Silesia, supported by feudal nobility and a few knights from military orders sent by Pope Gregory IX, attempted to halt the Mongol invasion of Poland. The battle took place two days before the Mongol victory over the Hungarians at the much larger Battle of Mohi. Historical disputations As with many historical battles, the exact details of force composition, tactics, and the actual course of the battle are lacking and sometimes contradictory. The general historical view is that it was a crushing defeat for the Polish and Moravian forces where they suffered heavy casualties. One of the Mong ... [...More Info...] [...Related Items...] OR: [Wikipedia] [Google] [Baidu] |